Blog
2026
2nd March 2026 - The EU Emissions Trading System ETS In A Nutshell
The European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) is the EU’s flagship carbon pricing mechanism. Introduced in 2005, it was the world’s first international carbon market and remains one of the largest globally. At its core, the EU ETS requires polluters to pay for their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. By putting a price on carbon, it helps drive emissions reductions while generating funding to support the transition to a low-carbon economy.

The system currently covers emissions from:
- Electricity and heat generation
- Energy-intensive industrial manufacturing
- Aviation
- Maritime transport (included from 2024)
Together, these sectors account for around 40% of the EU’s total greenhouse gas emissions. The EU ETS operates across all EU Member States, as well as Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway. Since 2020, it has also been linked to the Swiss Emissions Trading System.
How Does the EU ETS Work?
The EU ETS operates on a “cap and trade” principle.
The Cap
A limit (or 'cap') is set on the total amount of greenhouse gases that installations and operators covered by the system can emit. This cap is reduced every year in line with the EU's climate targets, ensuring that overall emissions decline over time. Since its launch, the system has delivered substantial results. By 2023, emissions from power generation and industrial plants covered by the EU ETS had fallen by approximately 47% compared to 2005 levels.
Emission Allowances
The cap is divided into emission allowances. Each allowance gives the holder the right to emit one tonne of CO2 equivalent (CO2e). Allowances are primarily sold through auctions, although some sectors receive a limited number of free allocations. Companies can also buy and sell allowances between themselves, depending on their operational needs. If a company reduces its emissions, it may:
-
Sell surplus allowances, or
-
Retain them for future use
All transactions are recorded in the EU’s Union Registry to ensure transparency and compliance. Companies must monitor and report their emissions annually and surrender enough allowances to cover their verified emissions. Failure to comply results in significant financial penalties.
Carbon Pricing and Market Dynamics
The price of allowances is determined by supply and demand in the EU carbon market, which operates under strict regulatory oversight. As the cap declines over time, allowances become scarcer, reinforcing their market value. This creates a financial incentive for companies to reduce emissions in the most cost-effective way. Since 2013, the EU ETS has generated more than €175 billion in revenue.
How Is the Revenue Used?
Most EU ETS revenue flows to Member States’ national budgets. Governments are required to use these funds to support:
- Renewable energy development
- Energy efficiency improvements
- Low-carbon technologies
- Industrial decarbonisation
In addition, dedicated funds — such as the Innovation Fund and the Modernisation Fund, use ETS revenues to support breakthrough clean technologies and help modernise energy systems across Europe.
In summary, the EU ETS is a market-based mechanism that limits emissions, puts a price on carbon, incentivises decarbonisation and funds the EU’s green transition.
#Protea #EmissionsMonitoring #CEMS #FTIR #GasAnalysers #ShippingEmissions #MarineEmissions #CarbonCapture #CCUS
Read More26th February 2026 - Rising Carbon Costs Drive The Need For Accurate Emissions Management In European Shipping
Owners and operators of vessels over 5,000 GT trading in Europe now face significantly increased compliance costs following the full implementation of the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS).

From 1 January, the transition phase ended and shipping entered full scope. This has increased fuel-related costs by around $100 per tonne for high and low sulphur fuel oil and marine gasoil, on top of the approximately $200 per tonne already associated with EU ETS Allowances. As a result, carbon exposure has become a material operational cost that must be actively managed rather than simply absorbed.
Under the updated framework, vessels operating entirely within EU/EEA waters must now surrender Allowances covering 100% of their carbon emissions. In addition, reporting obligations extend beyond CO2 to include methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O), further increasing compliance complexity. Ships trading in and out of the region must purchase allowances covering 50% of voyage emissions, while fuel consumed at EU/EEA ports must be fully accounted for.
In this environment, accurate and transparent emissions measurement is critical. Reliance solely on fuel consumption calculations can expose operators to the risk of over-reporting emissions and purchasing more Allowances than necessary. Direct CO2 measurement and real-time emissions monitoring provide a more precise, verifiable method of quantifying actual exhaust emissions. This supports stronger MRV (Monitoring, Reporting and Verification) compliance, reduces the risk of discrepancies, and may identify opportunities to lower Allowance requirements.
By implementing certified, traceable emissions measurement systems, operators can improve reporting confidence, optimise fuel efficiency, and potentially reduce their overall ETS exposure. With carbon costs now directly impacting voyage economics, proactive emissions management is becoming a key commercial and technical priority for shipowners trading in European waters.
Full compliance with the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) has significantly increased the cost of burning very low sulphur fuel oil on voyages within EU waters. Although the exact impact varies with carbon allowance prices and exchange rates, the added expense has made fuel efficiency a critical commercial priority.
Even minor combustion inefficiencies, such as poor ignition timing, uneven cylinder loads or injector wear, can gradually increase fuel consumption without triggering immediate alarms. Under the EU ETS, every extra tonne of fuel burned requires additional carbon allowances, directly raising operating costs. As a result, optimising engine performance and closely managing emissions are now essential to controlling compliance costs and protecting voyage profitability.
#Protea #EmissionsMonitoring #CEMS #FTIR #GasAnalysers #ShippingEmissions #MarineEmissions #CarbonCapture #CCUS
Read More16th January 2026 - Carbon Capture Utilisation & Storage (CCUS) In 2026
Here are the five key areas to watch for in Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS) in 2026 with critical indicators of how the sector could evolve this year and shape decarbonisation strategies globally.

- Scale-Up from Pilot to Gigaton-Scale Projects
- The CCUS industry is trying to move beyond isolated demonstration projects toward interconnected, gigaton-scale carbon management ecosystems. This transition involves boosting capture and storage capacity dramatically — the industry currently has growth in projects planned up to 2030 but is still far below what’s needed for climate goals.
- Why it matters: Success here will determine whether CCUS becomes material to global emissions reductions or remains a niche solution.
- Development of CO2 Infrastructure & Hub Models
- Shared transport and storage infrastructure (hub models) is becoming essential to make CCUS cost-effective and viable at scale. Connecting emitters to shared pipelines and permanent geological storage (e.g., saline aquifers or depleted oil/gas fields) can distribute risk and reduce costs.
- Watch for in 2026 with Major hub announcements (e.g., North Sea, Gulf regions) and Policy frameworks enabling cross-industry CO2 transport & storage.
- Technological Innovation & Cost Reduction
- Several emerging technologies and optimization strategies are gaining momentum.
- Advanced capture materials & AI-assisted solvent discovery to lower energy use and CAPEX/OPEX.
- AI and machine learning to optimize operations and performance.
- Novel capture approaches (e.g., solar-driven processes) are gaining industry attention.
- Why it matters: Cost reduction and performance gains are critical to wider deployment — and will influence investment flows in 2026.
- Policy & Incentive Frameworks
- Government policy — including subsidies, tax credits, carbon pricing and R&D roadmaps — remains a key driver for CCUS deployment. Several national initiatives are underway (e.g., India’s CCUS R&D roadmap to 2070 net-zero goals).
- To watch in 2026: New or expanded CCUS incentives in major markets (US, Europe, Asia) and Changes in carbon pricing regimes affecting project economics.
- Industrial Adoption Beyond Fossil Fuels
- While oil and gas companies still dominate CCUS capacity, hard-to-abate sectors like cement, steel and chemicals are ramping up interest — especially where decarbonisation options are limited or high-cost without CCUS.
- Implications for 2026: First commercial CCUS retrofits in heavy industry Emerging utilisation pathways (e.g., fuels, chemicals) and Increased integration with hydrogen and low-carbon energy systems.
During 2026, it should become clear whether CCUS can scale meaningfully to support climate targets, how infrastructure development and policy frameworks evolve to reduce costs and unlock new projects, which emerging technologies achieve commercial traction, and whether major industrial emitters and markets adopt CCUS beyond early movers. At the same time, ongoing criticism around cost, climate accountability and effectiveness, particularly concerns that CCUS may prolong fossil fuel use, will continue to influence investor confidence, policy direction and public support in key regions.
#Protea #EmissionsMonitoring #CEMS #FTIR #GasAnalysers #ShippingEmissions #MarineEmissions #CarbonCapture #CCUS
Read More2025
1st December 2025 - Global Underground CO2 Storage Data Offers Hope Amid Rising Emissions
Scientists have, for the first time, published a comprehensive record of how much carbon dioxide (CO2) has been permanently stored underground worldwide using carbon capture and storage (CCS). The new report from the London Register of Subsurface CO2 storage shows that since 1996 over 383 million tonnes of CO2 have been safely sequestered, roughly equivalent to taking 81 million cars off the road for a year.

A proven, global carbon-management effort. This milestone is not just a hopeful statistic with its evidence that CCS is already working at scale. The storage comes mainly from large projects in the United States, China, Brazil, Australia, and the Middle East, with continued expansion expected through 2024–2025. The report’s authors argue that CCS shouldn’t be viewed as a futuristic or speculative technology, but rather as a proven and scalable tool that can play a real role today in reducing atmospheric CO2.
The initiative is led by researchers at Imperial College London, collaborating with academic and industry partners globally, including institutions such as Stanford University, MIT, the Global CCS Institute, the Carbon Capture & Storage Association, IEAGHG, and CSIRO in Australia. According to Samuel Krevor, Director of the Register, this report “demonstrates a proven capability and accelerating momentum for geologic storage of CO2”. “We have found that industrial-scale carbon management is already a reality and can safely sequester CO2 deep underground, which will be a key strategy, alongside vital efforts to cut emissions, for decarbonising hard-to-abate industries and cutting the total CO2 in the atmosphere.”
How CCS works and why it matters
CCS operates by capturing CO2 emitted from power plants and industrial processes, then injecting it deep underground (commonly 1 km or more) where it is securely trapped in geological formations such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs. This makes CCS especially important for sectors that cannot easily shift to renewable electricity, for example, heavy industry like steel or cement production. Many international bodies, including the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), consider CCS a critical tool for achieving net-zero emissions.
Rapid growth in recent years - The new report identifies three broad phases of CCS growth:
- 1996–2007 ("Pioneering Phase") - when geological storage was first demonstrated as technically feasible.
- 2008–2015 ("North American Expansion") - when the number of storage sites increased significantly, proving injection worked on a larger scale.
- 2016–2023 ("Global Scaling") - when CCS deployment spread globally and storage rates surged.
In 2023 alone, CCS projects stored a record 45.2 million tonnes of CO 2, an increase of 8.4 million tonnes compared with the previous year. Leading projects include the Seminole San Andres Unit in the US (3.9 MtCO 2 in 2023) and the Santos Basin Pre-Salt oilfield in Brazil (13.0 MtCO 2 in 2023). Together, they accounted for more than a third of all CO 2 stored that year. Although data from 2024 remain incomplete, early indicators point to sustained, perhaps growing, CO 2 storage, especially in regions such as Brazil and China. To give a sense of scale: the CO 2 stored in 2023 alone roughly corresponds to the emissions avoided by all renewable energy produced in Australia or Italy that year, or to two thirds of the UK’s renewable-generated emissions avoided in the same period.
The road ahead: what’s needed for climate goals. Despite these encouraging numbers, researchers say much more must be done to reach climate targets. To keep global warming under 1.5 °C, projections suggest storage must scale up dramatically, to at least 1 billion tonnes (a gigatonne) per year by 2050.
The authors emphasise that while CCS is a powerful tool, it should work alongside, not instead of, deep cuts in emissions from energy and industry. CCS can help decarbonise sectors that are difficult to electrify, but the fundamental challenge remains reducing emissions overall. They also argue that renewed policy support and investment will be crucial. As more CCS projects come online, costs are likely to fall, just as they have done in other decarbonisation technologies.
A call for collaboration and commitment
The Register’s global consortium, spanning academia, industry, and government, shows how international cooperation can accelerate deployment of carbon-storage infrastructure. Given the urgency of climate change and the limitations of emission reductions alone, the success of CCS to date offers a “hopeful message”: the technology to capture and store CO 2 at scale already exists, and with determination, policy support, and continued collaboration, it can significantly contribute to the global fight against climate change.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More4th November 2025 - IMO Postpones Adoption Of Global Net-Zero Shipping Framework
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has postponed the adoption of its landmark Net-Zero Framework (NZF) for global shipping by one year, following a contentious vote at the Marine Environment Protection Committee’s (MEPC) extraordinary session in London.

The NZF was intended to establish a global fuel standard, a greenhouse-gas pricing system, and an IMO-managed Net-Zero Fund to finance decarbonisation and support developing countries. The framework was expected to be adopted in 2025 and take effect in 2027, but the vote has been deferred until October 2026.
The motion to delay, introduced by Singapore and formally submitted by Saudi Arabia, passed with 57 votes in favour, 49 against, and 21 abstentions. Supporters cited the need for more time to refine technical details and build consensus among developing states. Opponents warned the delay weakens global climate momentum and creates uncertainty for shipowners planning green investments.
Diplomatic tensions ran high during the meeting. Reports indicated that the United States and other major economies lobbied against the NZF’s emissions-pricing component, prompting accusations of “undiplomatic pressure” on smaller nations. IMO Secretary-General Arsenio Domínguez called the session “unusual” and urged delegates to return to constructive dialogue.
The postponement means regional climate rules such as the EU Emissions Trading System (EU-ETS) and FuelEU Maritime, will continue to shape decarbonisation efforts in the interim. Industry and environmental groups have expressed concern that fragmented regulations could complicate compliance and delay investment in zero-emission technologies.
Technical work on the NZF will continue through 2026, with member states expected to resume negotiations next October. The delay marks a setback for global shipping’s net-zero ambitions, but IMO officials insist the framework remains “on course, though with a longer horizon.” Find out more about the activities of Marine Emissions monitoring systems from Protea and the need to demonstrate environmental responsibility which is key for today’s marine and offshore industries at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More3rd October 2025 - Pioneering Carbon Capture Projects Ready For Construction
500 new skilled clean energy jobs will be created in North Wales and the North West as two pioneering carbon capture projects move into construction. The UK’s first carbon capture-enabled cement plant at Padeswood and one of the world's first full-scale carbon capture waste-to-energy plants in Ellesmere Port, have now signed final government contracts to begin building. Together, these projects will open up highly skilled roles for engineers, construction workers, technicians, and health and safety specialists.

Cement and waste-to-energy are among the most carbon-intensive industries, with no pathway to decarbonisation without carbon capture. As the UK drives towards net zero, the Padeswood and Protos plants will deploy cutting-edge technologies capable of removing 1.2 million tonnes of CO2 each year, delivering cleaner growth while securing long-term, high-quality jobs in the cement and waste-to-energy sectors.
These flagship projects will also act as springboards for exporting British carbon capture expertise, boosting global demand for UK innovation and creating fresh economic opportunities for homegrown companies in the green economy. They are the first anchor projects to connect into Eni’s Liverpool Bay Transportation & Storage system, part of the HyNet carbon capture cluster, which was finally approved by the Prime Minister in April after years of delay.
In June 2025, the government reinforced its commitment with a £9.4 billion funding package in the Spending Review, ensuring carbon capture becomes a cornerstone of the UK’s Industrial Strategy, revitalising industrial heartlands and supporting skilled jobs across the country. The recent announcement is that investment in action: shovel-ready projects, jobs secured, and growth locked in for decades across North Wales and the North West. Padeswood will capture around 800,000 CO2 emissions annually and Protos will capture 400,000, taking the total to 1.2 million a year. Find out more about the activities of Protea and CCUS at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/carbon-capture-and-storage-ccs
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More1st September 2025 - Methanol & Ammonia Deemed Ready As Zero-Emission Shipping Fuels
Methanol and ammonia have moved from theory to practical application as zero-emission fuels for shipping, according to a new report from the Global Maritime Forum’s Getting to Zero Coalition. The study, From Pilots to Practice: Methanol and Ammonia as Shipping Fuels, draws on insights from around 40 major industry organisations. It concludes that methanol is now ready for low-carbon operation, while ammonia has reached the piloting stage.

The report highlights rapid progress in developing both fuels but warns that technological readiness alone will not deliver the transition at the required pace. Strong policy signals from the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) and national governments remain critical to accelerate adoption.
While not yet widely deployed, methanol and ammonia are expected to play a central role in the sector’s decarbonisation. Because they cannot be seamlessly integrated into existing shipping infrastructure, their uptake requires coordinated investment in new technologies both onshore and at sea. Demonstration projects and pilot programs are therefore essential steps toward establishing reliable supply chains.
Methanol, in particular, has advanced beyond proof of concept and is scaling up: about 60 methanol-capable vessels are currently in service, with more than 300 additional ships on order and nearly 20 ports already offering green methanol bunkering. Still, the report cautions that both fuels must achieve full maturity by around 2030 to meet the industry’s climate goals. Building robust supply chains is the key challenge, expanding the production of green methanol molecules and establishing safe, commercial ammonia bunkering at major ports.
When used as marine fuel, methanol combustion produces carbon dioxide (CO2), water, and energy, along with lower levels of nitrogen oxides (NOX), sulfur oxides (SOX), particulates, and trace formaldehyde compared to heavy fuel oil. The emissions profile depends on several factors:
- Fuel Source: Green methanol, produced from renewable biomass, can achieve a net-zero lifecycle carbon footprint despite releasing CO2 during combustion.
- Combustion Conditions: Engine load, operating temperature, and the use of pilot fuels can influence emissions of NOX, methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O).
- Engine Technology: New designs are being developed to optimise combustion and further reduce pollutant output.
Protea have a range of technologies working within the marine and shipping sectors. More information can be found at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine.
?#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More13th August 2025 - Carbon Capture Storage Reaching A Turning Point In Decarbonisation
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is emerging as a critical tool in the global push toward net-zero emissions—particularly for hard-to-abate sectors such as cement, steel, and chemical manufacturing, where alternative decarbonisation options are limited. While CCS has struggled to scale in the past, new momentum suggests that is changing.

DNV’s Energy Transition Outlook: CCS to 2050 forecasts that global CCS capacity will quadruple by 2030, supported by advances in technology and a surge of industry activity. This projection is reinforced by real-world developments: in May, Northern Lights—the world’s first open-access CO2 transport and storage network in Western Norway, received its inaugural shipment of liquefied CO2 from Heidelberg Materials. In the U.S., 1PointFive’s STRATOS facility in Texas is nearing operation as the world’s largest direct air capture (DAC) plant.
Over the next five years, cumulative CCS investments are expected to total around $80 billion, with roughly two-thirds of new capacity located in North America and Europe. Policy support is set to play a pivotal role, driving cost reductions of about 14% by 2030 through lower capital expenses for capture systems and reduced transportation and storage costs.
CCS is especially important for industries where emissions are structurally embedded in the production process:
-
Cement production - Releases CO2 both from the chemical reaction in clinker production and from high-temperature heating, typically fueled by fossil energy.
-
Steel production - Relies on carbon-intensive, high-heat processes often powered by coal or gas.
-
Chemical and petrochemical production - Uses fossil feedstocks and energy, generating substantial CO2 emissions.
-
Energy generation - The burning of coal, oil, or natural gas for power and heat remains a major global source of emissions.
-
Other heavy industries - Aluminum production, refining, and certain food and beverage processes also have significant carbon footprints.
These sectors are essential to modern society, yet their emissions are difficult to eliminate without CCS. With accelerating investment, policy momentum, and breakthrough projects now underway, CCS is positioned to play a central role in cutting global carbon emissions in the decade ahead.
Closer to home in the UK we have the very large The Acorn Project which is an ambitious carbon capture, utilisation, and storage (CCUS) development in northeast Scotland. It leverages existing oil and gas infrastructure to move captured CO2 from industrial emitters to secure geological storage sites deep beneath the North Sea. Serving as the transport and storage backbone of the wider Scottish Cluster, it plays a pivotal role in the UK’s path to net zero. Critics argue that the project risks prolonging the use of fossil fuels by enabling continued oil and gas extraction in the North Sea, hindering the transition to renewable energy.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) could be key in the reduction in Carbon Dioxide (CO2) from industrial processes. Protea’s range of gas analysers have been used both in research into emerging technologies for CCS, but will also play an important role in the regulatory emissions monitoring from installations of CCS. Protea’s multi-gas FTIR technology is ideally suited to new processes involving carbon reduction, such as Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS).
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More29th July 2025 - CCS To Capture 15% Of Shipboard Carbon Emissions By 2050
Industrial carbon capture and storage (CCS) is set to surge with forecasts of a fourfold increase in capacity by 2030 backed by $80 billion in investment. The momentum is expected to continue through 2050 with the shipping industry playing a growing role.

DNV's first global forecast on the future of carbon capture and storage (CCS) predicts that onboard CCS technology will capture 15% of ship-based carbon emissions by 2050. The report marks a shift in perception, stating that CCS is no longer a niche or theoretical solution but is poised for substantial growth, especially within the maritime industry. According to DNV, deployment of shipboard CCS systems is expected to begin scaling up around 2040.
While CCS has long been considered a potential tool for decarbonization, it is now gaining traction in regions with regulatory support (such as Europe) and in sectors where it is most practical, like power generation and oil and gas. Government subsidies are accelerating deployment: Denmark is backing the Greensand and Bifrost projects, while Norway is covering 80% of the costs for the Longship CCS initiative. In the U.S., tax incentives from the Inflation Reduction Act have sparked a surge in new CCS developments.
CCS can also be implemented onboard ships, although there are challenges. Captured CO2 must be stored in pressurised tanks that take up valuable space, and offloading infrastructure is currently limited to a few ports. Additionally, the capture process itself consumes energy, slightly raising overall fuel use. However, it offers a notable benefit: compatibility with conventional marine fuels, including heavy fuel oil (HFO), when used with scrubbers.
DNV projects that onboard CCS could capture and store 15% of maritime CO2 emissions by 2050, with the maritime sector contributing 9% of the total carbon stored via CCS worldwide. Shipping will also be instrumental in supporting offshore CCS infrastructure, especially in regions like the North Sea and Mediterranean. DNV expects ships to play a central role in transporting CO2 from coastal terminals to offshore injection sites.
As a leading classification society and maritime advisory firm, DNV continues to help shape the industry’s response to climate challenges, focusing on safety, energy efficiency, and environmental performance across the global shipping and offshore sectors.
Shipping will also have a part to play in developing offshore subsea injection and storage facilities. "Ship transport, especially in the North Sea or the Mediterranean Sea, will likely play a key role in transporting CO2 between shore terminals or via offshore injection," DNV predicted. DNV, formerly known as Det norske Veritas, is a leading international certification body and risk management company with a significant presence in the maritime industry. They provide a range of services including classification, advisory, and software solutions for the global shipping and offshore sectors. DNV's core focus is on enhancing safety, quality, energy efficiency, and environmental performance within the maritime world.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) could be key in the reduction in Carbon Dioxide (CO2) from industrial processes. Protea’s range of gas analysers have been used both in research into emerging technologies for CCS, but will also play an important role in the regulatory emissions monitoring from installations of CCS. Protea’s multi-gas FTIR technology is ideally suited to new processes involving carbon reduction, such as Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS). For more information visit https://www.protea.ltd.uk/carbon-capture-and-storage-ccs/.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More21st July 2025 - Global Shipping Industry Struggles To Navigate Net Zero Transition
The shipping sector, responsible for 3% of global emissions, is under growing pressure to decarbonise. Upcoming International Maritime Organization (IMO) rules require shipowners to cut emissions by 65% by 2040. The EU has already extended its emissions trading scheme to shipping and introduced FuelEU Maritime, setting lifecycle GHG intensity limits.

Despite growing regulatory momentum, the path to net zero remains complex. A wide range of technologies and fuels are being explored:
- Ammonia: Fortescue's Green Pioneer is trialing ammonia as a marine fuel, but safety, infrastructure, and supply issues persist. Only 25 ammonia-capable ships are on order globally.
- Methanol: Maersk leads with dual-fuel vessels using green and e-methanol. It now operates 13 methanol-capable ships and has ordered 20 more. European and U.S. producers are scaling e-methanol production, though costs remain high.
- Biofuels: Demand is growing due to ease of adoption, but sustainability concerns loom. NGOs warn that by 2030, most marine biofuels may come from palm and soy oil, which could increase overall emissions.
- Wind-Assisted Propulsion: Technologies like rotor sails and suction wings are gaining traction. Around 50 ships use wind-assisted systems today, with 97 more on order. These can deliver fuel savings of 20%-40%.
- Operational Efficiency: Immediate gains are available through weather routing, slow steaming, and hull cleaning. Tech firms like Sofar Ocean are using real-time data to optimise voyages and cut emissions.
The Getting to Zero Coalition (a group of 200 maritime stakeholders) argues the sector must use scalable zero-emission fuels to meet 2050 targets. However, uncertainty around fuel availability, infrastructure, and regulation continues to delay investment. While some criticise the IMO’s plan as lacking ambition, industry leaders say it offers a critical signal to drive forward decarbonisation. “You can continue to pollute,” said Fortescue’s Sara Edmonson, “but delaying transition will be costly.”
According to a recent article by the Financial Times, global ocean temperatures in May 2025 reached their second-highest level on record, highlighting a concerning two-year trend of rapid marine warming. The data, sourced from the EU’s Copernicus Climate Change Service, shows the average sea surface temperature for the month was 20.79°C, just 0.14°C below the record set in May 2024.
At the same time, atmospheric CO2 levels continued to climb. Global concentrations peaked at an average of 426 parts per million (ppm) in March, up from 423ppm the previous year. For context, CO2 levels have surged from around 300ppm over the past six decades. This trend raises growing concerns about the oceans' capacity to absorb carbon dioxide and regulate the planet’s climate.
The most important gases in terms of emissions are currently sulphur oxides (SOx) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). The creation of Emission Control Areas and stringent limits on fuel sulphur content in port are challenging particularly for the shipping industry and its suppliers. Ship operators have near imminent decisions to make based on a complex set of circumstances and a fluid regulatory background. Find out more at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine/.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More14th July 2025 - Carbon Capture Surges as Economics Policy & Industry Demand Align
After years of skepticism and stalled progress, carbon capture and storage (CCS) is experiencing a dramatic resurgence. Once criticized as too costly, unreliable, or a lifeline for fossil fuels, CCS is now expanding rapidly—driven by technological improvements, strong policy support, and rising demand from sectors like AI and data centers.

"The pace of interest and investment has snowballed,” said Jessie Stolark, executive director of the Carbon Capture Coalition. “Companies with hard-to-abate emissions are increasingly seeing CCS as a necessary tool in their decarbonization strategy."
A Shift in Momentum
CCS works by capturing CO2 emissions from industrial facilities, such as coal plants, steel mills, and cement factories, compressing the gas, and injecting it deep underground for long-term storage. While the concept is straightforward, early efforts in the 2010s faced significant setbacks due to high costs and technical challenges.
That changed when economic incentives aligned. The U.S. federal tax credit for CCS, known as 45Q, was enhanced in 2018 and expanded further under the Inflation Reduction Act in 2022. These incentives sparked a surge in development: the number of global CCS projects grew from 392 in 2023 to 628 in 2024. The U.S. now leads the world in active and planned CCS initiatives, outpacing the next four countries, Canada, the U.K., Norway and China combined.
Europe’s Big Bet
In Europe, CCS is now a core pillar of long-term climate strategy. Industrial emissions account for roughly 25% of the EU’s total, and reaching climate neutrality by 2050 will require drastic reductions, many of which can only be achieved through CCS.
To meet this challenge, the European Commission has launched an Industrial Carbon Management Strategy. Its targets are ambitious: 50 million tons of CO2 storage capacity by 2030, scaling up to 280 million tons by 2040 and 450 million tons by 2050, equivalent to about 13% of the EU's current emissions.
Achieving this will require sweeping infrastructure investments. Capture systems must be installed on power plants, cement kilns, hydrogen and chemical facilities, and waste incinerators. These sources will need to connect to an estimated 19,000 kilometers of CO2 pipelines across Europe. Temporary storage hubs will be built at ports, supported by a new fleet of CO2 transport ships. Meanwhile, depleted oil and gas reservoirs, at least 800 meters underground, must be surveyed and converted for permanent storage.
A Tool, Not a Silver Bullet
Despite the momentum, CCS remains controversial in some circles. Critics argue that it risks prolonging fossil fuel dependency and diverting attention from renewable solutions. Yet the technology's rapid adoption suggests it’s becoming a key part of the global decarbonisation toolkit, particularly for sectors where emissions are difficult or impossible to eliminate entirely.
In a world racing toward net-zero targets, CCS is no longer just a backup plan. It’s becoming a strategic necessity. Estimates vary, but a recent assessment puts the number of operational coal-fired power plants in the European Union at around 256. This figure remains fluid, as some facilities are being phased out while others may be temporarily reactivated in response to changing energy market conditions.
The largest power station in the UK is Drax Power Station, located in North Yorkshire. It's also the biggest renewable power station in the UK, generating enough electricity for 4 million homes. While historically a coal-fired plant, Drax has transitioned to using sustainable biomass, primarily wood pellets, as its main fuel source. Drax Power Station is the UK's largest single source of CO2 emissions, primarily from burning wood pellets for electricity generation. In 2023, it emitted 11.5 million tonnes of CO2, accounting for 2.9% of the UK's total territorial emissions.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) could be key in the reduction in Carbon Dioxide (CO2) from industrial processes. Protea’s range of gas analysers have been used both in research into emerging technologies for CCS, but will also play an important role in the regulatory emissions monitoring from installations of CCS. Find out more about our CCS systems at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/carbon-capture-and-storage-ccs/.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More7th July 2025 - GHG Emissions At Ports On The Rise Despite Initiatives
A new study has revealed that greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions at major global ports are still rising, despite advances in technology and sustainability initiatives. The report, titled “Quantifying Port Carbon Footprints: Container Vessel Emissions Analysis in Major Global Terminals,” analyses emissions from container shipping operations at key ports in Europe, North America, and Asia. It shows that factors like port congestion and operational inefficiencies significantly affect emissions levels.

Among the findings, Shanghai port topped the emissions list with 140,000 tons, more than Singapore, even though it handled fewer vessels. This highlights that emissions are not solely tied to vessel numbers. U.S. ports experienced particularly high emissions and congestion in early 2025, due to a surge in shipping volumes ahead of new tariffs. Meanwhile, Singapore demonstrated that innovations like Digital Twin technology can help reduce emissions even under heavy traffic.
Additionally, ports around the world are adopting initiatives to reduce their emissions. For instance, earlier this month, the Port of Rotterdam Authority launched Carbonbid, a new sustainability initiative aimed at supporting companies in the port area to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The report emphasises that elements such as port layout, terminal capacity, vessel dwell times, and idle engine use are major emission drivers. Furthermore, the study underscores the need for smarter, more efficient port operations to reduce environmental impact.
The VesselBot report also finds that port congestion and operational inefficiencies have a substantial impact on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. U.S. ports recorded the highest congestion levels in January and February 2025, alongside record-breaking container volumes and related emissions. This surge was largely attributed to preemptive shipping in anticipation of new tariffs.
The report underscores the complex relationship between port activity and emissions, While an increase in vessel traffic typically results in higher emissions, our data shows that operational performance and efficiency are critical factors in managing environmental impact. The study uses a combination of vessel geospatial tracking, operational data, and cargo volume metrics to calculate container vessel GHG emissions. It also highlights how port design, terminal capacity, vessel dwell times, and engine use during idling periods significantly affect emission levels, offering a more nuanced view than simply counting vessel movements.
The need to demonstrate environmental responsibility is key for today’s marine and offshore industries. For more information on our Marine Emissions systems please visit https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More30th June 2025 - Carbon Capture Utilisation & Storage In A Nutshell
CCUS is a climate technology that captures carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial processes and power generation, then either uses it in other applications or stores it permanently underground to prevent it from entering the atmosphere
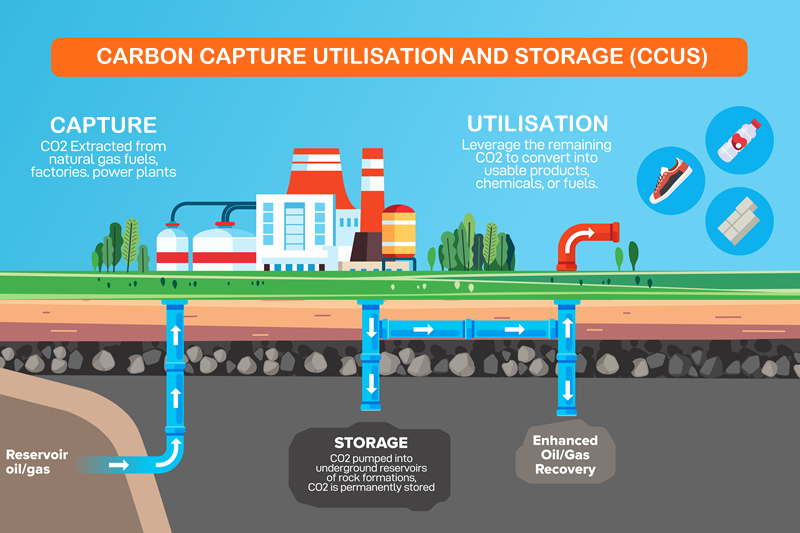
What is CCUS and Why Does it Matter?
Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage (CCUS) is a vital technology for reducing emissions from heavy industry and supporting low-carbon power generation. It captures carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions at their source, compresses them, and transports the CO2 by pipeline or ship for either reuse or safe, long-term storage deep underground. CCUS is essential for cutting emissions from heavy industries. It also supports low-carbon power from gas and enables hydrogen energy especially important when renewable sources like wind or solar aren't available.
How Does CCUS Work?
CCUS captures CO2 from industrial facilities or power plants and prevents it from entering the atmosphere. The CO2 is stored in porous rock formations, such as depleted oil and gas fields or deep saline aquifers, beneath layers of impermeable rock (called caprock), which trap the gas securely. Storage sites are continuously monitored to ensure safety and permanence.
Is CCUS Proven and Safe?
Yes, CCUS has been safely in operation since 1996 at Norway's Sleipner site in the North Sea. This experience paved the way for larger projects like Northern Lights, which now offers commercial CO2 storage for European industries. All components of the CCUS chain have been used globally for decades. In the UK, existing Health and Safety regulations, combined with offshore industry expertise, make CCUS a safe and manageable solution.
Can CCUS Help Fight Climate Change?
CCUS is the lowest-cost route to net zero. It's not just an option, it's a necessity. It allows us to cut emissions from sectors that can't otherwise be decarbonised and plays a critical role in reaching our climate goals.
Why Do We Still Need CCUS if Renewables Are Growing?
To keep the lights on in all conditions, we need low-carbon power that works 24/7. CCUS-equipped gas power stations provide this reliability. Beyond electricity, CCUS is also key to decarbonising industries like cement and steel, which have few other viable options.
What About the Cost of CCUS?
Costs vary depending on where CO2 is captured, how it's transported, and where it's stored. But compared to other decarbonisation options, CCUS is often the most practical, or the only, solution currently available.
Is There Enough Space to Store Captured Carbon?
The UK's North Sea could store up to 78 gigatonnes of CO2, enough to hold centuries of emissions. We believe the UK has a strong case to become a global carbon storage hub. CCUS is a safe, proven, and essential technology for cutting emissions in hard-to-abate sectors, ensuring reliable low-carbon power, and helping the world reach net-zero targets, at a cost that is often competitive and with ample storage capacity available.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More23rd June 2025 - Carbon Capture Reducing Maritime Shipping Emissions
Maritime shipping is responsible for around 3% of global greenhouse gas emissions, making decarbonisation of the sector essential to achieving international climate goals. Industry leaders have recognised the urgency, committing to net-zero emissions by 2050, but reaching that target will require overcoming significant challenges.

As one of the most difficult sectors to decarbonise, shipping will need a multi-faceted transformation. That includes stronger policy frameworks, real-time emissions monitoring, the adoption of breakthrough technologies like hydrogen fuel cells, and more efficient logistics and routing. Encouragingly, progress is being made on all fronts.
In a major development, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) recently adopted a Net-Zero Framework, a landmark move that introduces mandatory emissions caps and carbon pricing across the global maritime sector. Set to be formally adopted in October 2025 and enforced beginning in 2027, the regulations will apply to vessels over 5,000 gross tons, which account for 85% of international shipping’s CO2 output.
While the framework marks a major step forward for climate action, it also presents potential economic pressures for operators, particularly if implementation is uneven or delayed. However, a promising innovation from Scandinavia may offer a lifeline: a new technology that could allow existing, carbon-intensive fleets to drastically reduce emissions without the need for complete vessel replacement. This kind of innovation could help balance environmental responsibility with economic practicality, paving the way for a cleaner, more resilient global shipping industry.
Wärtsilä has officially launched its carbon capture solution (CCS) to the global maritime market, marking a major milestone in the industry's decarbonisation efforts. The system has demonstrated the ability to cut vessel CO2 emissions by up to 70%, offering shipowners a practical and immediate tool to comply with tightening environmental regulations.
The announcement follows the successful installation of the world’s first full-scale CCS system aboard Solvang ASA’s Clipper Eris. The technology captures emissions from all onboard exhaust gas sources, and has been operating since the vessel departed Singapore in February 2025.
Installed on the 21,000 m2 ethylene carrier for live testing and optimisation, the system supports Solvang ASA’s commitment to low-carbon shipping while advancing the industry’s progress toward the IMO’s 2050 greenhouse gas reduction goals. Wärtsilä’s breakthrough offers a scalable solution for existing fleets, potentially transforming the way the industry addresses shipboard emissions in the near term.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More16th June 2025 - UK Approves Viking CCS Pipeline to Support Major Carbon Capture Efforts
The UK government has granted formal approval for the Viking onshore pipeline, a £200 million (~$250 million) project that will play a central role in large-scale carbon capture and storage (CCS) initiatives off the coast of Lincolnshire.

The 34-mile underground pipeline will carry dense-phase CO2 from Immingham to the Theddlethorpe Gas Terminal, where it will then be transported offshore for permanent storage in the Viking gas fields beneath the North Sea. Led by Harbour Energy and supported by BP, the Viking CCS pipeline is a core element of a wider CCS strategy expected to attract £7 billion (~$9 billion) in investment to the Humber region by 2035. The project is forecast to deliver strong economic benefits, including:
- Creation of up to 10,000 construction-related jobs
- A projected £4 billion (~$5.2 billion) boost to the UK economy over the next decade
The development plan includes extensive infrastructure such as valve stations, inspection and venting systems, construction compounds, material storage facilities, and access roads. Approval followed a comprehensive six-month review by the Planning Inspectorate, which included input from local communities, councils, and statutory bodies. Based on its findings, the Inspectorate recommended approval, and final consent was granted by the Secretary of State for Energy Security and Net Zero.
The Viking fields are estimated to offer 300 million metric tons of COCO2 storage capacity, with the goal of reaching an annual injection rate of 10 million tons by 2030. Key Elements of a CCS Pipeline:
Purpose:
- To move CO2 in a safe, efficient, and sealed manner from the point of capture to the point of storage.
- It plays a critical role in the CCS chain, which includes:
- Capture of CO2 at source
- Transport (via pipeline, ship, or truck)
- Storage, usually in depleted oil/gas reservoirs or deep saline aquifers
Transport Method:
- CO2 is usually transported in a dense or supercritical phase, which means it's compressed into a fluid-like state to maximise efficiency and minimise pipeline size.
- CCS pipelines are similar in design to oil or gas pipelines but are specifically engineered to handle CO2's physical properties and prevent leaks.
- They include monitoring systems, valves, and safety features to manage pressure, temperature, and flow.
End Destination:
- The pipeline leads to permanent geological storage, often thousands of meters underground, where the CO2 is injected into porous rock formations capped by impermeable layers that prevent its release.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More11th June 2025 - Protea Sales Team & Alantra Panel Discuss Marine Decarbonisation
The Protea sales team recently visited Alantra, joining a panel discussing decarbonisation in the marine industry. The maritime industry is the backbone of global trade, but it faces a critical challenge, decarbonising while maintaining its vital role in enabling the flow of goods worldwide. Alantra have created a "Maritime Decarbonisation Leaders Report" which explores the transformative efforts underway in the shipping sector to address climate change.

With the industry currently reliant on oil-based fuels for 99% of its energy needs, rapid decarbonisation has become a priority for policymakers, customers, and industry leaders alike. This report delves into the challenges and opportunities in transitioning to cleaner technologies, featuring:
- An overview of the current state of maritime decarbonisation and the sector’s progress toward emissions reduction targets
- Key challenges, including the future of maritime fuels, investment needs, and infrastructure gaps for greener shipping
- Profiles of a dozen innovative maritime businesses leading the way in decarbonisation efforts
Alantra’s maritime and offshore team combines financial, technical, and commercial expertise to present these insights, offering a comprehensive view of the industry’s journey toward sustainability. As a trusted advisor in the maritime sector, Alantra is committed to supporting clients in navigating these challenges and achieving their sustainability goals.




#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture #Alantra
Read More9th June 2025 - Shipping Charts Course To Net Zero Under New IMO Climate Framework
The International Maritime Organisation (IMO) has taken a landmark step toward decarbonising global shipping, approving the first-ever regulatory framework targeting net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by around 2050. The decision, made during the IMO’s Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC 83) session in April 2025, sets the stage for transformative changes across the maritime sector.

At the core of the new framework is a mandatory reduction in the carbon intensity of marine fuels, assessed on a 'well-to-wake' basis, accounting for emissions from fuel production through to combustion. The rules apply to large vessels over 5,000 gross tons, which are responsible for the bulk of international shipping emissions. A central feature of the framework is a global emissions pricing mechanism. Vessels that exceed emissions thresholds will be required to purchase remedial units, while those using low- or zero-emission technologies may receive credits or financial incentives. Though the pricing structure is still being finalised, the IMO has made clear that carbon will come at a cost for the maritime industry.
Formal adoption of the regulations is expected in October 2025, with enforcement scheduled to begin in 2027. To support implementation and ensure a just transition, the IMO has also unveiled plans for a Global Net-Zero Transition Fund. Funded by revenue from emissions pricing, it will provide:
- Incentives for cleaner vessels
- Investment in green infrastructure and innovation
- Training and capacity-building, particularly in developing countries
The fund is specifically designed to help vulnerable regions, such as small island developing states and least developed countries, mitigate economic risks associated with the transition and maintain access to global trade. As momentum builds around climate action, the IMO’s decision marks a decisive shift: international shipping is moving beyond voluntary measures toward binding climate accountability. While final details will be refined in the coming months, the direction is clear, the era of unregulated maritime emissions is nearing its end.
- Approval of the IMO Net-Zero Framework (Mid-Term GHG Measures)
- MEPC 83 approved draft amendments to MARPOL Annex VI, introducing a new Chapter 5 that establishes the "IMO Net-Zero Framework."
- This framework includes:
- A technical element: a goal-based marine fuel standard designed to gradually lower the greenhouse gas (GHG) intensity of marine fuels.
- An economic element: a pricing mechanism for maritime GHG emissions.
- These measures are scheduled for formal adoption at an extraordinary MEPC session in October 2025 and are expected to enter into force on 1 March 2027.
- Review of Short-Term GHG Reduction Measures
- MEPC 83 completed Phase 1 of the review of short-term GHG measures, which include the Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index (EEXI), the Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan (SEEMP), and the Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII) rating scheme.
- Key actions taken:
- Adoption of amendments to the 2021 Guidelines on the operational carbon intensity reduction factors (CII reduction factors) for 2027 to 2030.
- Approval of draft amendments to Regulation 27 of MARPOL Annex VI to enhance transparency by making the IMO's data collection system (IMO DCS) on ship fuel consumption more accessible.
- Agreement on a work plan for Phase 2 of the review, to run from Spring 2026 to Spring 2028, focusing on enhancing the SEEMP framework and further developing CII metrics.
- Onboard Carbon Capture and Storage (OCCS)
- MEPC 83 approved a work plan for developing a regulatory framework for the use of onboard carbon capture and storage (OCCS) technologies, with expected completion by 2028.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More3rd June 2025 - Come & Visit Protea at Nor-Shipping 2025
Protea are exhibiting at Nor-Shipping 2025 from Tuesday 3rd to Friday 6th June 2025 in Oslo, Norway. Our booth number is D06-18 in Hall D. Nor-Shipping is at the centre of the oceans. Exhibition opening hours: Tuesday 3rd June to Thursday 5th June 10.00 - 17.00. Friday 6th June 10.00 - 15.00.

Nor-Shipping is at the centre of the oceans. This is where the maritime and ocean industries meet every two years. A natural hub for key decision makers from across the world to connect, collaborate and do deals to unlock new business opportunities. This is your arena for ocean solutions. Come and visit Protea by registering for your tickets at https://nor-shipping.com/

#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More2nd June 2025 - UK Unveils Maritime Decarbonisation Strategy For Emission Pricing & Fuel Regulations
The UK has launched a comprehensive new maritime decarbonisation strategy, building on international efforts while placing greater focus on domestic emissions and smaller vessels. Maritime Minister Mike Kane presented the strategy to the House of Commons, outlining the next phase in aligning the sector with the country’s climate goals.

In 2019, the UK’s domestic maritime sector generated approximately eight million tonnes of CO2-equivalent emissions on a full lifecycle basis. With a goal of achieving net-zero lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions by 2050, the UK has set interim targets of a 30% reduction by 2030 and 80% by 2040, relative to 2008 levels.
Key elements of the new strategy include:
- Expansion of the UK Emissions Trading Scheme to cover domestic maritime GHG emissions beginning in 2026.
- Support for global emissions pricing, with the UK advocating for the International Maritime Organization (IMO) to adopt a framework by 2027.
- Introduction of domestic fuel regulations, pending consultation in 2026, to drive the uptake of zero and net-zero GHG emission fuels and energy sources.
- Port-level initiatives to reduce emissions at berth and promote broader environmental planning.
A notable feature of the strategy is its inclusion of smaller vessels, particularly those under 400 gross tons. The government acknowledges that some sectors, such as fishing, may face challenges, while others—like offshore wind support vessels, could lead innovation. A call for evidence has been issued to guide policy development for this segment. The strategy also encourages ports to evaluate their own decarbonization efforts and consider wider environmental strategies, aligning infrastructure with national climate ambitions.
Despite acknowledging the complexity of the transition, the government sees significant economic potential. Conservative estimates suggest that decarbonizing the UK maritime sector could generate £130 to £180 million ($168 to $233 million) in gross value added annually and support 1,400 to 2,100 jobs per year through 2050. The UK Chamber of Shipping welcomed the new strategy, describing it as a timely successor to the 2019 Clean Maritime Plan and a crucial step forward for the industry. Maritime decarbonisation is critically important for both environmental and economic reasons. Here's a breakdown of why it matters:
- Global Emissions Impact
- Shipping accounts for ~3% of global greenhouse gas emissions—roughly equal to the emissions of a major industrialized country.
- Without action, maritime emissions could rise by up to 130% by 2050 due to growing trade volumes.
- Climate Goals Cannot Be Met Without It
- To achieve the Paris Agreement’s 1.5°C target, every sector—including shipping—must reduce emissions rapidly.
- Maritime transport is included in net-zero national strategies and must align with broader climate goals.
- Hard-to-Abate Sector
- Shipping is energy-intensive and difficult to electrify, making it one of the "hard-to-abate" sectors.
- Decarbonisation solutions (like alternative fuels, efficiency technologies, and carbon capture) are vital for progress.
- Regulatory Pressure is Increasing
- The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has set a target of net-zero emissions by 2050.
- Regional policies (e.g., EU ETS, UK Maritime Strategy) are introducing emission pricing, fuel mandates, and GHG intensity limits.
- Economic and Trade Implications
- Decarbonisation can create new markets and jobs (e.g., in green fuel production, retrofit technologies, port infrastructure).
- Ships that don’t comply with emerging standards risk losing market access or facing high carbon costs, impacting trade competitiveness.
- Environmental and Social Benefits
- Cleaner fuels and technologies reduce air pollution, including SOx, NOx, and particulate matter, improving health near ports and coastal areas.
- Supports sustainable development goals (SDGs) like climate action, health, and responsible consumption.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More27th May 2025 - World's First Wind Powered Carbon Removal Plant Planned in Texas
A groundbreaking project in Texas could become the world’s first direct air capture (DAC) facility powered primarily by on-site wind energy. The initiative, announced by three European companies, aims to address one of the biggest challenges in carbon removal - high operating costs. By using behind-the-meter wind power electricity generated and consumed on site, the facility will avoid grid reliance and benefit from low-cost, renewable energy.

Slated to begin operations in 2028, the plant is designed to eventually remove up to 500,000 metric tons of CO2 per year, more than the annual emissions of a typical natural gas power plant, according to EPA data. This would make it the largest DAC facility announced to date, though several similarly scaled projects are under development.
The project is a collaboration between Return Carbon, a Dutch development and investment firm; Skytree, a Netherlands-based DAC technology company; and the North American renewables division of EDF, the French state-owned utility. Captured CO2 will be permanently stored underground by Verified Carbon, a Texas-based firm. “This is a new framework we've agreed upon with EDF,” said Martijn Verwoerd, co-founder and managing director of Return Carbon. “That’s why we’re announcing it now.” As scientists stress the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions, mainly from burning fossil fuels, there is growing consensus that carbon removal technologies like DAC are also essential to draw down existing CO2 already in the atmosphere.
Here is a summary of the key benefits of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS):
- Significant Emissions Reduction
- Captures up to 90-95% of CO2 emissions from industrial sources (like power plants, steel, cement, and ships).
- Helps reduce emissions from hard-to-abate sectors where alternatives are limited.
- Supports Net-Zero Goals
- Essential for achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, especially in combination with other technologies.
- Can enable negative emissions when paired with bioenergy (BECCS).
- Enables Continued Use of Existing Infrastructure
- Allows continued use of fossil fuel assets (e.g., power plants, ships) with reduced climate impact.
- Helps manage the transition period before full decarbonisation technologies are ready.
- Industrial and Economic Benefits
- Preserves industrial competitiveness by offering a decarbonization pathway for emissions-intensive industries.
- Can create jobs in engineering, infrastructure, and CO2 transport and storage sectors.
- Enhances Blue Hydrogen Production
- CCS is critical for producing blue hydrogen (hydrogen from natural gas with captured CO2), a lower-carbon energy carrier.
- Flexible Deployment
- Can be applied to stationary sources (factories, refineries) and mobile ones (ships, in emerging technologies).
- Stored CO2 can be injected into depleted oil/gas fields or deep saline formations.
CCS is a critical tool in the climate solution portfolio, especially for cutting emissions in sectors that can’t easily switch to renewables. It’s not a silver bullet, but it's vital for buying time and achieving deep decarbonisation.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More21st May 2025 - Protea Exhibiting at Nor-Shipping 2025
Protea will be exhibiting at Nor-Shipping 2025 held in June this year. Dates of the event are Monday 2nd to Friday 6th June 2025 in Oslo, Norway (Trade show opens Tuesday 3rd). Our booth number is D06-18 in Hall D. Nor-Shipping is at the centre of the oceans. This is where the maritime and ocean industries meet every two years. A natural hub for key decision makers from across the world to connect, collaborate and do deals to unlock new business opportunities. This is your arena for ocean solutions. Come and visit Protea by registering for your tickets at https://nor-shipping.com/

Nor-Shipping has been since 1965 an activity-filled arena attracting key maritime industry players from across the world. The presence of leading heads from the entire maritime value chain and press, makes Nor-Shipping one of the world’s most recognized meeting places for strategic deal making and networking. Many of the best business relationships begin outside traditional meeting rooms. Nor-Shipping provides an unbeatable arena for professional networking and socialising.
Exhibition opening hours: Tuesday 3rd June to Thursday 5th June 10.00 - 17.00. Friday 6th June 10.00 - 15.00.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture #NorShipping
Read More19th May 2025 - LNG Retrofit Market Sees Revival Amid Regulatory Pressures
In 2024, a notable development in the maritime sector was the renewed interest in LNG retrofits, driven by shipowners seeking immediate carbon reduction solutions to meet tightening regulatory demands. Over 305 LNG-fuelled vessels were ordered last year, representing roughly 14% of global newbuild orders and significantly outpacing alternatives like methanol and ammonia.

In 2024, a notable development in the maritime sector was the renewed interest in LNG retrofits, driven by shipowners seeking immediate carbon reduction solutions to meet tightening regulatory demands. Over 305 LNG-fuelled vessels were ordered last year, representing roughly 14% of global newbuild orders and significantly outpacing alternatives like methanol and ammonia.
Although LNG offers a viable near-term compliance pathway, the report cautions that deeper decarbonization efforts will be required in the longer term. Persistent challenges include methane slip and uncertainties around the availability of bio- and e-LNG. Still, with zero-emission fuel infrastructure in early stages of development, many operators view LNG as the most practical retrofit solution currently available.
Supply chain readiness remains a key concern. The report highlights that without improved collaboration among engine manufacturers, fuel system providers, and shipyards, conversion lead times could exceed 18 months. Recent amendments to the MARPOL Annex VI NOx Technical Code are expected to ease certification hurdles for converted engines, offering some regulatory relief.
Another constraint is the limited number of shipyards equipped to handle alternative fuel conversions. While the number has grown to about 16, primarily in China and the Middle East, current global capacity supports only around 465 vessel retrofits annually, well below the anticipated peak demand of more than 1,000 conversions per year.
Despite a modest pace of retrofit orders in 2024, engine designers are actively preparing for rising future demand. The shorter lead time of retrofit projects compared to newbuilds suggests that more retrofits, targeted for completion in 2026 and 2027, may be announced as early as 2025. LNG (liquefied natural gas) reduces shipping emissions primarily by replacing traditional marine fuels like heavy fuel oil (HFO), which are more carbon-intensive. Here's how LNG helps cut emissions:
- Lower CO2 Emissions
- Up to 20-25% reduction in CO2 emissions compared to HFO.
- LNG has a higher hydrogen-to-carbon ratio, resulting in less carbon dioxide per unit of energy when burned.
- Virtually Eliminates Sulfur Oxides (SOx)
- LNG contains almost no sulfur, so it virtually eliminates SOx emissions - a major cause of acid rain and respiratory problems.
- This helps ships comply with IMO's 0.5% global sulfur cap and emission control area (ECA) regulations.
- Significantly Reduces Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
- When used in low-pressure dual-fuel engines, LNG can cut NOx emissions by up to 90%.
- This helps meet Tier III NOx regulations in ECAs.
- Particulate Matter (PM) Reduction
- LNG combustion produces far fewer particulates than HFO or marine diesel oil (MDO).
- Lower PM emissions are beneficial for both air quality and human health.
In Summary
LNG can significantly lower local air pollutants and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, making it a practical near-term option for shipping decarbonization. However, its role in a net-zero future depends on managing methane slip and scaling up renewable LNG alternatives.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More12th May 2025 - Approaches To Carbon Management & The UK Strategy
Carbon management technologies are designed to cut CO2 emissions from industries and power plants, and to remove existing CO2

Why It Matters
Carbon capture, utilisation, and storage (CCUS) is seen as essential for hitting global climate targets. Every scenario from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) that limits warming to 1.5°C or 2°C includes carbon management to reduce both current and past emissions, especially from hard-to-decarbonise sectors.
Types of Technologies
Carbon management spans several methods, from engineered solutions to nature-based approaches:
- Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) - Captures CO2 from biomass power generation and stores it underground.
- Biochar - A carbon-rich by-product of biomass pyrolysis that can be added to soil to lock away carbon.
- Nature-Based Solutions (NbS) - Includes reforestation and wetland restoration to absorb and store CO2 naturally.
- Point Source Capture - Captures emissions directly from industrial facilities and power plants.
- Enhanced Weathering - Speeds up natural rock weathering to absorb CO2 from the atmosphere.
- Direct Air Capture (DACCS) - Uses chemical processes to pull CO2 directly from ambient air for storage or reuse.
- Geological Storage - Stores captured CO2 in deep underground rock formations, a key part of the CCUS chain.
The Road Ahead
R&D is focused on making capture technologies more efficient and less costly. Large-scale pilot projects are testing their real-world effectiveness in industrial settings.
The UK’s Role
The UK is investing heavily in carbon management as part of its net zero strategy. It aims to capture 20-30 million tonnes of CO2 annually by 2030 through a mix of these technologies. Protea is a major commercial partner for UK and global based initiatives in respect to CCUS with more information at our dedicated resource location https://www.protea.ltd.uk/carbon-capture-and-storage-ccs.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More6th May 2025 - 2025 Is a Crucial Year for Shipping Decarbonisation Post MEPC 83
Shipping powers the global economy, carrying over 80% of world trade—but it comes at a climate cost. The maritime sector is responsible for around 3% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, making it the sixth-largest emitter if it were a country. Efforts to decarbonise the industry have been underway for years, but 2025 marks a turning point. In April, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) was expected to adopt key measures to implement its climate strategy and move the sector toward net-zero emissions by 2050.

These decisions made at MEPC 83, the 83rd session of the IMO’s Marine Environment Protection Committee and the regulations agreed on will be formally adopted in autumn 2025 and are expected to come into force in 2027, applying to all IMO member states.
For many in the shipping industry, the top priority is regulatory clarity. While there's strong support for the IMO’s climate goals, companies are awaiting concrete rules—particularly on a global fuel standard and possible carbon levy. These will shape the industry's approach to alternative fuels and investment.
The main obstacle to decarbonisation is the cost gap between conventional marine fuels and low- or zero-emission options like green ammonia or e-methanol. Ensuring a fair transition is also key. The IMO’s strategy calls for a “just and equitable” shift that supports vulnerable countries and regions.
While the transition may raise trade costs, it also offers economic opportunities—especially for nations that can invest in clean fuel production and port infrastructure to support zero-emission shipping. The outcomes from the MEPC 83 meeting will be public domain and we will be expanding on the key elements in due course.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More28th April 2025 - Scaling Up Carbon Dioxide Removals In The EU
EU scientific advisors are urging a rapid scale-up of carbon dioxide removal (CDR) to help fight climate change. Both natural methods, like reforestation, and technological solutions will be essential, according to the European Scientific Advisory Board on Climate Change.

CDR captures and stores CO2, helping offset emissions from hard to decarbonise sectors like cement production. It will also be crucial for reaching net-negative emissions in the future, the board said.
The report highlights the need to restore natural carbon sinks in EU land areas, which have declined by about a third over the past decade. While plants offer temporary CO2 storage, technologies like Direct Air Capture (DAC) can provide permanent storage in geological formations.
The board recommends binding targets for both short- and long-term removals, warning that CDR must complement (not replace) emission cuts. Caps on removals should prevent companies from using them as a loophole to delay reducing emissions.
The EU and Germany have proposed carbon management strategies that include CDR, as well as carbon capture and storage (CCS) and carbon capture and utilization (CCU). However, a fully functioning carbon management system in Europe is still a work in progress.
The European Scientific Advisory Board on Climate Change is an independent scientific advisory body providing the EU with scientific knowledge, expertise and advice relating to climate change. The Advisory Board identifies actions and opportunities to achieve the EU’s climate neutrality target by 2050. The Advisory Board was established by the European Climate Law of 2021 with a mandate to serve as a point of reference for the EU on scientific knowledge relating to climate change by virtue of its independence and scientific and technical expertise.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More22nd April 2025 - The IMO Must Tighten Rules On Shipping Carbon Emissions
Most global trade relies on shipping, which accounts for about 3% of global climate emissions due to heavy fuel use. One of the simplest and most effective ways to cut these emissions is to slow ships down. A 10% speed reduction can cut a ship’s emissions by nearly 20%, even if more ships are needed overall. This strategy requires no new technology and can be implemented immediately.

Cutting fuel use also reduces other harmful byproducts, like health-damaging particulates and oily sludge, which is often illegally dumped at sea. It also lessens the toxic waste generated by exhaust gas scrubbers, a largely unregulated and growing source of marine pollution.
Few actions offer such broad environmental benefits. Recent IMO meetings must seize this moment to adopt bold climate measures, including a global low-GHG fuel standard and a levy on ship emissions, to steer the shipping industry toward a cleaner, fairer future. An IMO working group met in London recently to discuss strategies for cutting greenhouse gas emissions from shipping, including a potential carbon tax. While the IMO is looking to approve emissions reduction measures at its Marine Environment Protection Committee meetings in the Spring, it is yet to commit to a carbon levy.
Supporters of a levy disagree on the price. Some suggest $20 per tonne of CO2, the EU proposes $100, and the 6PAC+ group of island nations advocates for $150. Research from University College London indicates that a $150 starting price could generate enough revenue to fund the energy transition and support a fair, equitable shift for vulnerable communities.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More16th April 2025 - DNV Statement of Compliance Achieved
Exciting News from Protea Ltd!
We are proud to announce that Protea Ltd has been awarded a Statement of Compliance by DNV for our Protea Marine Mass Emissions Systems for reporting into EU MRV!

This certification is a strong endorsement of our commitment to delivering high-quality, accurate, and compliant emissions monitoring solutions for the maritime industry. As global regulations tighten, our technology ensures that vessels stay ahead of environmental standards while enabling sustainable operations at sea.
Here's to a cleaner, more compliant future for maritime emissions!
#ProteaLtd #DNV #EmissionsMonitoring #MarineTechnology #Sustainability #Compliance #MaritimeInnovation
Read More15th April 2025 - Protea Featured in Spring Edition of Clean Shipping International
We’re excited to be part of the Spring edition of the Clean Shipping International, sharing our voice in the ongoing journey towards a cleaner, greener shipping industry.

As the maritime industry moves towards a low-emission future, we’re proud to share ideas and meaningful insights that go beyond just meeting regulations, by helping raise awareness and spark real change.

This issue highlights the people, technologies, and partnerships that are helping shape a more sustainable future for global shipping.

https://www.cleanshippinginternational.com/csi-magazine/
#CleanShipping #SustainableShipping #Spring2025 #CleanSeas #MaritimeInnovation #GreenFuture #Protea
Read More14th April 2025 - Marine Scrubber Market To Reach 20 Billion US Dollars By 2031 With New Emission Rules
Ships are vital for global trade, transporting goods across oceans. Their engines, however, emit significant exhaust gases. Marine scrubbers and exhaust gas cleaning systems are used to reduce these emissions. The marine scrubber market includes the production, installation, and maintenance of these systems.

According to Allied Market Research, the market was valued at $4.9 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $20.3 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 16.2%. Stricter global environmental regulations, especially in Europe and North America, are driving demand for cleaner technologies and emission control systems.
In the U.S., the EPA enforces major environmental laws like the Clean Air Act and the Pollution Prevention Act, focusing on reducing hazardous air pollutants. By technology, wet scrubbers accounted for nearly 90% of the market in 2021 and are expected to remain dominant, driven by strict emission standards. However, dry scrubbers are projected to grow fastest, at a CAGR of 22.6%, due to rising demand in Asia-Pacific, North America and Europe.
By application, bulk carriers held the largest share in 2021, as they transport key raw materials like coal and grain. The cruise segment, focused on passenger comfort and entertainment, is expected to grow fastest at a 21.0% CAGR through 2031. The Protea 2000 emissions monitoring system is approved for the analysis of exhaust gases from the engines and boilers of ships and offshore rigs. Robust and with proven reliability, up to six gases can be measured including SO2, CO2 and NOx.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More9th April 2025 - Protea Exhibits at Cem Middle East in Bahrain
We’re excited to announce that Protea is exhibiting at the CEM Middle East Conference in Bahrain! Come and meet us at Stand 52.
- Event: CEM Middle East
- Location: Bahrain
- Stand: 52
- Date: 8th-10th April 2025

We’ll be showcasing our latest product range in emissions monitoring. Whether you're looking to enhance compliance, improve process efficiency, or explore the latest in gas analysis technologies, our team will be there to connect and engage.



#CEMMiddleEast #Protea #EmissionsMonitoring #EnvironmentalTechnology #ProcessAnalysis #BahrainEvents #CEM2025 #CleanAirSolutions #Stand52
Read More8th April 2025 - Protea Attending CEM Middle East 2025 In Bahrain
Protea is making an impact at CEM Middle East 2025 in Bahrain from 8th to 10th April exhibiting at Stand 52. The CEM Middle East Conference and Exhibition on Emissions and Air Quality Monitoring will be taking place in Bahrain on the 8th-10th April 2025 at the Gulf Hotel and Convention Centre in Manama. The CEM Middle East exhibition will follow on from over 35 successful CEM Air Emission and Air Quality meetings that have been organised since 1997.

Don't miss this opportunity to explore our cutting-edge CEMS technology, learn how our solutions are applied in real-world industries and connect with our expert team on Stand 52 at the Bahrain International Exhibition Centre. Let us talk about emissions monitoring, innovation, and the future of environmental compliance. We will be here, ready to connect.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture #CEMMiddleEast
Read More1st April 2025 - Ankersmid M&C at M+R Antwerp
Our trusted distributor, Ankersmid M&C, is at the M+R Exhibition in Antwerp, displaying our P2000 equipment! If you’re attending on the final day, be sure to stop by, take a look, and ask any questions to their knowledgeable team.
This is a great opportunity to explore the Protea Portfolio and discover our advanced gas analysis solutions. Whether you're looking for high-performance emissions monitoring, process control, or Automotive Emission Testing, our experts at Ankersmid are ready to provide insights and guidance.
#MRAntwerp #Ankersmid #P2000 #Exhibition #Protea #Emissions #EmissionMonitoring

 Read More
Read More 31st March 2025 - EU Maritime Shipping Emissions Continue To Rise Driven By LNG
Methane emissions from the EU’s maritime sector more than doubled between 2018 and 2023, largely due to the rising use of liquefied natural gas (LNG) as a marine fuel, according to the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA).

In 2022, shipping accounted for 26% of methane emissions from the EU’s transport sector. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential 80 times higher than CO2 over 20 years. Despite legislative efforts to curb emissions, EMSA and the European Environment Agency (EEA) have raised concerns over LNG’s effectiveness in reducing the maritime industry’s environmental impact.
New Report Highlights Environmental Pressures
The second edition of the European Maritime Transport Environmental Report examines the sector’s key environmental challenges, including:
- Oil and water discharges
- Marine litter
- Port expansion and its impact on biodiversity
- Emissions from greenhouse gases and air pollutants
Regulatory measures, such as the inclusion of shipping in the EU Emissions Trading System and the expansion of sulphur emission control areas, are helping reduce some emissions. However, the report highlights gaps in mandatory reporting for pollutants like particulate matter and black carbon, making it difficult to assess the sector’s full environmental footprint.
The Need for Data and Workforce Retraining
The report also calls for more comprehensive data on ship manufacturing, decommissioning, and maintenance to better understand the full life cycle emissions of vessels. It warns that the adoption of alternative fuels and propulsion systems will require harmonized international guidelines and workforce retraining to ensure a smooth transition.
European Oceans Pact and Future Policy
The findings will inform the development of the European Oceans Pact, an EU-backed initiative to promote sustainable ocean management and a competitive blue economy. A public consultation closed in February 2025, with the European Commission set to announce its plans in June 2025.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More31st March 2025 - Sales & Service Training & Sea Asia Expo 2025 – Singapore
This week Protea hosted a series of Sales and Service Training sessions with our key distributors/customers ahead of the Sea Asia 2025 exhibition.




These sessions were focused on expanding product knowledge and providing a hands-on understanding of our portfolio. We were thrilled to see the engagement as we explored ways to enhance both sales and service.
A huge thank you to all the participants for their involvement. Together, we are building stronger partnerships and ensuring that our solutions continue to meet and exceed customer expectations.
We were excited to see everyone on the final day of #SeaAsia2025!
#Protea #SeaAsia2025 #SalesTraining #ServiceExcellence #Distributors #CustomerSuccess #MarineIndustry #ProductKnowledge #Innovation #Teamwork
Read More24th March 2025 - Protea Attending Sea Asia 25-27 March In Singapore
Protea is attending the 10th Sea Asia in Singapore at the Marina Bay Sands, 10 Bayfront Ave, Singapore 018956, at Booth number B2-B26. Sea Asia, organised by Informa Markets, the world’s largest trade show organiser, in partnership with Singapore Maritime Foundation will mark its 10th edition in Singapore from March 25th to 27th, 2025. In its last iteration in 2023, the event drew over 18,000 attendees from 90 countries and welcomed more than 400 exhibitors, including representation from 12 national pavilions.

For the last 20 years, Sea Asia has served as a crucial platform for industry leaders to connect, collaborate, and drive innovation within the maritime sector. The year 2025 holds special significance as it marks the 10th biennial edition of Sea Asia.
Originally launched in 2007 as a collaboration between Seatrade and the Singapore Maritime Foundation (SMF) to highlight Asia, particularly Singapore’s strategic role in the maritime industry, Sea Asia has evolved into a flagship event on the global maritime calendar. Sea Asia has grown to be the largest event in the region, the previous edition welcomed over 18,000 participants, underscoring its remarkable growth and influence.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More17th March 2025 - A Combined CCUS & Shipping Strategy Starts In 2025
The UK government is making significant strides in establishing a comprehensive carbon capture, utilisation, and storage (CCUS) supply chain, though integrating non-pipeline transport (NPT) clusters into the network remains in its early stages.

Following the publication of a CCUS roadmap in December 2023, the government approved £21.7 billion (US$26.5 billion) in funding for Track-1 clusters last October. These clusters will serve as the UK’s first two large-scale sequestration sites, with pipeline-connected emitter networks in Teesside and Merseyside. The government has confirmed that construction of the UK’s carbon capture industry will commence in 2025.
UK’s First CO
The Northern Endurance Partnership (NEP), responsible for CO2transport and storage within the East Coast Cluster, reached financial close in December, allowing its infrastructure network to move into execution. Initially, the system will support three carbon capture projects in Teesside:
- NZT Power
- H2 Teesside
- Teesside Hydrogen CO2 Capture
Backed by BP, Equinor, and TotalEnergies, NEP’s network is expected to transport and store up to 4 million tonnes of CO2 annually, with construction set to begin in mid-2025 and operations scheduled for 2028.
Expanding CCS Beyond Oil and Gas
Globally, carbon capture and storage (CCS) has been primarily used for enhanced oil and gas recovery, particularly in the US, where economic incentives and existing expertise support deployment. However, by 2030, CCS is expected to play a growing role in:
- Blue hydrogen production
- Abated power generation (gas, coal, and waste-to-energy plants)
- Industrial applications, including cement, petrochemicals, and steel
CCS is particularly crucial for the cement sector, where emissions reductions are difficult without carbon capture. While the steel industry is increasingly adopting electrification and hydrogen solutions, CCS remains a viable option for cutting emissions.
Currently, the vast majority of captured CO2 is permanently stored underground, with just 2% used in industries such as greenhouse cultivation. However, future applications include producing plastics and synthetic fuels for ships, planes, and trucks, a key potential market in a net-zero economy where fossil fuel-derived carbon must be replaced by captured or recycled sources.
Non-Pipeline Transport (NPT): The Next Phase of CCUS
To further expand CCUS adoption, the UK government is exploring non-pipeline transport (NPT) clusters. In this model, pipelines transport CO2 from emitters to terminals, but ships, rail, or trucks deliver it to storage sites instead of dedicated pipelines.
In April 2024, the government issued a Call for Evidence on NPT, later summarising responses in November. Findings indicate strong industry interest in NPT, with several projects expected to be ready to capture significant CO2 volumes by 2030.
7CO2: A Pioneering Non-Pipeline Transport Hub
One of the UK's leading NPT projects is 7CO2, a carbon capture and shipping hub in southwest England. A coalition of regional energy producers, CO2 storage firms, and maritime transport providers has signed an agreement to assess its feasibility.
How 7CO2 Works:
- Captured CO2 is transported by pipeline or rail to Avonmouth Docks.
- The CO2 is then liquefied, stored, and shipped to permanent geological storage.
- Alternatively, captured CO2 may be used to produce low-carbon fuels for aviation and shipping.
The 7CO2 hub aims to be a national catalyst for CO2 shipping and rail transport, supporting regional job creation, investment, and industrial decarbonisation. As the UK’s CCUS industry evolves, NPT solutions like 7CO2 could play a vital role in broadening access to carbon capture technology, enabling industries beyond pipeline-connected clusters to participate in decarbonisation efforts.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More10th March 2025 - IMO Looks To Finalise Proposed GHG Emissions Pricing Mechanism
Shipping emissions are a significant contributor to global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, impacting both the environment and public health. The maritime industry alone is responsible for nearly 3% of global CO2 emissions, largely due to its reliance on fossil fuels such as heavy fuel oil (HFO) and marine diesel.

Governments worldwide are now moving closer to finalising a historic carbon levy on shipping emissions, with major agreements coming from the recent 18th International Maritime Organisation (IMO) meeting in London. Countries across Africa, Asia, the Caribbean, Europe, and the Pacific, representing a large portion of the global shipping fleet, are in favor of implementing a flat-rate tax on each tonne of greenhouse gas emitted by vessels.
Widespread Support for Carbon Levy
The proposal has gained the backing of key shipping nations, including Greece, South Korea, Japan, and the UK, alongside major regulatory bodies such as the European Commission and the International Chamber of Shipping (ICS).
The suggested levy ranges between $18 and $150 per tonne of emissions, with a study by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) analysing its economic impact. The goal of this initiative is to narrow the cost gap between conventional marine fuels and zero/near-zero GHG emission alternatives, such as green methanol, ammonia, and hydrogen, thereby incentivising their adoption. Revenue generated from the tax would be used to reward cleaner fuel production and encourage uptake, while also providing billions of dollars annually to help developing countries reduce maritime emissions.
Addressing Concerns and Finalising Negotiations
“While a large number of governments now support a universal flat-rate GHG contribution by ships, or something similar, a minority of governments still have concerns," said ICS Secretary General Guy Platten. "Working in cooperation with all IMO Member States, we will do our best to address these concerns in the final stages of these critical negotiations.”
Co-Sponsors of the MARPOL Proposal
The proposed MARPOL regulatory text has been co-sponsored by the following countries and organisations: Austria, Bahamas, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Fiji, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Jamaica, Japan, Kenya, Latvia, Liberia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Marshall Islands, Montenegro, Netherlands, Nigeria, Palau, Panama, Poland, Portugal, Republic of Korea, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Solomon Islands, Spain, Sweden, Seychelles, Tonga, Tuvalu, Ukraine, United Kingdom, Vanuatu, the European Commission, and the International Chamber of Shipping.
With growing momentum behind this initiative, the IMO meeting could mark a pivotal moment in the global effort to curb shipping emissions and transition towards a more sustainable maritime industry.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More3rd March 2025 - Protea Attending LNGCON 2025 10-12 March In Amsterdam
Protea is attending the 11th International LNG Congress (LNGCON) in Amsterdam at the Van der Valk Hotel Schiphol, A4 3, 2132 MA Hoofddorp, Netherlands at Booth number 27. LNGCON 2025 serves as the annual closed-door networking platform, uniting stakeholders across the entire LNG chain and industry leaders. This 11th edition, hosted in the Netherlands, attracts over 350 decision-makers globally and runs from 10th March to the 12th March 2025.

Sustainability has always been one of the dominant themes throughout these events. The time is now for us to play a bigger part in achieving the global Sustainable Development Goals. Protea is committed to organising events in an eco-friendly way. To minimise the environmental impacts we are making a shift towards greener practices and meaningful partnerships. We are focused on continuous improvement and strive to make our events more environmentally conscious. Join us on our journey to a sustainable future covering the following subjects at LNGCON 2025.
- 2-day Business Programme - more than 45 case studies from LNG professionals
- Panel Discussion On LNG - projects legislation and financing
- Hot Topics - including Operations and Maintenance in the LNG industry
- Low-carbon LNG - opportunities and challenges
- Market Trends - how to increase LNG supply to Europe?
- Technical Focus - covering small-scale LNG projects
- LNG In Road And Marine Industry - LNG usage as fuel for trucks and fleet
- Green Standards - alternative fuels influencing Green mobility
- New Initiatives - of the industry including Bio-LNG and Hydrogen
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More27th February 2025 - UK Distributor Service Training
At Protea, we believe that continuous learning is key to delivering the best solutions for our customers. This week, we kicked off an in-depth training session for our distributors, focusing on the P2000 instrument- diving into its capabilities, applications, and best practices.

But the learning doesn’t stop there! For the rest of the week, we’re exploring FTIR technology in detail, ensuring our distributors gain a deeper understanding of its principles and applications.

By equipping our partners with the latest knowledge, we’re strengthening our global network and ensuring the highest level of service and support for our customers.
#Protea #Training #FTIR #P2000 #Innovation #Spectroscopy #ContinuousLearning
Read More25th February 2025 - FuelEU Maritime Regulation In Force For 2025
The FuelEU Maritime Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2023/1805), introduced as part of the European Commission’s Fit for 55 legislative package, represents a transformative step toward decarbonising the maritime sector. Fully effective from January 1, 2025, the regulation incentivises the adoption of renewable, low-carbon fuels and clean energy technologies, setting ambitious targets for the shipping industry's greenhouse gas (GHG) reductions.

Key Highlights of the FuelEU Maritime Regulation:
- Greenhouse Gas Intensity Reduction Targets
- Applicable to ships over 5,000 gross tons calling at EU ports, regardless of their flag.
- Requires a 2% reduction in GHG intensity of marine fuels starting in 2025, scaling up to an 80% reduction by 2050.
- Covers CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide emissions over the full lifecycle of fuels, using a Well-to-Wake (WtW) analysis.
- Shore Power for Zero-Emission Operations
- From January 1, 2030, passenger and container ships at berth in ports specified under the Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulation (AFIR) must use on-shore power supply (OPS) or equivalent zero-emission technologies.
- By 2035, this requirement extends to all EU ports with OPS capabilities, although Member States may implement the rule earlier.
- Technology-Neutral and Flexible Compliance
- Adopts a goal-based approach, allowing operators to choose fuels and technologies that best suit their needs, including biofuels, LNG, methanol, ammonia, and hydrogen.
- Includes mechanisms to support existing fleets in achieving compliance and rewards early adopters of sustainable solutions.
Broader Context and Industry Impact:
With shipping contributing roughly 3% of global emissions, this regulation is integral to achieving the EU’s Fit for 55 initiative, targeting a 55% emissions reduction by 2030. The phased approach is designed to encourage innovation and align with the sector’s operational realities, while ensuring that GHG reductions are met progressively.
Challenges Ahead:
While the regulation provides flexibility, significant hurdles remain:
- High Costs: Transitioning to low- and zero-emission fuels requires substantial investment in technology and infrastructure.
- Fuel Availability: Developing and scaling up sustainable fuel production to meet demand is a critical concern.
Despite these challenges, the FuelEU Maritime Regulation is a bold step forward, positioning the EU as a leader in maritime decarbonisation and fostering global advancements in sustainable shipping practices.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More17th February 2025 - Northern Lights Pioneering Open-Source CO2 Transport & Storage Project
Northern Lights is developing the world’s first open-source infrastructure for CO2 transport and storage, providing a groundbreaking solution for industrial companies to manage and reduce their emissions. Owned equally by TotalEnergies, Equinor, and Shell, the project became operational in September 2024 and has the capacity to store 1.5 million tonnes of CO2 annually in its first phase.

With strong backing from the Norwegian Government and its owners, Northern Lights offers a practical pathway for decarbonising industries in Norway and across Europe, making significant strides toward achieving net-zero goals.
How Northern Lights Works
The project's innovative infrastructure enables:
- CO2 Transport - Captured CO2 is transported from industrial capture sites by ship to a receiving terminal on Norway's western coast.
- Intermediate Storage - CO2 is temporarily stored at the onshore terminal.
- Permanent Storage - The CO2 is transported via pipeline to a secure reservoir located 2,600 meters beneath the seabed in the North Sea for permanent sequestration.
Phase 1: Longship Collaboration
Northern Lights forms the transport and storage component of Longship, the Norwegian Government’s full-scale carbon capture and storage (CCS) project. Longship showcases the viability of CCS as a decarbonisation strategy, with the goal of inspiring similar initiatives across Europe and globally.
Key elements of the Longship project include:
- Capturing CO2 from industrial sites in the Oslo-fjord region (e.g., cement and waste-to-energy facilities).
- Shipping liquefied CO2 to the onshore terminal.
- Transporting CO2 via pipeline to the offshore subsea storage site.
A Commercial CCS Market for Europe
Northern Lights is designed to be open and flexible, creating opportunities for third-party participation in CO2 transport and storage. By developing a scalable and accessible infrastructure, the project aims to foster the growth of a commercial CCS market in Europe. This cross-border initiative offers industries across the continent the ability to safely and permanently store their CO2, reducing emissions while supporting economic growth. Phase 1, operational since 2024, will be followed by future expansions to further increase storage capacity.
Norwegian Leadership in CCS
The Norwegian Government’s leadership and investment in CCS have been instrumental in bringing Longship and Northern Lights to life. These projects represent Norway’s ambition to establish a full-scale CCS value chain, demonstrating the potential of carbon capture as a critical solution for industrial decarbonisation.
Looking Ahead
With its open-source model and pioneering infrastructure, Northern Lights is a beacon of innovation in the fight against climate change. It positions Norway and Europe at the forefront of industrial decarbonization, providing scalable solutions for reducing emissions and achieving climate targets. By demonstrating the viability of CCS as a service, Northern Lights is paving the way for a sustainable and net-zero future.
From a shipping and marine perspective The arrival of the liquefied CO2 carrier Northern Pioneer represents a significant milestone in advancing carbon capture and storage (CCS) within the maritime sector. Fully operational, the vessel is designed to transport liquefied CO2 from capture facilities to Northern Lights’ receiving terminal in Øygarden, where the CO2 will be permanently stored underground. This confirms the converging path of both the CCS and shipping industry sectors which is occuring more often now and in the future.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More10th February 2025 - US Maritime Energy & Emissions Action Plan Targets Net Zero By 2050
The United States has unveiled its Action Plan for Maritime Energy and Emissions Innovation, laying out a comprehensive roadmap to drastically reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the maritime sector and achieve near-total decarbonisation by 2050. Central to this plan is the Sustainable Maritime Fuel Grand Challenge, a collaborative public-private initiative aimed at accelerating the development and deployment of low- and zero-emission fuels, such as green ammonia and methanol, alongside modernising shipbuilding and port infrastructure.

Key Actions for Decarbonisation
The plan identifies three primary strategies to decarbonise the maritime industry:
- Sustainable Maritime Grand Challenge - Coordinating with industry to rapidly deploy affordable, competitive, and scalable low-emission fuels and technologies.
- Fuel Transition and Technology Adoption - Promoting the use of green ammonia, methanol, sustainable drop-in fuels, vessel electrification, and hydrogen fuel cell technologies for ocean-going vessels.
- International Leadership - Strengthening commitments through global partnerships such as the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) and initiatives like the Green Shipping Challenge.
Building on the 2023 National Blueprint for Transportation Decarbonisation, the plan focuses on technology solutions tailored to specific vessel types:
- Electrification for harbour craft.
- Biofuel and methanol adoption for ocean-going vessels.
- Hybrid solutions for non-commercial vessels.
Global and Economic Impacts
Aligning with IMO goals, the plan targets increasing the use of zero emission fuels to at least 5% of global maritime energy by 2030. Achieving net zero emissions in the maritime sector is expected to bolster the US economy by:
- Promoting clean energy innovation.
- Enhancing global competitiveness.
- Reducing climate change and air pollution impacts on communities.
The plan calls for strategic initiatives to support:
- Design and production of low and zero-emission vessels.
- Development and bunkering of sustainable maritime fuels.
- Construction of critical port and energy infrastructure.
By 2025, the USA will define standards for sustainable maritime fuels, focusing on both environmental and socio-economic sustainability.
Positioning the USA as a Global Leader
With maritime shipping contributing significantly to global emissions, the US plan positions the nation as a leader in decarbonising international logistics. It also reinforces domestic infrastructure growth and the clean energy transition, aligning economic development with environmental stewardship. This bold roadmap underscores the US's commitment to a sustainable maritime future and its role in shaping global efforts to combat climate change. The need to demonstrate environmental responsibility is key for today’s marine and offshore industries. Protea has a complete Marine emissions monitoring section on our website at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More3rd February 2025 - First UK Commercial Carbon Capture Facility Moves Ahead
In early 2024, we reported on plans for the UK’s first commercial carbon capture, usage, and storage (CCUS) facility in the North East. Now, one of these groundbreaking projects has secured financial approval, paving the way for construction to begin in mid-2025. The Net Zero Teesside Power (NZT Power) project, a 742-MW gas-fired power plant with integrated carbon capture and storage (CCS), is set to become one of the world’s first commercial-scale facilities of its kind. Captured CO2 emissions will be transported and permanently stored beneath the North Sea.

The consortium behind this transformative initiative includes Technip Energies, GE Vernova, Balfour Beatty Group, and Shell Catalysts & Technologies. Project ownership lies with NZT Power, a joint venture comprising bp and Equinor (each holding a 45% share) and TotalEnergies (10%). Together, these companies also form the Northern Endurance Partnership (NEP), tasked with developing the CO2 transportation and storage infrastructure.
Key Features of the Project
- Flexible Low-Carbon Power: The plant will produce up to 742 MW of dispatchable, low-carbon electricity enough to meet the annual needs of more than 1 million UK homes.
- Carbon Capture Goals: The facility will capture 2 million tonnes of CO2 annually, significantly contributing to the UK’s net-zero targets.
- Economic Impact: Construction is expected to create over 3,000 jobs, with around 1,000 permanent jobs required annually during operations through 2050.
- Decarbonisation Hub: The plant will act as a central node for other Teesside industries to share CO2 transportation and storage infrastructure.
Government Support and Future Prospects
The UK government has set a target to capture and store 20 million tonnes of CO2 annually by 2030 as part of its clean energy transition. The London School of Economics and Political Science notes that this project aligns with national efforts to reinvigorate industrial regions like Teesside. Prime Minister Keir Starmer commented: "Backing the carbon capture industry will help reignite industrial heartlands and drive investment in communities like Teesside. This investment reflects a commitment to the industries of the future."
Timeline and Milestones
- March 2023: NZT Power was included in the Track 1 Project Negotiation List by the Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (DESNZ).
- December 2024: Financial close was achieved.
- Mid-2025: Construction is scheduled to commence.
- 2028: Facility start-up, supporting the government’s Clean Power 2030 ambition.
A Major Step Toward Net Zero
The Net Zero Teesside Power project is poised to become a landmark in the UK’s journey toward decarbonisation. By delivering clean energy and supporting local industries, this initiative represents a vital step in meeting national climate goals while driving economic regeneration in the North East. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) could be key in the reduction in Carbon Dioxide (CO2) from industrial processes and our full offering is found on our website at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/carbon-capture-and-storage-ccs
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More27th January 2025 - Optimising Port Arrivals Could Cut Voyage Emissions Significantly
Optimising port arrivals to account for congestion and waiting times could reduce voyage emissions by as much as 25% for certain vessel types, according to a new report from UCL and UMAS. The study, which analysed ship movements from 2018 to 2022, highlights significant emissions savings if port arrival inefficiencies are addressed.

The report estimates potential emissions reductions of around 10% for containerships and dry bulk carriers, 16% for gas carriers and oil tankers, and nearly 25% for chemical tankers when port arrival scheduling is optimised. Between 2018 and 2022, waiting times for chemical tankers, gas carriers, and bulk carriers at anchor before berthing increased sharply, reaching 5.5% to 6% of their annual operating time by 2022. In contrast, waiting times for oil tankers and container ships remained relatively stable, at approximately 4.5% to 5.5%.
The rise in delays for certain vessel types stems from several factors, including port congestion exacerbated during the COVID-19 pandemic and a post-pandemic surge in maritime trade. These delays have underscored the broader inefficiencies within the maritime system.
The study also notes that port congestion disproportionately affects low-income member states, hindering their decarbonisation efforts. While these equity concerns were not examined in detail, the findings suggest that improving ship-port interface efficiencies could play a role in supporting a just and equitable transition as part of mid-term decarbonisation measures. Marine and shipping emissions will be in focus throughout the year with a mixture of gains being seen across increased port and journey efficiencies, improved fuel and engine systems and emissions monitoring technologies.
- University Maritime Advisory Services (UMAS) - University Maritime Advisory Services (UMAS) is a commercial consultancy that helps the shipping, maritime, and energy sectors transition to a carbon-free future.
- Energy Institute Shipping Research Group (UCL) - The research group is the leading authority in the understanding of barriers to decarbonisation in the shipping sector and using socio-technical transitions frameworks to provide interpretation to key decision makers in international, regional, national levels across both public and private stakeholders.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More20th January 2025 - Europe Wanting To Take A lead In Carbon Capture Projects & Technology
Since the beginning of the decade, the European Commission has pushed for legislation to integrate carbon capture and storage (CCS) into the EU carbon market. This initiative gained urgency during the gas crisis following Russia's invasion of Ukraine. As coal power plants ramped up production to offset reduced Russian gas deliveries, emissions surged, sending carbon market prices skyrocketing and straining industries across Europe. Meanwhile, the UK Government has committed billions to next-generation CCS projects, positioning itself as a global leader in carbon management and sustainability innovation.

CCUS in the USA
The United States remains the global frontrunner in carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS), accounting for 50%-60% of global capacity and half of planned capacity worldwide. However, the sector's trajectory may shift with the next presidential administration in January 2025, potentially reshaping federal climate commitments.
The U.S. federal production tax credit, 45Q, incentivises companies by offering per-ton rewards for securely storing carbon dioxide in geological reservoirs. California’s Low Carbon Fuel Standard further drives demand for CCUS-enabled products, with similar policies spreading across states like Washington, Oregon, and British Columbia, and being considered in 14 other states.
CCUS in China
China’s “double carbon goal” aims for peak emissions by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060. Meeting this target necessitates substantial CCUS deployment, with projected emission reductions reaching up to 1.45 billion tons annually by 2050.
While China has made strides with around 40 CCUS projects in operation or intermittent use, the cumulative emissions reduction over 15 years (2005–2020) stands at only 3.298 million tons. Analysts stress the importance of developing robust strategies and processes to achieve the ambitious targets for 2040 and beyond.
CCUS in Europe
Europe has embraced diverse approaches to CCUS implementation, driven by ambitious climate goals. This is seen across the EU nations and those outside of the union such as the UK, Switzerland and Norway :
- United Kingdom: The UK is fostering CCUS hubs, including Net Zero Teesside, with over 60 projects in the pipeline. Policies include contracts for difference, capital co-funding, and regulated asset fees to support emitters and transport/storage operators.
- Norway: Norway’s Longship/Northern Lights project, operational from 2024, combines industrial carbon capture with shared transport and storage infrastructure, aiming to scale global CCUS deployment.
- Netherlands: Through the Rotterdam/Porthos hub, the Dutch government subsidises the gap between EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) costs and capture expenses, targeting significant industrial emission reductions by 2030.
- Germany: Germany’s Carbon Management Strategy (CMS) seeks carbon neutrality by 2045. The program includes subsidies for raw material industries and proposed amendments to the Carbon Dioxide Storage Act.
- Denmark: The Danish CCUS Fund provides DKK 2.15 billion in subsidies over 20 years, aiming for annual CO2 reductions of 0.4 million tons by 2025/2026 and 0.9 million tons by 2030.
- France: In 2023, France proposed a CCUS strategy targeting 4–8.5 million tons of CO2 captured annually by 2030 and 15–20 million tons by 2050.
- Spain: Leveraging its Ebro Basin, Spain plans to deploy CCUS technology capable of reducing 4.42 megatons of CO2 emissions annually by 2050.
Carbon capture is emerging as a pivotal tool for global decarbonisation. While regions vary in their approaches, the momentum behind CCUS underscores its critical role in achieving climate targets and fostering economic transformation.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More16th January 2025 - Protea is Featured Within the Winter Edition of the Clean Shipping International!
We’re thrilled to share that Protea is featured within the Winter Edition of the Clean Shipping International! Inside, you'll find an in-depth article highlighting how Protea is exceeding regulatory demands and setting a new standard for environmental compliance.

This recognition highlights our commitment to sustainable shipping and delivering exceptional solutions that not only meet but exceed the evolving global standards.
Together, we are steering towards a cleaner, greener future for the shipping industry.
Check it out now: https://www.cleanshippinginternational.com/csi-magazine-winter-2024/

#Protea #CleanShipping #Sustainability #Innovation #MaritimeExcellence
Read More14th January 2025 - Exciting Plans for 2025!
Our Peterborough Site recently came together for an engaging session focused on our 2025 goals and R&D projects. This productive meeting was a fantastic opportunity to discuss live projects, share new ideas, and spark creativity.
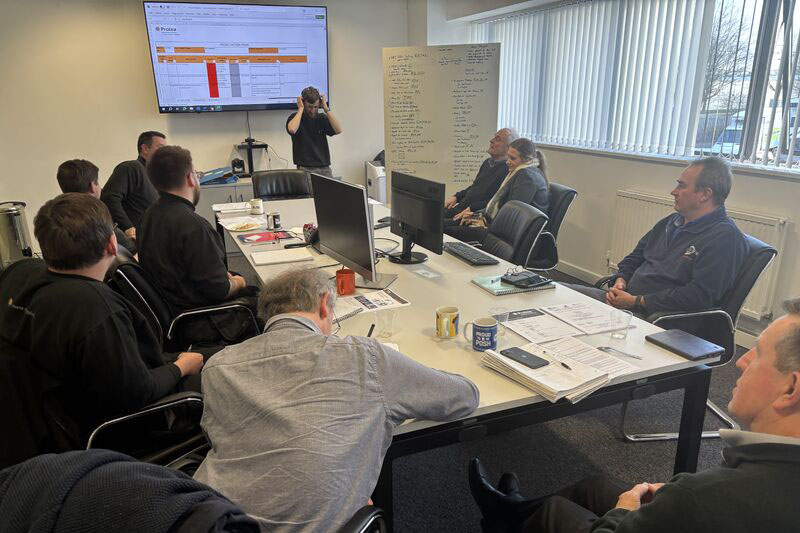

Team members shared personal and team goals for the upcoming year, ensuring that everyone is working together and excited for the amazing journey ahead.
Stay tuned! Follow Protea to keep up with the exciting projects and developments coming your way in 2025.

#Teamwork #Innovation #Protea #RandD #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers
Read More13th January 2025 - Shipping Emissions Significantly Reduced By Sailing Slower Analysis Shows
Slow Steaming and Emissions Reduction: Insights from Transport & Environment (T&E) has reinforced its advocacy for slow steaming by publishing models on its website. According to their analysis, a container ship traveling between Rotterdam and Shanghai at 75% of its maximum speed could reduce carbon emissions by 47%. Although this approach decreases container capacity, T&E concludes that adding one additional ship for every four vessels would still result in a net reduction of CO2 emissions by 34%, provided all ships operate at three-quarters speed.

Fuel Prices & Ship Speeds A new study commissioned by T&E reveals no significant link between fuel prices and ship speeds, which are a critical factor in operational efficiency. While the study indicates that shipping companies tend to order more efficiently designed ships approximately six years after global oil prices increase, it found no correlation between fuel prices and actual sailing speeds. This conclusion is supported by the EU’s Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) data from 2018 to 2023.
Policy Implications & Efficiency Measures Many policy-makers in the European Union (EU) and the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) argue that higher fuel prices resulting from emissions pricing and fuel standards will incentivise energy efficiency and emissions reductions. However, there is no scientific consensus or real-world evidence to substantiate this claim. To investigate further, T&E commissioned CE Delft to study the relationship between fuel prices and technical and operational efficiency over three decades. The findings indicate:
- Technical Efficiency: Shipping companies order slightly more efficient ships in response to higher fuel prices, albeit with a six-year delay.
- Operational Efficiency: No clear link exists between higher fuel prices and improved operational practices, such as reduced sailing speeds
These results highlight the need for targeted actions to drive energy efficiency. T&E urges policy-makers in the EU, IMO, and other regions to ensure their emissions reduction policies include explicit, concrete measures to enhance energy efficiency in the shipping sector.
MO Reforms & Future Steps This call for action comes as the IMO continues addressing perceived shortcomings in the Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII), which recently came into effect. Reforms to the CII were a focal point at last year’s Marine Environment Protection Committee and are expected to feature prominently in the 2025 vote on the IMO’s next steps toward a net-zero shipping policy.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More6th January 2025 - DESNZ Carbon Capture Business & Waste Industrial Model Launched
The Subsidy Advice Unit (SAU) has released a detailed report offering advice to the Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (DESNZ) on proposed subsidy schemes for Industrial Carbon Capture (ICC) and Waste ICC business models.

Overview of the Report
The report evaluates DESNZ’s assessment of the compliance of the proposed schemes with the requirements outlined in the Subsidy Control Act 2022. This evaluation forms a critical part of ensuring that the ICC and Waste ICC subsidy schemes align with legislative standards while addressing the UK’s decarbonisation goals.
Objectives of the ICC and Waste ICC Schemes
The Industrial Carbon Capture (ICC) and Waste ICC business models aim to:
- Incentivise the deployment and operation of Carbon Capture, Usage, and Storage (CCUS) technology.
- Support industrial users and residual waste management facilities, which often lack viable alternatives for achieving deep decarbonisation.
The budget for these schemes is up to £8.35 billion, contributing to a broader suite of measures designed to deploy CCUS at the scale and pace necessary to meet Carbon Budget 6 and achieve Net Zero by 2050.
Challenges Addressed by the Schemes
Industrial and waste emitters currently face significant barriers to adopting CCUS due to:
- High Costs: The expense of constructing and operating CCUS systems exceeds the costs incurred through carbon dioxide emissions penalties under the UK Emission Trading Scheme (UK ETS).
- Market Gaps and Risks: Emitters encounter challenges such as cross-chain risks and first-mover disadvantages, further disincentivizing CCUS deployment.
Key Features of the Schemes
1. Revenue Support Contracts:
- A private law contract for up to 15 years, structured as an initial 10-year period with annual extensions for up to five additional years.
- Payments per tonne of captured CO2 to cover operational expenses, CO2 Transport and Storage (T&S) charges, and capital investment repayment with a rate of return.
- For ICC projects, protection of UK ETS Free Allowances revenues to reduce emitter risks and minimize market distortions.
- A framework modelled on the Contract for Difference structure.
2. Capital Grant Co-Funding:
- Co-funding to bridge financing gaps for CCUS projects.
- Designed to reduce overall subsidies required, improving affordability and ensuring value for money for the government.
Funding Sources
- Revenue Support Contracts: Financed through the Industrial Decarbonisation and Hydrogen Revenue Scheme.
- Capex Co-Funding: Provided via the CCUS Infrastructure Fund.
About DESNZ
The Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (DESNZ) was established on February 7, 2023, during a cabinet reshuffle under the previous Prime Minister Rishi Sunak. This new department assumed the energy policy responsibilities previously managed by the Department for Business, Energy, and Industrial Strategy (BEIS). DESNZ’s mission includes advancing the UK’s energy security and progressing toward net zero targets.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More1st January 2025 - Happy New Year From Protea
As we welcome the New Year, we want to take a moment to thank you for your continued support and custom. You are the heart of everything we do, and we are so grateful to have you as part of our journey.

To our valued customers, thank you for trusting us with your needs and allowing us to serve you. Your support inspires us to strive for excellence every day. To our incredible staff, your hard work, dedication, and creativity make everything we do possible. You are the heart of our business, and we couldn't be prouder of all we've achieved together. To our trusted suppliers and partners, thank you for your collaboration, reliability, and commitment to helping us deliver the very best to our customers. We look forward to another year of shared success, innovation, and growth. Here’s to making 2025 even brighter together. Wishing you all a year filled with happiness, health, and prosperity.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More2024
29th December 2024 - Energy From Waste Combined With Carbon Capture & Storage
Deploying Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) in the UK’s Energy from Waste (EfW) sector could deliver significant economic and environmental benefits. According to a new report by ERM, commissioned by Viridor, this initiative could attract £19 billion in investment by 2050, create over 14,000 green jobs, and generate nearly £40 billion in Gross Value Added (GVA). These developments are expected to stimulate further CO2 transport and storage infrastructure, providing a boost to the UK’s historic industrial regions and aligning with the government’s regional growth strategies.

The Role of CCS in Decarbonisation
ERM’s report highlights CCS in EfW as a pivotal component of the UK’s path to net zero. By integrating CCS technology, EfW facilities could dramatically reduce carbon emissions, achieving near-zero levels or even "negative emissions" by removing more CO2 from the atmosphere than they produce. This innovative approach not only addresses climate targets but also creates opportunities for sustainable economic growth, positioning EfW as a cornerstone in the UK’s decarbonisation strategy.
How CCS Works in EfW Facilities
CCS in EfW facilities employs Carbon Capture, Usage, and Storage (CCUS) technology to permanently remove CO2 from the atmosphere. The process begins with waste being incinerated to generate energy, producing flue gas that contains carbon dioxide. The flue gas is then cooled and treated to remove contaminants before entering an absorber column. Here, a chemical reaction extracts the carbon dioxide, which is subsequently dehydrated, compressed, and transported via pipelines for long-term storage.
Economic and Environmental Potential
The integration of CCS in EfW offers dual benefits:
- Economic Growth: CCS could generate substantial investment, green jobs, and economic value, especially in regions historically dependent on industrial activities.
- Environmental Impact: The technology’s ability to achieve negative emissions makes it a crucial tool for meeting the UK’s net zero targets by 2035.
Roadmap to Deployment
The report identifies 30 EfW assets that are well-positioned to deploy CCS by 2035. Key developments include:
- Protos ERF and Viridor Runcorn: Two EfW facilities are currently in negotiations for UK government funding to deploy CCS by 2027.
- Additional Projects: Four more facilities have applied for government funding under competitive schemes.
- CO2 Hubs and Shipping Development: Establishing CO2 hubs in Teesside and Merseyside, with future expansion to areas such as Grangemouth and Humber, and developing CO2 shipping hubs in Medway and Avonmouth.
Conclusion
By integrating CCS technology into the EfW sector, the UK has an opportunity to lead in sustainable innovation while addressing critical climate targets. The potential for economic revitalisation, combined with substantial reductions in carbon emissions, underscores the importance of investing in CCS as a transformative solution for a greener future.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More24th December 2024 - Season's Greetings From Protea 2024
Season’s greetings from all of us and we wish you a Merry Christmas and a Happy New Year. Our last working day before Christmas will be Tuesday 24th December 2024, reopening on Thursday 2nd January 2025. We would like to thank everyone involved with our company including our employees, customers, suppliers and people who have been involved in projects and related activities.

As a UK manufacturer of analysers using a range of technologies - IR, UV, FTIR, TDL and QMS - Protea can support the entire system from the analyser, software optimisation, systems automation and on-going service and support. Our core areas of expertise are for stack and marine emissions, where we are leading in the development of controlling global environmental emissions, pollution reduction and process improvement. Protea’s analysers can be applied to fixed applications, often in demanding environments, or portable monitoring tools to support environmental test laboratories and researchers.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More23rd December 2024 - Shipping Emissions In 2024 Return To 2008 Levels
Rising GHG emissions and slowing carbon intensity reductions in shipping. A new report from UCL and UMAS reveals increasing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and slowing reductions in carbon intensity in international shipping between 2018 and 2022. Building on the IMO’s Third and Fourth GHG Studies, to which both organisations contributed, the report provides critical insights into the sector’s response to global events and policy developments.

It examines the factors influencing emissions trends in key segments, including container ships, oil tankers, bulk carriers, and cruise ships, which collectively account for approximately 70% of the sector’s emissions. While efficiency improvements are observed in certain segments, the persistent growth in transport work necessitates more decisive action to meet the IMO’s Revised GHG Strategy targets adopted last year.
The Impact Of The Covid-19 Pandemic
The Covid-19 pandemic caused a temporary but significant disruption to shipping emissions trends. In 2020, reduced trade led to lower transport work and emissions. However, this trend reversed post-pandemic, with a surge in trade in 2021 driving increased transport work, faster average speeds, and reduced efficiency, ultimately boosting emissions.
Trends In Ship Types & Sizes
The Covid-19 pandemic caused a temporary but sig
The report delves into emissions trends by ship type and size, shedding light on the modest progress in carbon intensity between 2018 and 2022. Many shipping segments experienced declining productivity during this period. Ships spent more time at berth and less time at sea, with the median ship performing less transport work annually. For example, ships often carried smaller cargoes in 2022 than in 2018. This occurred alongside an increase in tonnage, despite decreasing demand in certain segments like large oil tankers.
This imbalance explains a key divergence in efficiency metrics. For oil tankers, the Annual Efficiency Ratio (AER), which assumes 100% cargo utilization, improved between 2018 and 2022. However, the Energy Efficiency Operational Indicator (EEOI), which accounts for actual cargo carried, deteriorated. As the EEOI reflects long-term absolute emissions trends linked to transport demand, the lack of alignment between AER and EEOI underscores the need to prioritize operational improvements.
Opportunities for Improvement
The Covid-19 pandemic caused a temporary but sig
The challenges identified in the report also present opportunities. Aligning demand in various shipping segments with fleet capacity could lead to rapid improvements in operational carbon intensity as measured by the EEOI. Larger average ship sizes, modestly lower technical efficiency, and low average speeds in 2022 provide a foundation for potential gains. Optimizing fleet utilisation and aligning transport supply with demand are critical steps to achieve meaningful reductions in shipping emissions.
Conclusion
The Covid-19 pandemic caused a temporary but sig
The report underscores the urgency of addressing the factors behind rising GHG emissions and stagnating carbon intensity improvements. By focusing on operational measures, fleet optimisation, and aligning supply with demand, the international shipping sector can make significant progress toward achieving the IMO’s ambitious emissions reduction targets. As we see the end of 2024 and head into a new year we are closer to targets set across the world for reductions in emissions for both 2030 and 2050. These targets will present a number of challenges but will be supported and analysed by continuous emissions monitoring systems (CEMS).
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More19th December 2024 - Annual Service For An In Situ Protea P2000
One of Protea’s service engineers recently visited one of our oldest, most loyal customers to perform an annual service on their Protea P2000. The Protea P2000 is a true example of durability and performance, built to be robust and reliable for many years. We’re proud to see our solutions consistently delivering value and reliability for our customers.

To find out more about the Protea P2000 visit: https://www.protea.ltd.uk/in-situ-continuous-emissions-monitoring

#ServiceExcellence #ProteaP2000 #Engineering #LongTermPerformance #Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More17th December 2024 - A Day of Festive Fun & Team Spirit At The Protea Christmas Party 2024
This holiday season, the Protea team got together for an unforgettable Christmas celebration! From strikes at Roxy Ballroom with bowling, shuffleboard, and crazy pool to the festive magic of Nottingham Winter Wonderland, Protea made the most of the holiday cheer.

Finishing the day off with an enjoyable dinner at Le Bistrot Pierre – the perfect way to celebrate a successful year and great company. We wish everyone a wonderful holiday season and a fantastic New Year!
#ProteaTeam #ChristmasParty #FestiveFun #TeamBuilding #Nottingham #RoxyBallroom #WinterWonderland #LeBistrotPierre




#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More16th December 2024 - North Atlantic Shipping Emission Control Zone Proposed
Designating a North Atlantic Emission Control Area (ECA) could yield substantial environmental and public health benefits, according to a new analysis by the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT). The report highlights how such a zone could prevent thousands of premature deaths by reducing harmful emissions from shipping in the region.

The Case For A North Atlantic ECA
As one of the world’s busiest shipping routes, the North Atlantic sees significant daily traffic from cargo vessels, tankers, and cruise ships. International shipping is a major source of pollutants such as sulfur oxides (SOx), particulate matter (PM), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). These emissions are linked to health problems, including premature deaths, and contribute to environmental damage affecting marine ecosystems, critical marine mammal habitats, and culturally significant areas.
To mitigate these impacts, the establishment of an ECA could enforce stricter regulations on shipping emissions. A previous ICCT assessment found that implementing a North Atlantic Emission Control Area (AtlECA), covering the territorial seas and exclusive economic zones of the Faroe Islands, France, Greenland, Iceland, Ireland, Portugal, Spain, and the United Kingdom, could significantly reduce shipping emissions by 2030. Additionally, the AtlECA would bridge existing ECAs in the Baltic, North, and Mediterranean Seas with newly approved ECAs in the Norwegian Sea and Canadian Arctic.
Population & Port Cities In The AtlECA Region
The proposed AtlECA encompasses a population of approximately 193 million people, with over 90% residing in France, Spain, and the United Kingdom. While most member states are projected to experience population growth from 2021 to 2030 and 2050, Portugal, Spain, and Greenland are expected to see gradual declines. Major port cities within the region include Lisbon, Porto, Dublin, Liverpool, and Bilbao, which are hubs of shipping activity and air pollution hotspots.
Protecting Marine Biodiversity & Cultural Sites
Beyond public health, the AtlECA could play a vital role in preserving marine biodiversity and cultural heritage. The proposed zone includes over 1,500 marine protected areas, 17 important marine mammal habitats, and 148 UNESCO World Heritage sites. Reducing SOx and NOx emissions from shipping would help mitigate pollutant deposition and ocean acidification, benefiting ecosystems and safeguarding these significant sites.
The Potential Impact Of An AtlECA
Although member states have implemented land-based air quality measures that have improved air quality in most regions, shipping remains a significant, under addressed contributor to air pollution. According to ICCT’s analysis, establishing the AtlECA could reduce shipping-attributable SO2 concentrations by 86%, PM2.5 by 59%, and NO2 by 3% in the region. It could also halve population-weighted exposure to PM2.5 from shipping emissions in the median member state by 2030.
Conclusion
Establishing a North Atlantic Emission Control Area offers a practical and effective strategy to address the environmental and public health challenges posed by shipping emissions. By reducing harmful pollutants, the AtlECA could protect vulnerable populations, preserve marine biodiversity, and safeguard cultural and natural heritage sites while fostering sustainable development in the region.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More13th December 2024 - Protea Analyser Demo for Alternative Fuel Testing
We recently had the opportunity to demo our portable Protea FTIR Analyser alongside a fixed CEMS at a leading marine engine manufacturer. The focus? Testing engines running on alternative fuels like biofuels and hydrogen blends.

Our analyser seamlessly provided real-time, high-resolution emissions data, measuring multiple components in parallel with the existing fixed system. This allowed for a direct performance comparison while capturing detailed insights into the impact of new fuels on exhaust emissions.
The Protea FTIR’s flexibility and accuracy proved valuable for rapid testing during R&D phases, ensuring compliance with regulations and optimising engine efficiency. We're proud to support the maritime industry in navigating toward a cleaner, greener future!
#MarineEngines #AlternativeFuels #EmissionMonitoring #CEMS #ProteaAnalyser #Sustainability #GreenMaritime



#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More12th December 2024 - A Four-Way Approach to Decarbonising Shipping
Decarbonising the shipping industry is critical for achieving global emissions targets. The industry currently employs four main strategies: legislation and government controls, transitioning to low-emission fuels, enhancing energy efficiency, technological advancements in engine monitoring and boosting energy efficiency in shipping. These complementary approaches can significantly reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and are pivotal for achieving net-zero goals.

Legislation and Government Controls
International shipping plays a vital role in the global economy, facilitating about 80% of international trade. Recognising its environmental impact, regulatory measures are being expanded. For instance, the European Union has incorporated international shipping into its Emissions Trading System (EU ETS), while the International Maritime Organization (IMO) is advancing a GHG pricing mechanism for the sector. These efforts increase the likelihood of international shipping being subject to multiple pricing instruments.
Governments are leveraging various legislative tools, such as emissions trading systems, to establish compliance frameworks. Examples include New Zealand’s NZ ETS and California’s Cap-and-Trade Program. Emissions trading, a flexible regulatory approach, enables markets and organisations to determine the most efficient means of achieving policy targets. This contrasts with traditional command-and-control regulations, like best available technology (BAT) standards and subsidies.
Transitioning to Low-Emission Fuels
Enhancing energy efficiency alone cannot fully eliminate emissions, making the transition to low-emission fuels indispensable for reaching net-zero goals. Promising alternatives include biodiesel, which can be used in existing diesel engines with minimal modification, and biomethane, a renewable fuel compatible with LNG engines. However, these solutions face challenges such as limited sustainable biomass availability and high production costs. While drop-in fuels are easier to implement, they often face competition from other sectors, like aviation, which may drive up costs.
Technological Advancements In Engine Monitoring
Technological innovation in monitoring systems, engine management, and waste management could further support decarbonisation efforts in shipping. diesel engines, a longstanding choice for marine propulsion due to their reliability and efficiency, have benefited from continuous improvements in engine management systems and exhaust control technologies. The industry’s growing emphasis on environmental responsibility is driving the adoption of advanced systems to meet high performance and reliability standards.
Regulations, such as IMO MARPOL Annex VI, focus on limiting air pollution from ships and extend to mobile offshore drilling units and oil industry platforms. These advancements not only enhance compliance but also support the industry’s broader sustainability goals.
Boosting Energy Efficiency in Shipping
Operational measures like 'slow steaming', reducing ship speeds, offer a straightforward way to improve energy efficiency. This approach reduces fuel consumption without requiring vessel modifications. However, slow steaming can also increase operational costs, as maintaining shipping capacity may require deploying additional vessels. This poses challenges for industries reliant on just-in-time delivery systems, where timeliness is critical.
Conclusion
The path to decarbonising shipping involves a multifaceted approach encompassing regulatory measures, fuel transitions, technological advancements, and operational improvements. By combining these strategies, the shipping industry can play a pivotal role in global efforts to mitigate climate change and achieve sustainable economic growth.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More4th December 2024 - Celebrating A Remarkable Journey At Protea
Today, we say goodbye to one of our Calibration Technicians, a cherished member of the Protea family, as they retire after 20+ years of dedicated service in the field of emission gas analysis.

Gianni has been a valuable member of our team, helping drive forward Protea’s mission of providing cutting-edge solutions for environmental monitoring and industrial process control.
As we gathered for this special group photo, it was a moment to reflect on the countless milestones we’ve achieved together. While we’ll miss their day-to-day presence, we’re excited for this new chapter in their life and wish them nothing but the best in their retirement adventures.
#Protea #Emissions #Monitoring #CEMS #FTIR #Gas #Analysers #Shipping #Marine #Carbon #Capture
Read More2nd December 2024 - Container Shipping Carbon Emissions Reach Record High
In Q3, the ocean container shipping industry experienced record-high carbon emissions, driven by the ongoing conflict in the Red Sea, escalating freight rates, and global supply chain congestion. The Xeneta and Marine Benchmark Carbon Emissions Index (CEI), which tracks emissions across Xeneta’s 13 main ocean container routes, reached an unprecedented 107.9 points. This figure represents a 12.2% increase compared to the previous year, prior to the Red Sea crisis.

The routes between the Far East and the Mediterranean were notably affected, emerging as the poorest performers in 2024. These routes illustrate how the Red Sea conflict impacts emissions, as ships are rerouted around the Cape of Good Hope instead of using the Suez Canal, resulting in longer journeys and extended transit times.
The CEI, which is benchmarked against Q1 2018 data (with readings above 100 indicating higher emissions per tonne of cargo than in that period), has only surpassed the 100-point threshold twice: once in Q1 2024 following the Red Sea conflict escalation and again in Q3 2024. Other routes, such as those from North Europe to the South America East Coast, also saw significant CEI increases of over 30% year-on-year in Q3, even without traversing the Red Sea or the Suez Canal.
On the other hand, five routes recorded lower emissions compared to Q3 2023, primarily those unaffected by the need to bypass Africa. The backhaul route from the US East Coast to the Mediterranean reported the most significant year-on-year decrease in emissions for Q3, dropping by 26.5%.
A decrease in container filling factors also contributed to higher emissions per tonne of cargo. This trend is mainly due to an imbalance in trade flows, with European and US exports back to the Far East increasing at a slower pace than the volumes on the outbound routes. Xeneta provides extensive market intelligence on ocean and air freight, including data on market spreads, carrier rates, surcharges, and capacity.
Despite global initiatives to cut marine emissions and introduce new technologies across the shipping industry, emissions are at records levels. The Protea 2000 emissions monitoring system is approved for the analysis of exhaust gases from the engines and boilers of ships and offshore rigs. Robust and with proven reliability, up to six gases can be measured including SO2, CO2 and NOx. The advanced Protea 2000 analyser utilises an in-situ (inside the exhaust) sample cell so avoiding the need to extract gas. Importantly this avoids the use of costly, high maintenance sample handling systems, and enables analysis of an unmodified, truly representative gas sample.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More25th November 2024 - Marine Environment Protection Committee MEPC 82 Update
The Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC) convened for its 82nd session at the IMO Headquarters in London, concluding a pivotal year for environmental challenges in the marine and shipping sectors. MEPC 82 covered a broad range of topics, including proposed mid-term strategies for reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from ships, enhancing shipping energy efficiency, managing marine litter, addressing ballast water management, and mitigating underwater noise.

Designation of Emission Control Areas (ECAs)
A significant focus of the session was the adoption of amendments to MARPOL Annex VI, establishing new Emission Control Areas (ECAs) for Nitrogen Oxides (NOx), Sulphur Oxides (SOx), and Particulate Matter (PM) in the Canadian Arctic Waters and the Norwegian Sea. These new ECAs will become effective on 1 March 2026, mandating stricter emission controls to safeguard human health and the environment by reducing air pollution from ships.
Air Pollution and Black Carbon Emissions
The committee reviewed a report from the Secretariat on the implementation of the 0.50% sulphur limit, which came into effect on 1 January 2020, reducing the allowable sulphur content in ships' fuel oil from 3.5% to 0.50%. Notably, in 2023, only two non-compliance reports (FONARs) were filed with the IMO's GISIS platform, out of a total of 67 since the regulation's introduction.
Two key resolutions were adopted:
- Guidance on goal-based control measures for minimising Black Carbon's impact on the Arctic from international shipping.
- Guidelines for Black Carbon emission measurement, monitoring, and reporting, facilitating data collection for future regulations.
Black Carbon, a specific carbonaceous compound produced during combustion of carbon-based fuels, poses significant environmental and health risks, especially in Arctic regions. These new guidelines aim to help ship operators reduce emissions and support data collection for policy development.
NOx Technical Code Amendments
The committee approved draft amendments to MARPOL Annex VI and the NOx Technical Code 2008, incorporating multiple operational profiles for marine diesel engines and clarifying engine test cycles. These amendments will be circulated for adoption at MEPC 83, with an expected enforcement date coinciding with the revised MARPOL Annex VI in autumn 2025. Additional amendments concerning the certification of engines subject to significant modifications or new tier certifications will also be reviewed for adoption at MEPC 83.
Comprehensive GHG and Environmental Initiatives
The committee’s efforts formed part of a larger strategy encompassing multiple environmental initiatives, including:
- Reducing GHG emissions from ships
- Improving ship energy efficiency
- Establishing new ECAs and Particularly Sensitive Sea Areas
- Implementing advanced ballast water management practices
- Combating marine litter
- Preventing air pollution
- Addressing underwater radiated noise from commercial vessels
- Enhancing pollution response measures and ship recycling standards
These comprehensive measures reinforce the IMO's commitment to tackling climate change and promoting sustainability across the global shipping industry. Protea have a full range of technologies for the monitoring and tracking of shipping emissions using marine emissions analysers such as the Protea 2000 In-Situ Infra-red gas analyser which is connected to a Protea Control Unit forms the basis of a Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS). Find out more at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine-emissions-analysers.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More19th November 2024 - Sales, Support and Service Training for Beijing Leshi Tech
Protea would like to extend our warm thanks to Bejing Leshi Tech for hosting us for a week of training and plans for continue growth together in PRC. Lorna and William were most hospitable and Leshi Tech’s marketing and technical support teams very eager to learn, as well as providing important feedback for continued improvements of our gas analyser product range.
We are looking forward to further success in 2025 together!


 #protea #gas #analysers #leshi #prc #training #growth
Read More
#protea #gas #analysers #leshi #prc #training #growth
Read More 18th November 2024 - UK Government Commits £3.9bn To Fund Carbon Capture & Storage Projects Between 2025-2026
The UK's new government has released its first budget since assuming office over the summer, committing billions to support clean hydrogen subsidies and carbon capture and storage (CCS) infrastructure. Among the key allocations, £3.9 billion has been earmarked for CCS projects between 2025 and 2026. According to the budget, this funding aims to “decarbonise industry, support flexible power generation, and leverage the UK’s geographic and technical advantages.”

The central crux of all initiatives involves the creation of a zero carbon economy especially focused on energy. Earlier in October, the government announced up to £21.7 billion in long-term funding to launch the UK’s initial CCS projects over the next 25 years. This substantial investment is set to facilitate the development of two undersea carbon storage sites and associated pipelines, designed to sequester more than 8.5 million tonnes of CO2 annually. The current budget adds £3.9 billion (approximately USD 5.1 billion or EUR 4.7 billion) for 2025/2026 to advance Carbon Capture, Usage, and Storage (CCUS) Track-1 projects and secure contracts with 11 green hydrogen producers.
Speaking at the Carbon Capture and Storage Association (CCSA) conference in October, Sarah Jones MP, Minister for Industry at the Department for Energy Security and Net Zero and the Department for Business and Trade, underscored the critical importance of carbon capture projects in the UK. "
Jones also noted the UK’s significant “storage potential” and envisioned the creation of extensive “carbon highways” extending to Europe, suggesting an opportunity to develop an export market for the UK’s expanding CCUS capabilities.
The CCSA conference reflected a widespread sense of optimism regarding CCUS's future. Olivia Powis, CEO of the CCSA, commented on the momentum: "The global ambition to scale up carbon capture projects to meet our net zero targets is evident from the enthusiasm at this year’s CCSA conference."
The Labour government has made clear its full commitment to achieving a net-zero economy. Over the next five years, substantial investment in CCS will position the UK as a global leader in this field. This approach is supported by bipartisan consensus, with both major political parties recognising and committing to the importance of advancing carbon capture initiatives in the coming years. Protea is a UK leader in CCUS technologies with a full section being found on our website at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/carbon-capture-and-storage-ccs.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More12th November 2024 - Reducing Shipping Greenhouse Gas Emissions Guidance Announced By The ICS
The International Chamber of Shipping (ICS) has released an updated guide focused on reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from ships. As one of the largest global transportation sectors, shipping faces significant regulatory hurdles in meeting international GHG reduction targets. This new edition consolidates complex regulations, offering a thorough overview that aids compliance with the 2021 amendments to MARPOL Annex VI, the revised 2023 IMO GHG Strategy, and the newly implemented EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS).

The EU ETS, applicable to international shipping as of early 2024, requires shipping companies to surrender EU allowances by 2025. The guide introduces an exclusive chapter detailing the application of EU ETS to vessels operating in and out of the EU. Readers can gain insights into:
- The obligations of shipping companies under the EU ETS
- Coverage specifics for voyages
- Requirements for emissions monitoring plans
- Allowance calculations and more
The guide also explores the link between reducing underwater radiated noise (URN) and GHG emissions, featuring an appendix with around 100 reduction strategies. Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Guide to International Regulatory Compliance clearly outlines current IMO regulations, including the Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI) for new vessels, the Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index (EEXI), Carbon Intensity Indicators (CII), and the submission of Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plans (SEEMPs).
Chris Waddington, ICS Technical Director and contributor, noted: “This updated edition arrives at a pivotal moment for the maritime sector. The new EU ETS chapter tackles one of the most complex and pressing regulatory challenges today, clarifying its current application and impact on global shipping.”
Waddington highlighted: “We are particularly enthusiastic about the section linking GHG reduction with URN measures, showing how emission reduction efforts can yield additional benefits, such as mitigating underwater noise pollution.”
The guide comprehensively covers maritime emissions, spanning current regulations to future expectations. It simplifies complex topics into accessible segments, serving as an essential resource for maritime professionals.
“With this clear and detailed guide, we aim to enhance understanding and promote more effective action throughout the industry,” Waddington added. “Special attention has been given to the tanker sector, which faces particularly intricate CII regulations. This guide provides key insights for boosting environmental performance while staying competitive.”
Protea has a complete Marine Emissions section at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine which focuses on the need to demonstrate environmental responsibility which is key for today’s marine and offshore industries.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More4th November 2024 - Direct Air Capture (DAC) Testing With FTIR
Removal of CO2 from the atmosphere itself, rather than at the emission source, has been proposed as a technology to slow the rate of global temperature rises. Protea’s analysers are used to test this technology. Using Protea’s FTIR gas analyser, developers of Direct Air Capture (DAC) technology have been able to show the efficiency of removal of CO2 from the atmosphere. By using a hybrid FTIR that can be used in a fixed cabinet but also removed for portable use, technologists have carried out testing across multiple sample locations within pilot plants.
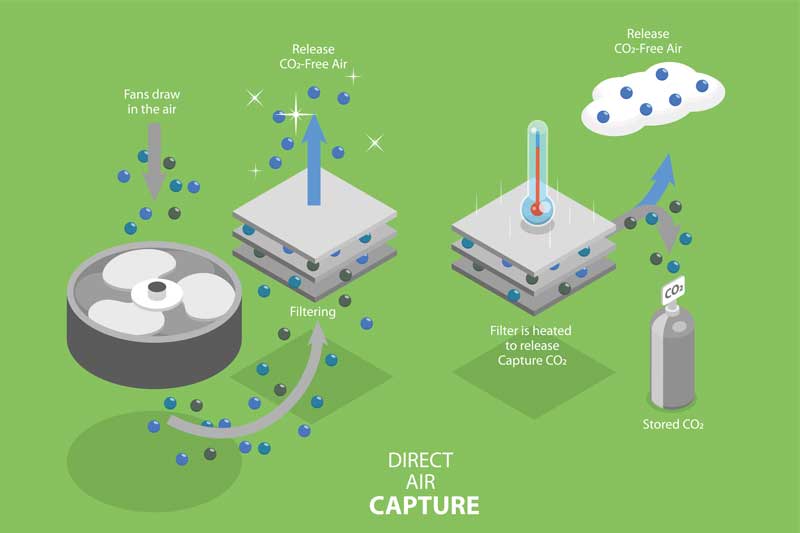
The FTIR analyser is optimised to measure low range, 0-500ppm CO2, so that ambient air and then CO2-free air can be tested. Not only CO2, but the benefit of FTIR is that other gases in ambient air such as CH4 and N2O can also be monitored. Installing the plants near to more highly polluting processes, even ambient NOx can be measured through the process. Find out more about Direct Air Capture (DAC) Testing with FTIR at our dedicated page here https://www.protea.ltd.uk/direct-air-capture-dac-via-ftir.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More30th October 2024 - Protea’s Marine Emissions Monitoring System Performs on Prestigious Cruise Liner
Protea recently demonstrated the performance of our marine emissions monitoring system aboard a prestigious cruise liner.

Our system combines the AtmosFlo Flowmeter with the Protea 2000 In-Situ Infra-red gas analyser, allowing the Protea Control Unit to calculate and report mass emissions, quantifying direct emissions to the atmosphere.
The Protea 2000 is Type Approved for analysing exhaust gases from ship engines, boilers, and offshore rigs. Known for its robustness and reliability, it can measure up to six gases, including SO2, CO2, and NOx, even at very low emission levels. This makes it ideal for monitoring emissions post-scrubber to confirm compliance with regulations, such as the equivalent of 0.1% sulphur fuel.

Our solutions are adaptable for all exhaust sizes, and ATEX/IEC-approved options are available for use in hazardous environments typical of offshore and tanker operations.
To learn more about how our accreditation can meet your requirements, please visit our website www.protea.ltd.uk/marine
#protea#emissions#monitoring#cems#ftir#gas#analysers#shipping#marine
Read More28th October 2024 - Onboard Carbon Capture From Shipping
Protea’s marine approved gas analysers have been successfully used on several carbon capture projects for the marine sector. Removal of CO2 from ship emissions is a key area to achieve net zero. With increasing pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, the marine industry is turning to carbon capture technology as a key strategy to meet regulatory requirements and achieve environmental goals. Carbon capture systems onboard vessels are designed to capture CO2 emissions before they are released into the atmosphere, significantly reducing the carbon footprint of maritime operations.
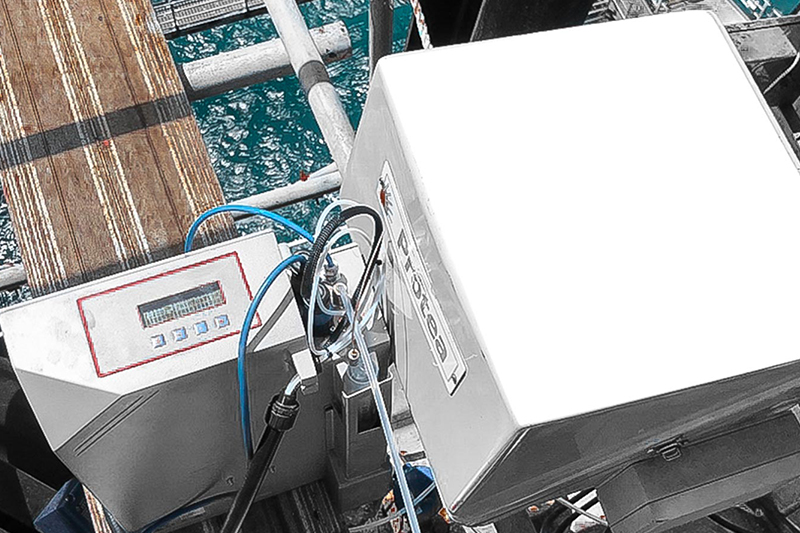

Protea has been actively involved in multiple carbon capture storage (CCS) research and development projects tailored to the marine sector, exploring innovative methods such as:
- Absorbent pebbles
- Electrolysis
- Non-pressurised gas separation membranes
These technologies offer various approaches to capturing and storing CO2 from ship exhausts. Accurate monitoring of these systems is crucial to ensure their efficient performance. Protea’s analysers play a key role in this process. Designed for real-time monitoring, they measure CO2 and other exhaust gases with high precision, enabling operators to continuously assess the effectiveness of carbon capture systems.
By delivering accurate and reliable data, Protea supports future regulatory compliance and optimises carbon capture performance, making its technology a vital tool in the industry's decarbonisation efforts. Find out more at Onboard Carbon Capture from Shipping at our dedicated page here https://www.protea.ltd.uk/onboard-carbon-capture-from-shipping.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More21st October 2024 - Amine Emission Monitoring With Multi-Gas FTIR Technology
Protea have wide experience detecting and monitoring a wide range of amine-based compounds and their derivatives within CCS processes. Protea’s multi-gas FTIR technology is proven in both continuous and portable applications to detect and measure amine species from CO2 capture processes.
The use of amine solvents to remove CO2 from flue gas emissions is well-proven and indeed Protea have been involved in monitoring gases from this process for more than a decade. The amine-based chemicals used to 'wash-out' the carbon from a gas stream can end up, or 'slip', into the post-carbon capture flue gas. Amines themselves have harmful effects to the environment and so also need to be detected, measured and their emissions controlled. The most common amine species used has been Monoethanolamine or MEA.
Protea can measure this species in low ppm or mg/m3 levels in emission stacks. Numerous technology providers of CCS have their own recipes of amine solvents to remove the CO2 from the stack that can make use of a broader range of amines. Protea has the experience of measuring dozens of such species, which more information can be found athttps://www.protea.ltd.uk/amine-emission-monitoring.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More16th October 2024 - Protea Team Attends AQE and WWEM Gala Dinner
Last week, Protea's team had the privilege of attending the AQE and WWEM Gala Dinner. The event provided an excellent opportunity for our team to network with other professionals and businesses across the industry.

The evening allowed us to gain valuable insights into emerging market trends and advancements within the environmental monitoring sector.
By engaging with industry peers, we were able to explore potential collaborations and stay at the forefront of innovation, ensuring Protea remains well-positioned to meet evolving market demands. It was a productive and enjoyable evening that reinforced our commitment to excellence and growth in the field.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture #AQE #WWEM2024
Read More14th October 2024 - UK Government Commits £22bn To Carbon Capture & Storage Technology
The UK government’s pledge of £22bn to fund carbon capture and storage (CCS) has been hailed as a potential safeguard for certain industry jobs. While this costly technology is seen as essential to meeting the UK's climate goals, environmental groups have raised concerns that its misuse could extend reliance on fossil fuels.

In an announcement last week, the new Labour government outlined plans to allocate £22bn in subsidies for CCS over the next 25 years. The initiative aims to help the UK reach its climate targets and boost the nation’s industrial revitalisation. Energy Security and Net Zero Secretary Ed Miliband declared on Sky News that “a new era begins today,” with CCS offering "good jobs" while preventing carbon from entering the atmosphere, showcasing the government's commitment to domestic investment.
Prime Minister Sir Keir Starmer emphasised that the investment would "reignite our industrial heartlands by focusing on the industries of the future." However, questions remain regarding the most effective use of this costly technology. Of the total funding, £21.7bn will be directed towards three major projects in Teesside and Merseyside. These projects will involve building the necessary infrastructure to transport and store captured carbon, helping to develop industrial clusters in these regions.
The funding will also support two carbon transport and storage networks, carrying captured emissions to deep geological storage sites in Liverpool Bay and the North Sea. The government believes this move will inspire confidence in UK industry, attract £8bn in private investment, directly create 4,000 jobs, and support 50,000 jobs in the long term. Officials estimate that the projects will remove 8.5 million tonnes of carbon emissions annually, with operations set to begin by 2028. These projects are part of a broader initiative, first announced in 2023, to capture and store 20-30 million tonnes of CO2 per year by 2030.
Protea has a complete Carbon Capture and Storage, CCS section with more information at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/carbon-capture-and-storage-ccs. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) could be key in the reduction in Carbon Dioxide (CO2) from industrial processes.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More10th October 2024 - Come & Visit The Protea Team At The AQE Exhibition
AQE is free to attend, there are over 100 hours’ worth of presentations on regulation, testing methods and training plus there are free lunches and onsite parking! Your AQE visitor badge will also give you access to the Co-located WWEM Water & Environmental Monitoring show. To gain Fast Track entry please register today at https://www.ilmexhibitions.com/aqeshow/, we look forward to seeing you at the show.

Protea would like to invite you to join us at the AQE Air Quality and Emissions Monitoring exhibition and conference on the 9th & 10th October. Protea will be exhibiting on stand Stand L4 & M4. Please come and see us to discuss your product and service requirements or for a technical demonstration and catch up. The location of the exhibition is is at Hall 2, The NEC, National Exhibition Centre, Pendigo Way, Marston Green, Birmingham B40 1NT, UK.



AQE, the Air Quality and Emissions show, is an in person event that focuses on Instrumentation and services for air quality and emissions monitoring. AQE offers a technical program aimed at keeping you up to date with the latest trends, regulations, methods, techniques and technologies. Furthermore, you can also network with all industry stakeholders including suppliers, regulators and end-users from industry that need to monitor, test and analyse air quality and emissions.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More4th October 2024 - Protea At The AQE Air Quality & Emissions Monitoring Exhibition 2024
Protea would like to invite you to join us at the AQE Air Quality and Emissions Monitoring exhibition and conference on the 9th & 10th October. Protea will be exhibiting on stand Stand L4 & M4. Please come and see us to discuss your product and service requirements or for a technical demonstration and catch up. The location of the exhibition is is at Hall 2, The NEC, National Exhibition Centre, Pendigo Way, Marston Green, Birmingham B40 1NT, UK

AQE is free to attend, there are over 100 hours’ worth of presentations on regulation, testing methods and training plus there are free lunches and onsite parking! Your AQE visitor badge will also give you access to the Co-located WWEM Water & Environmental Monitoring show. To gain Fast Track entry please register today at https://www.ilmexhibitions.com/aqeshow/, we look forward to seeing you at the show.
AQE, the Air Quality and Emissions show, is an in person event that focuses on Instrumentation and services for air quality and emissions monitoring. AQE offers a technical program aimed at keeping you up to date with the latest trends, regulations, methods, techniques and technologies. Furthermore, you can also network with all industry stakeholders including suppliers, regulators and end-users from industry that need to monitor, test and analyse air quality and emissions.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More30th September 2024 - As Cruise Ships Increase In Size Carbon Emissions Follow Suit
The rapid growth in cruise ship sizes and the rising popularity of cruise holidays come at a steep environmental cost, according to a new report by Transport & Environment (T&E). The world’s largest cruise ships are now twice as big as they were in 2000, and if this trend continues, by 2050, cruise ships could reach 345,000 gross tonnage, nearly eight times the size of the Titanic.

The global cruise industry has experienced a massive expansion over the last 50 years, with the number of ships increasing from just 21 in 1970 to 515 today. This boom, along with the growing size of ships, has resulted in a 20% increase in CO2 emissions from cruise ships in Europe in 2022 compared to pre-pandemic levels in 2019.
Despite carrying 36 million passengers annually, cruise ships are largely exempt from fuel duties and most consumer taxes. If growth continues at the same pace, by 2050, the largest ships could carry up to 10,500 passengers with a gross tonnage of 345,000. "The cruise industry is the fastest-growing tourism sector, and its emissions are spiralling out of control," said Inesa Ulichina, sustainable shipping officer at T&E. "Cruising is a luxury business, and operators must take responsibility for their environmental impact. If they don’t clean up their act, they risk becoming unwelcome visitors."
The world’s largest cruise ship to date, Icon of the Seas, began operation in January 2024. This massive "floating city" features 40 restaurants, 7 swimming pools, and can accommodate 7,600 passengers. It is longer than 15 blue whales and five times larger than the Titanic. In response to environmental concerns, many cruise operators are transitioning to liquefied natural gas (LNG) as an alternative to heavy fuel oil. LNG-powered ships account for 38% of global cruise ship orders today. However, while LNG produces fewer pollutants and CO2, it releases methane, a greenhouse gas over 80 times more potent than CO2, which can make LNG-powered ships even more harmful to the climate than traditional fuels due to methane slip from engines.
Transport & Environment (T&E), one of Europe’s leading advocates for clean transport, envisions a zero-emission transport and energy system that is affordable, circular, and minimally harmful to health and the environment. Over the past 30 years, T&E has played a key role in shaping European environmental laws, including setting ambitious CO2 standards for vehicles, exposing the "dieselgate" scandal, and securing a global ban on dirty shipping fuels. In 2022, their efforts contributed to the EU’s decision to end the sale of new combustion engine cars and vans by 2035. Protea has a full shipping emissions section on our website offering direct in-situ measurement (CEMS) at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More23rd September 2024 - US Congress Urge For An Executive Order On Maritime Decarbonisation
A group of U.S. Congress members is urging President Joe Biden to issue an Executive Order (EO) to accelerate maritime decarbonisation. Their proposals include implementing a goal-based fuel standard for ships entering U.S. ports, phasing out and banning sulphur scrubbers in U.S. waters, and eliminating in-port ship emissions by 2030.

Led by Congresswoman Nanette Barragán, co-author of the 2022 Clean Shipping Act, the lawmakers submitted an open letter to President Biden. In the letter, they expressed gratitude for his leadership in tackling the global climate crisis and for his commitment to reducing all greenhouse gas emissions from the U.S. transportation sector by 2050.
The group is calling for the EO to immediately establish a system for monitoring, reporting, and verifying fuel consumption and emissions data from all ships operating in U.S. waters and ports. They also requested funding to support the electrification and noise reduction of the federal ferry and harbor craft fleet.
The letter was co-signed by several Congress members, including Representatives Suzanne Bonamici, Adriano Espaillat, Robert Garcia, Jimmy Gomez, Jared Huffman, Pramila Jayapal, Barbara Lee, Doris Matsui, Kevin Mullin, Chellie Pingree, Katie Porter, Delia Ramirez, Mark Takano, Shri Thanedar, and Rashida Tlaib.
Supported by environmental organisations like Ocean Conservancy and Pacific Environment, the letter also urged the government to back U.S. shipbuilders and maritime stakeholders in developing low and zero-emission vessels. Additionally, it called for investment in the research, demonstration, and supply chains for zero-emission fuels and technologies in the maritime industry. Protea endorses the call to move to a more positive action plan for marine shipping in the US and globally.
Meanwhile in the UK there have been similar calls made regarding maritime decarbonisation. The UK Chamber of Shipping, along with seven other maritime trade organisations, has written to the UK's maritime minister, Mike Kane, calling for the development of a long-term strategy to decarbonise the shipping industry. The letter was signed by the UK Chamber of Shipping, the British Ports Association, the British Tugowners Association, Cruise Line International, Maritime London, the Society of Maritime Industries, the UK Major Ports Group, and the Workboat Association.
In their appeal, the maritime bodies urged that creating a successor to the Clean Maritime Plan should be a top and immediate priority. They emphasised the sector's commitment to reducing its carbon footprint and achieving net-zero emissions. Protea have a full shipping emissions section on our website offering direct in-situ measurement (CEMS) at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More19th September 2024 - FTIR Theory and Advanced Data Analysis Course: Enhance Your Expertise with Protea
Following the success of our previous training session, Protea is pleased to offer another FTIR Theory and Advanced Data Analysis Course led by our in-house experts. This course is designed to provide in-depth knowledge of FTIR technology, along with advanced techniques for data analysis, offering valuable insights and practical skills to enhance your understanding.
The course will consist of lectures and interactive workshops with data analysis of real process and emissions data.
For more details or to register your interest, please contact Victoria Brewster at victoria.brewster@protea.ltd.uk or call us at +44 (0) 1270 872000.
We look forward to welcoming you to this exciting learning opportunity!
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More11th September 2024 - Protea At The Leading Event For Industrial Air Emissions, Stack Monitoring, & Air Quality Management
Protea is proud to exhibit at the leading event for industrial air emissions, stack monitoring, and ambient air quality management. This event brings together industry experts, professionals, and companies dedicated to advancing environmental monitoring technologies and solutions.

We invite you to visit our stand, where you'll have the opportunity to engage in insightful conversations with our team and industry specialists. Discover our innovative product range designed to meet the ever-evolving challenges of air quality management. We look forward to welcoming you!
APC, NEC, Birmingham, UK
11th-12th September 2024
Protea Stand: AP-E41


#Protea #EmissionsMonitoring #CEMS #FTIR #GasAnalysers #CarbonCapture
Read More6th September 2024 - Protea Sales Team Excels At SMM Hamburg Building New Connections & Showcasing Innovation In Maritime
The Protea Sales team had a highly successful week at the SMM Hamburg, engaging in networking opportunities with other professionals in the maritime industry. The team established valuable connections and exchanged insights on the latest market trends.
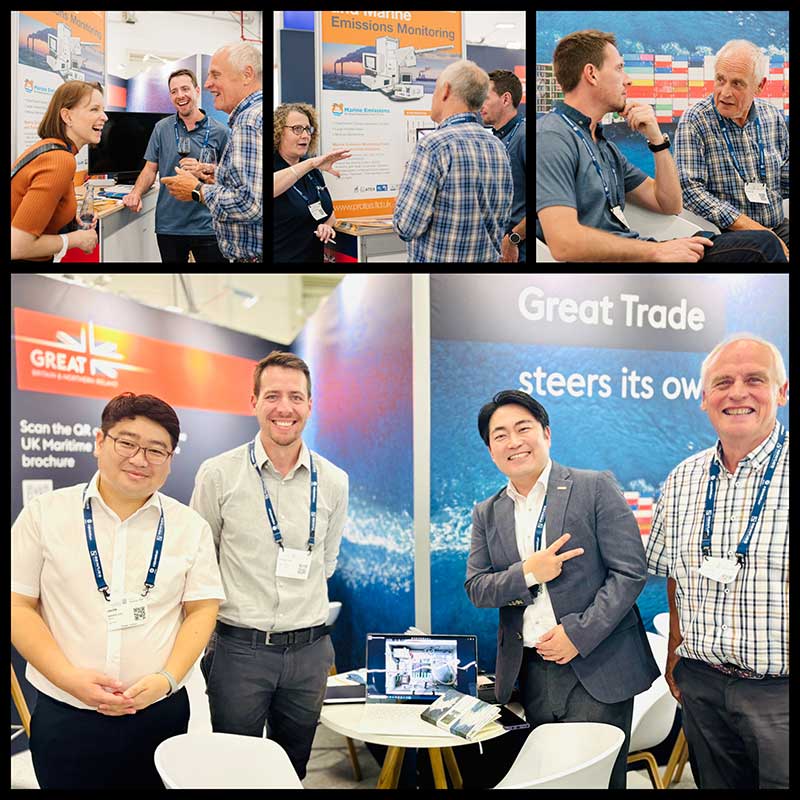

In addition to networking, the team showcased their innovative products and services, highlighting their commitment to excellence and customer satisfaction. Overall, the event proved to be an excellent platform for the Protea Sales team to discuss our product range, build new partnerships, and strengthen existing ones.
To explore the upcoming exhibitions where you can meet the Protea team, visit https://www.protea.ltd.uk/protea-exhibitions. We look forward to welcoming you at our stands!
Society of Maritime Industries (SMI) | Department for Business and Trade
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More3rd September 2024 - Protea Exhibiting At APC Air Pollution Control Expo 2024 At The NEC Birmingham
Protea will be exhibiting at the APC Air Pollution Control 2024 exhibition at the NEC in Birmingham, UK between 11th September and 12th September 2024 on Stand AP-E41. Come and visit the team to discuss FTIR and CEMS technologies and air quality control solutions.

This expo is the premier event for professionals engaged in air quality improvement and pollution reduction strategies. It provides an essential platform for exploring the latest advancements in air pollution control technologies, emission reduction solutions, and sustainable environmental practices. Featuring leading exhibitors and a lineup of air quality experts, the expo offers insightful discussions on the most recent pollution control technologies, strategies for effective emission reductions, and innovative approaches to improving air quality. It's a vital assembly for those seeking actionable solutions and networking opportunities in the air pollution control industry.
Join hundreds of engaging conversations, strategic meetings, and thought-provoking presentations at this two-day event dedicated to air quality monitoring, emissions reduction technologies, and regulatory compliance. Network with potential customers, suppliers, and partners who can revolutionise your perspective and open doors to new opportunities. The full address is Air Pollution Control 2024 Exhibition, National Exhibition Centre, North Ave, Marston Green, Birmingham, B40 1NT, UK. Opening hours are from 09:30 to 16:30 on Wednesday and 09:30 to 16:00 on Thursday. Book your tickets at https://www.ess-expo.co.uk/five-shows/apc
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More2nd September 2024 - Breakthrough Carbon Storage Technology Promises Rapid Chemical-Free Solution
Researchers at The University of Texas at Austin have developed a groundbreaking method for storing carbon captured from the atmosphere, which outpaces current techniques in both speed and environmental impact. Their recent study, published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, introduces a novel approach for the ultrafast formation of carbon dioxide hydrates. These ice-like compounds can be submerged in the ocean, effectively sequestering carbon dioxide and preventing its release back into the atmosphere.

Vaibhav Bahadur, a professor in the Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering and the study’s lead researcher, highlighted the significance of this advancement. "We face the enormous challenge of removing gigatons of carbon from the atmosphere. Hydrates present a universal solution for carbon storage, and for them to play a major role in carbon sequestration, we need a technology that allows for rapid, large-scale production," Bahadur said. "Our research demonstrates that we can efficiently grow these hydrates without relying on harmful chemicals that negate the environmental benefits of carbon capture."
Carbon dioxide, a primary greenhouse gas, is a key contributor to climate change. Carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) is essential for removing CO2 from the atmosphere and storing it permanently, a crucial step toward global decarbonization. Traditionally, CCS involves injecting CO2 into underground reservoirs, which not only traps carbon but also boosts oil production. However, this method faces challenges such as CO2 leakage, groundwater contamination, and seismic risks. Additionally, suitable geological sites for injection are not always available.
Hydrates offer an alternative approach to large-scale carbon storage. While they have been considered a secondary option, they could become the primary solution if key challenges are addressed. The process of forming these carbon-trapping hydrates has historically been slow and energy-intensive, limiting their scalability.
In this study, researchers achieved a sixfold increase in the rate of hydrate formation compared to previous methods. This rapid and chemical-free process enhances the feasibility of using hydrates for large-scale carbon storage, marking a significant advancement in the field.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More28th August 2024 - Protea Exhibiting At SMM 2024 In Hamburg
Protea will be exhibiting at the SMM 2024 exhibition at the Hamburg Messe and Congress Hall in Hamburg, Germany between 3rd September and 6th September 2024. The Exhibitor hall is B1.OG on Stand 332. Come and visit the team to discuss FTIR and CEMS technologies and Marine applications.

More than a trade fair, SMM 2024 offers you a diverse program. You can look forward to international greats from the maritime industry as speakers. Get to know the leading forces of the maritime industry personally and exchange your ideas and experiences in a unique environment. Discover for yourself why visitors from all over the world come to Hamburg especially for these events.
SMM 2024 will bring together about 40,000 participants from over 120 countries and serve as a unique platform for business, the exchange of ideas and cooperation. The full address is Hamburg Messe und Congress GmbH, Messeplatz 1, 20357 Hamburg, Germany. Opening hours are from 10:00 to 18:00 on Tuesday, Wednesday & Thursday and 10:00 to 16:00 on Friday. Book your tickets at https://www.smm-hamburg.com/
Image source: Hamburg Messe und Congress/Michael Zapf
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More27th August 2024 - LR Report Offers Insight Into Nuclear Powered Shipping
A new report titled "Fuel For Thought" undertaken by is stating that nuclear power holds the potential to revolutionise the maritime industry by enabling emissions-free shipping, extending vessel life cycles, and eliminating uncertainties related to fuel and refueling infrastructure. However, the widespread commercial adoption of nuclear power in shipping hinges on addressing critical regulatory and safety concerns, according to Lloyd’s Register’s (LR) "Fuel for Thought - Nuclear" report.

Nuclear power holds the potential to revolutionise the maritime industry by enabling emissions-free shipping, extending vessel life cycles, and eliminating uncertainties related to fuel and refueling infrastructure. However, the widespread commercial adoption of nuclear power in shipping hinges on addressing critical regulatory and safety concerns, according to Lloyd’s Register’s (LR) "Fuel for Thought: Nuclear" report.
Redefining Commercial Relationships
The report suggests that nuclear power could change the dynamics between shipowners and energy producers. Shipowners might lease power from reactor owners, thereby sidestepping the complexities of licensing and operating nuclear technology. Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are highlighted as a significant advancement in reactor design, prioritising safety, efficiency, and modularity to facilitate streamlined production. As SMR technology evolves and regulatory frameworks become clearer, ship designs optimised for nuclear propulsion will likely emerge, heralding a new era of efficient and eco-friendly vessels.
Emphasising Safety Protocols
The report underscores the critical need for stringent safety protocols to protect seafarers and the environment. It proposes that Lloyd’s Register’s Risk Based Certification (RBC) could be a viable approach for certifying novel designs and nuclear technology in the short term. This certification would demonstrate an equivalent level of safety to conventional oil-fueled systems, thus in theory, enabling first movers to certify their projects with confidence.
Advances in Nuclear Technology
According to "Fuel for Thought: Nuclear," the technological readiness of nuclear power is improving, as highlighted in the LR Maritime Decarbonisation Hub’s Zero Carbon Fuel Monitor. Promising technologies for maritime applications include pressurised water reactors (PWR), micro reactors, and molten salt reactors (MSR). However, community readiness levels (CRL) and investment readiness levels (IRL) remain low due to public perception and uncertainties surrounding the broader adoption of nuclear technology in commercial shipping.
The report concludes that while nuclear power has the potential to significantly decarbonise the maritime industry, overcoming regulatory, safety, and public perception challenges is crucial for its successful implementation. Currently over 160 ships are powered by more than 200 small nuclear reactors. Most are submarines, but they range from icebreakers to aircraft carriers.
The drive for reducing greenhouse gas emissions is gaining pace and there are a number of competing technologies offering to provide a solution and achieve climate change targets. It would be a fair assessment to state that no one single technology will solve the problem of climate change and most of the marine sector is moving towards greener options. Lloyd's Register Group Limited, trading as Lloyd's Register (LR), is a technical and professional services organisation and a maritime classification society.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More23rd August 2024 - Protea Celebrates 25 Years of ISO 9001 Certification!
Protea is proud to announce the renewal of our ISO 9001:2015 certification following a successful surveillance audit of our Quality Management System by TÜV Rheinland. This milestone marks 25 years of our unwavering commitment to maintaining the highest standards of quality.

Our joint-factory management system approval further demonstrates Protea's dedication to delivering top-tier gas analysers and associated services to our global customer base.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture #iso9001
Read More21st August 2024 - Real Time Marine Fuel Consumption Data Analysis
As the maritime sector transitions away from traditional analogue methods, data logging has become crucial for optimising emission efficiency. With advancements in computing and technology, it is essential that data collection and transmission are not only accurate but also actionable. Our system provides key metrics, such as engine performance, which can be leveraged to predict fuel consumption and forecast emissions.
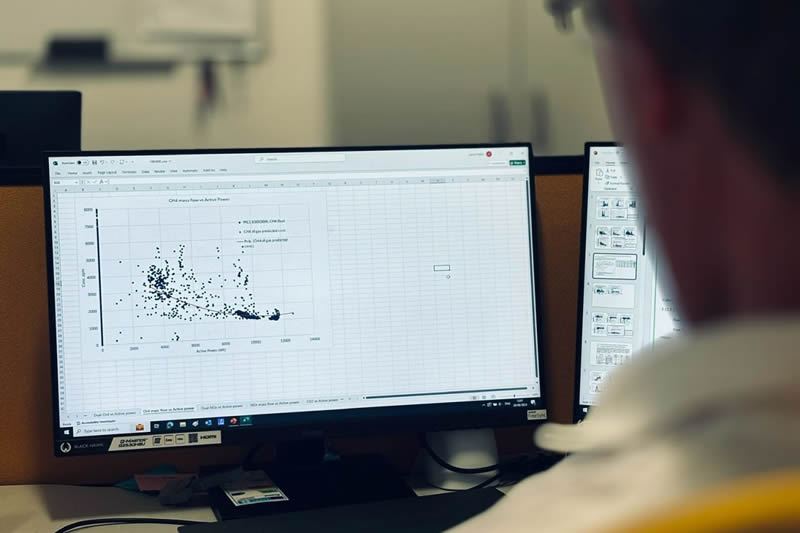

Proteas Marine P2000 system, designed to equip the offshore industry with the necessary tools and data to ensure compliance and actively reduce emissions globally. Protea offers comprehensive on-board monitoring of emissions from ships' exhaust stacks while at sea. Our advanced system provides detailed insights into the matrix of emissions, aiding in the long-term efficiency improvements for vessels.
Our team of Data Analysts and Analyser Specialists have been engaged in significant projects, comparing analyser measurements with vessel engine predicted readings to ensure accuracy and reliability. For more information on how Protea can support your maritime requirements, please contact us at marine@protea.ltd.uk
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More19th August 2024 - Direct Air Capture As A Crucial Tool for Achieving Climate Goals
In 2023, global carbon dioxide emissions exceeded 37 billion metric tons, setting a new record. As a result, the concept of removing CO2 from the atmosphere has gained significant traction. Governments worldwide are increasingly investing in direct air capture (DAC) technology to meet climate targets and mitigate the worst effects of climate change.
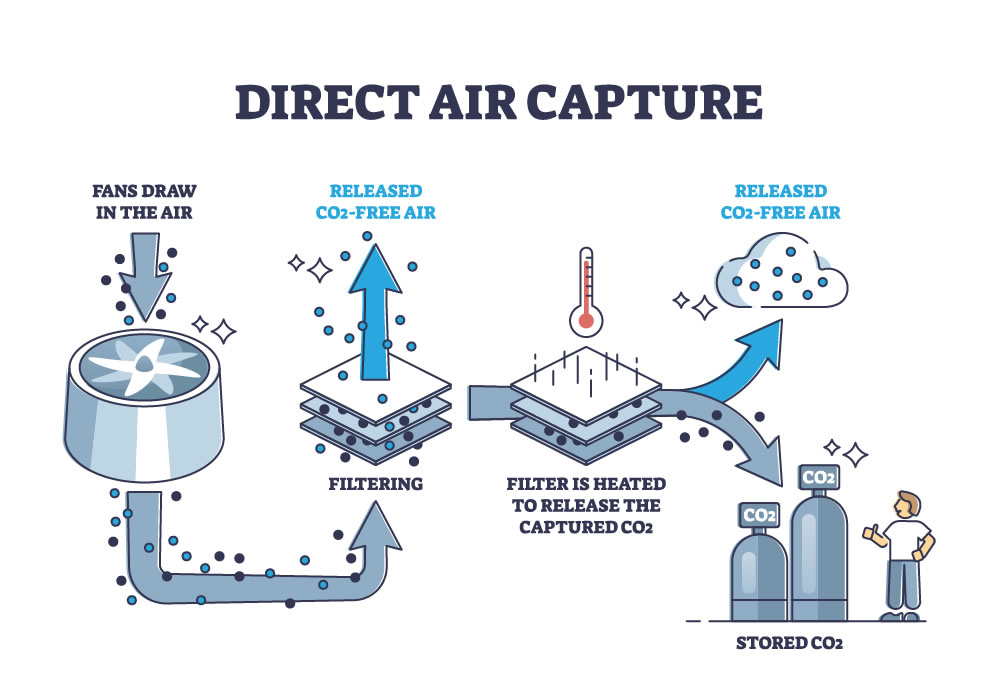
How Direct Air Capture Works
One prevalent method of DAC involves the use of air contactors as large fans that draw air into chambers containing a basic liquid solution. Since CO2 is acidic, it reacts with the basic solution, forming either carbonate (a primary component of concrete) or bicarbonate (found in baking soda).
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) states that carbon dioxide removal is essential to achieve global and national net zero CO2 and greenhouse gas emission targets. Currently, over 20 DAC plants operate worldwide, with an additional 130 under construction.
Understanding Direct Air Capture
Direct air capture (DAC) technology extracts CO2 directly from the atmosphere, unlike traditional carbon capture, which typically occurs at emission sources like steel plants. The captured CO2 can be stored permanently in deep geological formations or utilised in various applications. If the CO2 is securely sequestered (a process known as direct air carbon capture and sequestration or DACCS), DAC functions as a "negative emissions technology" (NET), effectively removing CO2 from the atmosphere.
Challenges of Direct Air Capture
Capturing CO2 from the air is notably more expensive than other forms of carbon capture due to the lower concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere compared to sources like power station flue gas. This results in higher energy demands and costs for DAC. While reducing greenhouse gas emissions remains a priority, achieving climate goals will also necessitate carbon dioxide removal (CDR) through technologies like DAC. Compared to other leading CDR methods, such as reforestation, DAC requires less land per tonne of CO2 removed, making it a viable option for large-scale deployment. Protea’s atmosFIR FTIR gas analyser has proven a valuable tool in research into the effective storage of Carbon Dioxide (CO2).
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More12th August 2024 - European Commission Approves €3 Billion Swedish Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage Project
The European Commission has approved a €3 billion (SEK 36 billion) Swedish State aid scheme to support carbon capture and storage (CCS) initiatives aimed at reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from biomass combustion or processing. This measure aligns with Sweden's climate targets and the EU's strategic objectives under the European Green Deal, particularly the goal of climate neutrality by 2050.

The Swedish Initiative - Sweden has notified the Commission of its plans to introduce a €3 billion scheme to support projects that permanently remove biogenic CO2 emissions through CCS. This initiative aims to establish CCS as a viable and effective tool for mitigating climate change, thereby boosting investor confidence, reducing future application costs, and facilitating the development of a CCS value chain within the EU.
The aid will be distributed through a competitive bidding process, with the first auction expected in 2024. These auctions will be open to companies operating in Sweden that emit biogenic CO2 and can implement projects with the capacity to capture and store at least 50,000 tonnes of biogenic CO2 annually.
Beneficiaries will receive grants per tonne of biogenic CO2 permanently stored under 15-year contracts. The aid amount will be adjusted based on potential revenues from the projects, such as voluntary carbon removal certificates, and any other public support received for the same project.
The scheme will run until 31 December 2028. By enabling the capture and storage of significant amounts of biogenic CO2, the initiative will support Sweden's efforts to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions by 85% by 2045 compared to 1990 levels. It will also aid Sweden and the EU in achieving climate neutrality by 2050.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More5th August 2024 - Study Finds Ammonia As Marine Fuel Poses Risk To Public Health
Carbon-free ammonia has been touted as the future of green shipping fuel, with orders already placed for the first ammonia-powered dual-fuel vessels. However, a new study from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) reveals that burning ammonia could worsen air quality and lead to hundreds of thousands of premature deaths annually.

The study warns that, under current legislation, switching ships to ammonia fuel could result in approximately 600,000 additional premature deaths each year. The maritime industry, which currently accounts for nearly 3% of global CO2 emissions, already causes about 100,000 premature deaths annually due to its negative impact on air quality.
MIT's research suggests that, with stronger regulations and cleaner engine technology, switching to ammonia could potentially reduce premature deaths by about 66,000 compared to current maritime emissions, while also lessening the impact on global warming.
Ammonia combustion produces nitrous oxide (N2O), a greenhouse gas 300 times more potent than CO2, and nitrogen oxides (NO and NO2, known as NOx). Unburnt ammonia may also escape, forming fine particulate matter in the atmosphere. These particles can be inhaled deeply into the lungs, causing severe health issues such as heart attacks, strokes, and asthma.
Ammonia is traditionally produced by extracting hydrogen from natural gas and combining it with nitrogen at high temperatures, a process with a significant carbon footprint. The maritime industry is looking towards "green ammonia," made using renewable energy to produce hydrogen via electrolysis and generate heat.
However, even green ammonia generates N2O and NOx when burned, with some unburnt ammonia escaping. This nitrous oxide remains in the atmosphere for over a century, while nitrogen emissions can damage ecosystems. Bacterial digestion of these emissions further produces N2O. NOx and ammonia also mix with other atmospheric gases to form fine particulate matter, a primary air pollution contributor that causes an estimated 4 million deaths annually.
A significant challenge in assessing ammonia's impact is the lack of real-world data, as no ammonia-powered ships are currently in operation. Researchers relied on experimental ammonia combustion data from collaborators to build their models.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More29th July 2024 - Onboard Carbon Capture (OCC) Is Gaining Increasing Interest
A new white paper from DNV states that the successful commercial adoption of onboard carbon capture (OCC) hinges on collaboration among regulators, policymakers, industry stakeholders, classification societies, and suppliers. The white paper, titled "The Potential of Onboard Carbon Capture in Shipping," examines OCC as a decarbonisation solution for the shipping industry. It addresses the technical, economic, operational, and regulatory challenges, as well as its integration into the carbon capture, utilisation, and storage (CCUS) value chain.

“OCC is expected to be part of a range of future options that will help shipping achieve its decarbonization goals,” said Chara Georgopoulou, head of maritime R&D and advisory in Greece at DNV. However, it was emphasised that further collaboration and testing are needed to verify its performance. The commercial viability of OCC will depend on the regulatory frameworks that credit the removal of carbon emissions and the seamless integration into the expanding CCUS value chain.
The paper reviews the regulatory landscape, underscoring the necessity for environmental regulations that recognise captured CO2. It also explores how onboard carbon capture can connect to a future, fully developed CCUS value chain and presents the status of global storage locations and capacities.
Currently, the EU ETS is the sole regulatory framework offering commercial incentives for OCC. To motivate shipowners to adopt this technology, future environmental and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions regulations must also provide credit for captured CO2. As time progresses and technology advances, the potential for carbon capture in shipping and marine emissions is accelerating. Protea is at the forefront of these developments with its range of technologies.
Det Norske Veritas (DNV), formerly DNV GL is an international accredited registrar and classification society headquartered in Høvik, Norway. DNV provides services for several industries, including maritime, oil and gas, renewable energy, electrification, and healthcare.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More22nd July 2024 - Long Term Potential For Increased Shipping Efficiency Report Released
Maritime shipping is highly fuel-efficient, but its vast scale and rapid growth make it a major energy consumer and a significant source of carbon emissions. As the shipping industry and governments seek ways to reduce the sector's overall energy and carbon footprint, many questions remain unanswered. Key among these are the extent of variation in real-world fleet efficiency and the speed at which the industry can adopt best technical and operational practices to enhance efficiency.
Progress on climate action at the International Maritime Organisation (IMO), the body tasked with regulating the industry, has been painfully slow. Last year, governments agreed to increase ambition, setting a near-term 2030 target to cut emissions by at least 20% while “striving” for 30%. There are checkpoints along the way to a somewhat vague goal of achieving net zero emissions “by or around” 2050.
The International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) calculates that this timeline would allow shipping to remain within a carbon budget compatible with “well below” 2 degrees Celsius average warming, but not the more stringent 1.5-degree target set by the Paris Agreement.
This study offers a novel analysis connecting 2011 in-use fleet characteristics, global satellite data on ship movement, and literature on ship technology to assess the long-term prospects for increasing shipping efficiency. The satellite-based data provides deeper insights into real-world operational ship speed and its relation to efficiency than previous analyses. The study also examines how factors such as age, size, technology, and operational practices influence fleet efficiency and develops a ship stock turnover model to independently track technical and operational efficiency practices in ships.
The findings indicate that industry-leading ships are about twice as efficient as lagging ships across major types. For instance, the top 5% of container ships have a carbon dioxide (CO2) emission intensity 38% lower than the industry average. Similar efficiency variations are seen across other major ship types. This variation is partly due to the speed at which new technology enters the fleet, with newer, larger ships being more efficient and equipped with sophisticated engine controls that benefit more frequently from speed reduction.
The analysis suggests that by fully adopting the available technical and operational practices of today's low-carbon industry leaders, there is potential to reduce CO2 emissions in absolute terms, even as business-as-usual freight movement doubles. Embracing industry-leading efficiency practices could result in reductions from business-as-usual efficiency practices of 300 million metric tons of CO2 per year and 2 million barrels of oil per day by 2030.
This study has significant implications for the shipping industry, shippers, and ultimately consumers. The analytical approach used here suggests that shipping companies can use data and methods to compare their practices more precisely with those of their peers. Shippers could increasingly demand precise accounting of ships’ age, technical efficiency, and in-use shipping efficiency. Based on this assessment, there is potential to develop tools for shippers to quantify, evaluate, and compare their supply chain carbon footprints without relying on aggregated fleet-average simplifications.
The full study can be found on the ICCT website. The International Council on Clean Transportation is a multinational non-profit public policy think tank and research institute that provides technical, scientific, and policy analysis to environmental regulators on issues related to environmental, energy, and transportation policy.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More18th July 2024 - Protea Showcasing Our Latest Technologies
Over the next few months, Protea will be showcasing our latest technologies and innovations at several exhibitions. These events present an excellent opportunity for us to network with industry professionals, exchange ideas, and explore new business opportunities on a global stage. We are excited to announce our participation in the following exhibitions:

SMM, Hamburg, Germany
3rd- 6th September 2024
Protea Stand: B1.0G.332
As one of the leading international maritime trade fairs, SMM provides a platform for industry leaders to discuss the future of the maritime industry. We are thrilled to present our advanced solutions and engage with the maritime community.

APC, NEC, Birmingham, UK
11th-12th September 2024
Protea Stand: AP- D62
This event is part of the larger ESS Expo, focusing on the latest advancements in air pollution control. We are eager to share our cutting-edge technologies that address critical environmental challenges and contribute to cleaner air.

AQE, NEC, Birmingham, UK
9th-10th October 2024
Protea Stand: M4&L4
AQE is a specialized event dedicated to air quality and emissions monitoring. We look forward to discussing our innovative monitoring systems and how they can help industries comply with stringent environmental regulations.
We look forward to welcoming you to our booths and engaging in meaningful conversations that drive innovation and progress in our industry.
Read More17th July 2024 - We Have Recently Welcomed Heather and Sophie at the Peterborough Factory for Work Experience
We have recently welcomed Heather and Sophie at the Peterborough Factory for Work Experience. Both having scientific backgrounds they have worked with our Gas Analyser Specialist and Chief Scientists on our recent development of Projects, New Applications and our FTIR Spectrometer.

To develop an understanding of the day-to-day tasks involved with Protea’s Sales and Marketing, they have also covered tasks such as, Quotations, Exhibition Planning and the Sales Order Process.

We hope that Heather and Sophie enjoyed their time at Protea, and they have a fantastic summer break!
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #marine #training
Read More15th July 2024 - Report Highlights Nine Billion Tonnes Removal Of CO2 Annually to Meet Climate Goals
A recent report co-led by researchers from the University of Oxford, the 2024 State of Carbon Dioxide Removal, indicates that to meet the 1.5°C target set by the Paris Agreement, the world must remove approximately 7 to 9 billion tonnes of CO2 from the atmosphere each year by mid-century. The report emphasises that while reducing emissions remains the primary strategy for achieving net-zero, Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) is also crucial.

Sustainability & CDR
The analysis incorporated multiple Sustainable Development Goals to ensure the proposed CDR targets align with broader sustainability criteria. The estimated "Paris-consistent" range for CDR was derived with these goals in mind.
Current State Of CDR
CDR involves human activities designed to capture CO2 from the atmosphere and store it for extended periods, ranging from decades to millennia. There are various CDR methods, each with differing levels of readiness, potential, and durability. Each method also carries sustainability risks that could affect its long-term viability. When these risks are addressed, certain CDR methods can offer additional benefits beyond climate mitigation.
Currently, around 2 Gt CO2 per year of CDR is achieved, primarily through conventional methods like afforestation and reforestation, which are part of land use, land-use change, and forestry (LULUCF) activities. These traditional methods have maintained a relatively stable rate of CDR over the past twenty years. In contrast, novel CDR methods, which are still in early development stages, only contribute about 1.3 million tonnes (0.0013 Gt) of CO2 removal annually.
The Need For Rapid Scaling
To meet climate goals, the report calls for a rapid scale-up of a diverse array of CDR methods. Although there has been significant growth in research, public awareness, and the number of start-up companies focusing on CDR, recent indicators suggest a slowdown in development.
Despite increasing investments in novel CDR methods, government policies and proposals have yet to effectively target these new technologies. Currently, investment in CDR accounts for just 1.1% of climate-tech start-up funding. Dr. Steve Smith from the Smith School of Enterprise and the Environment at the University of Oxford highlights the urgency: "Given that the world is off track from the decarbonisation needed to meet the Paris temperature goal, this underscores the necessity to increase investment in CDR as well as zero-emission solutions across the board."
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) could be key in the reduction in Carbon Dioxide (CO2) from industrial processes. More information on this can be found at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/carbon-capture-and-storage-ccs
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More8th July 2024 - Support For A Global Shipping Industry Emissions Levy Grows
Following on from the two new Emission Control Areas (ECAs) in the world's seas and oceans in the Canadian Arctic Waters and in the Norwegian Sea, the majority of UN International Maritime Organisation (IMO) member states have called for a standard levy on greenhouse gases. This proposed new levy, along with a fuel standard requiring ships to gradually increase their use of green energy, has the potential to transform global trade into a zero-carbon industry. However, it must first navigate challenging political waters at the UN agency.

In a statement following the IMO meeting, Sandra Chiri of the Ocean Conservancy and the Clean Shipping Coalition said, "The UN is on the verge of adopting the world's first global emissions price, but its success depends on the commitment of the countries involved.
"The March IMO talks gave us hope, as a clear majority of countries – including those in the Caribbean, the Pacific, Africa, as well as the EU and Canada recognise the significant opportunity that pricing shipping emissions presents for the industry's clean transition and for benefiting all developing countries. It's unfortunate that a small but persistent minority seeks to undermine this crucial climate measure."
Achieving these ambitious goals remains a key challenge. During the March IMO meeting, member states agreed on the need for a new global fuel standard and a global pricing mechanism for maritime GHG emissions, along with tougher efficiency rules.
The next steps on reducing greenhouse gas emissions from shipping have been outlined as follows. Other items relating to environmental issues are summarised below all relating to shipping pollution including some wider elements outside of greenhouse gas issues.
- Approved the establishment of two new Emission Control Areas (ECAs), in Canadian Arctic Waters, for Nitrogen Oxides, Sulphur Oxides and Particulate Matter; and in the Norwegian Sea for Nitrogen Oxide and Sulphur Oxides.
- Approved new recommendations for the carriage of plastic pellets by sea in freight containers, covering stowage, packaging and correct transport/cargo information.
- Endorsed, in principle, the draft action plan for the reduction of underwater noise from commercial shipping, with a view to further consideration and final endorsement at MEPC 82.
- Endorsed the updated work plan for the development of guidelines for new alternative fuels, including the development of guidelines for hydrogen and ammonia as fuels, low flash-point fuels and mandatory instruments for methyl/ethyl alcohols.
- Endorsed the list of provisions and instruments for revision and/or development under the Ballast Water Management Convention and approved the interim guidance on the application of the BWM Convention to ships operating in challenging water quality conditions, as well as the Guidance for the temporary storage of treated sewage and/or grey water in ballast water tanks.
More information on new and existing marine emissions requirements are satisfied by Protea’s range of emissions analysers and fuel oil test equipment. The need to demonstrate environmental responsibility is key for today’s marine and offshore industries. Charterers and the public demand high standards of performance and reliability. Fuels and exhaust gas emissions are also the subject of international, regional and national controls. The most significant is the International Marine Organisation (IMO) MARPOL Annex VI.
Regulations for the Prevention of Air Pollution from Ships, which also applies to mobile offshore drilling units and other oil industry platforms. All of these ships will have diesel engines of one sort or another, even the very small number of vessels that have turbine driven powerplant. More information can be found at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine-requirements.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More3rd July 2024 - German Government Approves Carbon Capture and Hydrogen Plans
The German government has recently approved significant draft legislation aimed at accelerating the integration of hydrogen and carbon capture technologies into the country’s energy and industrial systems. These technologies are viewed as essential for Germany's goal of becoming carbon neutral by 2045 while maintaining its heavy industries, according to government sources.

Carbon Capture and Storage
The legislation allows companies to store CO2 in the bed of the North Sea or inland, provided federal states permit it on their territory. Germany has an estimated 1.5 billion to 8.3 billion tons of CO2 storage capacity under the North Sea and could deposit up to 20 million tons annually. Additionally, the plans permit CO2 exports, contingent on Berlin ratifying a clause in the London Protocol international treaty on cross-border waste exports.
The Federal Government's draft revision of the Carbon Storage Act aims to establish clear regulations for the development of CO2 pipeline infrastructure and to permit offshore CO2 storage. The draft legislation will now be submitted to the Bundestag and the Bundesrat for parliamentary discussion and review.
Hydrogen Acceleration Law
The Hydrogen Acceleration Law grants hydrogen infrastructure "overriding public interest" status, prioritizing it in the approval process. The law aims to simplify and digitize permitting procedures and shorten legal cases challenging hydrogen projects and environmental impact assessments, facilitating rapid expansion of the hydrogen sector.
This new legislation covers:
- Green hydrogen production facilities
- Hydrogen pipelines
- Hydrogen and ammonia import terminals
- Ammonia crackers
Specific power lines that supply electrolyser installations and other infrastructure, including import terminals and processing facilities for liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHC) The law also aims to streamline planning, giving green hydrogen developers privileged access to water, which is crucial for hydrogen production.
Streamlining Environmental and Procurement Requirements
The Hydrogen Acceleration Law represents a major shift by overriding certain environmental and procurement requirements imposed on developers. It introduces or shortens deadlines for officials to make decisions on key planning milestones. This change will significantly impact companies involved in granting access to water, digital infrastructure, and environmental permitting.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More2nd July 2024 - Protea Host Westminster Commission for Road Air Quality
Last week Protea Ltd hosted an event for the Westminster Commission for Road Air Quality on ‘How to identify and eliminate the dirty emissions tail, both on diesel and petrol vehicles / The Horizon AeroSolfd Project.’

The day included Live PN-PTI Demos and guest speakers discussing the project. It was great to host and network with those who attended.
For more information on how Protea’s atmosFIRt can carry out emission road testing, visit www.protea.ltd.uk



#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #roadtesting #analysers
Read More28th June 2024 - Protea Visited Achema in Frankfurt Am Main, Germany This Month
Manufacturers and service providers attended the show, presenting their products for chemical, pharmaceutical and biotech research/ manufacturing as well as energy and environmental services. It was great to network with those who attended.

Protea has been at the forefront of emissions monitoring systems for 20 years. Protea’s range of equipment covers almost all areas of emissions testing, and we have solutions for most emissions gases – from combustion gas emissions to non-standard organic VOC emissions, CFC emissions and more.
Visit https://www.protea.ltd.uk for more information on our Product Range.

#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More26th June 2024 - P2000 CEMS Service Training Session
This month Protea has welcomed its P2000 users for our Service Training Session. Our recent attendees have multiple P2000 instruments and operate them in a wide range of applications to support emissions control and reduction. Topics covered included P2000 Familiarisation, Infrared photometer principles, P2000 site service, Control Units and Analyser Software, P5000 Site Service and Troubleshooting and fault finding.

Our Training courses are run throughout the year, covering locations such as Asia, Europe and within the UK. For more information on our Sales and Service Training Events, please email sales@protea.ltd.uk. Find out more at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/news.


#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #training
Read More24th June 2024 - Wealthy Nations Must Cut Emissions Quicker Than Developing Peers
Wealthy states must accelerate emission cuts, court rules in climate justice milestone. The International Tribunal on the Law of the Sea (ITLOS) has issued an advisory opinion asserting that wealthy states must reduce their emissions more rapidly than their developing counterparts, marking a significant step for climate justice. Advocacy groups celebrate this "landmark opinion" as it strengthens the legal framework for addressing climate change impacts on the marine environment and is expected to clarify international law in the context of the law of the sea.

The tribunal concluded that "anthropogenic greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions into the atmosphere" constitute pollution of the marine environment. State parties to the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) are therefore obligated to "take all necessary measures to prevent, reduce, and control marine pollution from anthropogenic GHG emissions."
In its unanimous opinion, the tribunal highlighted that oceans are warming and becoming more acidic due to carbon dioxide emissions from human activities. This results in harm to marine life, hazards to human health, and disruption of marine activities such as fishing. The Tribunal also mandated that state parties must "take all measures necessary to ensure that anthropogenic GHG emissions under their jurisdiction or control do not cause damage by pollution to other states and their environment," and to prevent such pollution from spreading beyond their own sovereign areas.
Furthermore, the tribunal emphasized the need for wealthy states to assist developing nations, particularly vulnerable ones, in addressing marine pollution from anthropogenic GHG emissions. The obligation to protect and preserve the marine environment is broad, encompassing "any type of harm or threat to the marine environment," according to ITLOS. This includes taking measures to restore degraded marine habitats and ecosystems due to climate change impacts and ocean acidification.
Wealthy countries like the UK, Australia, and EU member states argued that climate change is already being addressed at the international level through the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, which led to the Paris Agreement in 2015. Under this agreement, countries set their own climate targets without an international enforcement mechanism. However, the tribunal declared that the Paris Agreement alone is insufficient; the law of the sea imposes specific legal obligations on states, with consequences for non-compliance.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More17th June 2024 - Calls For A Europe Carbon Capture & Storage Tsar
Industry groups and major oil companies are urging the European Union (EU) to appoint a dedicated carbon capture and storage (CCS) envoy to promote this climate solution, despite ongoing skepticism. Euronews Green reported Wednesday that supporters believe a dedicated envoy could enhance the EU's efforts in capturing and permanently storing carbon dioxide underground. However, critics argue that focusing on CCS might distract from the urgent need to reduce fossil fuel consumption.

CCS Europe, a Brussels-based trade association, proposed the idea in May 2024, emphasising the need for political leadership to meet climate targets. Despite the EU’s Net-Zero Industry Act mandating an annual injection capacity of 50 million tons by 2030, the industry acknowledges it is not on track to meet this goal, with projected capacity at only 42 million tons if all projects proceed.
“Political leadership from the Commission is required, and an appointed representative with expert knowledge could provide the commitment that no Commissioner will have the time to offer,” said Chris Davies, a former UK MEP who steered the EU’s first CCS legislation through the European Parliament and now chairs the lobby group. Davies further stated that to meet the Commission’s target of capturing 280 million tons of CO2 annually by 2040, the construction of no fewer than 650 carbon capture plants of similar scale must commence over the next 14 years—equivalent to one every eight days.
The largest current project, Northern Lights in Norway, has an initial capacity of just 1.5 million tons per year. Financial challenges and a lack of final investment decisions hinder the progress of numerous small pilot projects. Protea supports the need for a European CCS lead, offering access to high-level government support and associated stakeholders to ensure that CCS becomes a vital component of global objectives for reducing CO2 emissions and tackling global warming.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More10th June 2024 - Research Reveals Significant Emissions From Ship Scrubbers
In just one year, ships using exhaust gas abatement technology, known as scrubbers, released 200 million cubic meters of environmentally and health-hazardous washing water into the Baltic Sea. This unique study, commissioned by the Swedish Transport Agency and the Swedish Agency for Marine and Water Management, investigated the environmental impact of scrubbers in the Baltic Sea compared to other sources of environmental contaminants.

Discharges from ships equipped with scrubbers cause significant damage to the Baltic Sea. A study by Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, reveals that these emissions have led to pollution with socio-economic costs exceeding EUR 680 million between 2014 and 2022. Despite these costs, shipping companies have recouped their investments in this controversial technology, which "washes" exhaust gases and discharges the resulting water into the sea. Consequently, the industry is profiting billions of euros by running ships on cheap heavy fuel oil instead of cleaner alternatives.
The Baltic Sea is one of the world's most polluted seas. New research from Chalmers University of Technology identifies scrubber discharge water as a relatively unknown environmental culprit. The study found that this discharge is responsible for up to nine percent of certain emissions of carcinogenic and environmentally harmful substances in the Baltic Sea, a figure considerably higher than previously known. Moreover, the number of ships with scrubbers has tripled since the study was conducted.
The researchers, Anna Lunde Hermansson, Erik Ytreberg, and Ida-Maja Hassellöv, have been studying the environmental impact of shipping for many years, contributing their expertise in both international and national contexts. Their work highlights the urgent need for regulatory measures to address the environmental and health hazards posed by scrubber discharges in the Baltic Sea.
Protea’s marine emissions analyser plays an important role in the operation and control of on-board emissions scrubbers. With regulations as laid out in the IMO publication MARPOL Annex VI, control of SO2 emissions from vessels is critical for operators. To reduce emissions, Sea Water Scrubber Flue Gas Desulphurisation (SWS FGD) is operated in both Open Loop and Closed Loop modes.
Protea works closely with scrubber manufacturers and suppliers and partnership with our analyser can give vessel operators the peace of mind that the scrubber is operating effectively. The ability for the emissions analyser to also measure non-scrubbed emissions, under fuel switching operation, give the flexibility of operation for vessels.
With the Protea P2000 marine emissions analyser installed, the reduction of SO2 emissions can clearly be demonstrated, and scrubber operation controlled to ensure efficiency.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More7th June 2024 - How Do We Actually Decarbonise Maritime Shipping Activity?
To successfully decarbonise and mitigate climate change, industry stakeholders, governments, and regulatory bodies should collaborate and promptly establish a consensus on future regulatory frameworks and greenhouse gas (GHG) mitigation measures. Such regulations are governed by the International Maritime Organization (IMO), which has set short and long-term goals for the Marine industry, including ambitious net-zero emissions for the maritime industry.

The industry’s reliance on heavy fuel oils and other high-emission fuels exacerbates its environmental impact. Maritime, often regarded as the backbone of global trade, plays a significant role in the climate emergency. Accounting for almost 3% of total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions globally, if the maritime industry were a country, it would be the sixth-largest emitter of greenhouse gases in the world. Countries or a group of countries such as the EU have independently implemented regulations that penalise ships for releasing GHGs within their waters (EU ETS, FUEL EU). The need to demonstrate environmental responsibility is key for today’s marine and offshore industries.
Charterers and the public demand high standards of performance and reliability. Fuels and exhaust gas emissions are also the subject of international, regional and national controls. The most significant is IMO MARPOL Annex VI – Regulations for the Prevention of Air Pollution from Ships, which also applies to mobile offshore drilling units and other oil industry platforms.
The most important gases in terms of emissions are currently sulphur oxides – SOx, and nitrogen oxides – NOx. Annex VI has a schedule for significant reductions in both over the next 5 to 10 years. The creation of Emission Control Areas and stringent limits on fuel sulphur content in port are challenging particularly for the shipping industry and its suppliers. Ship operators have near imminent decisions to make based on a complex set of circumstances and a fluid regulatory background. The penalties for non-compliance are potentially huge. Whilst the pace of change has created uncertainty and appears to have pushed the boundaries for some technologies, the Protea 2000 emissions monitoring system has been proven in long-term service onboard ship as a robust and reliable method of confirming compliance with emissions regulations.
Direct In-situ Shipping Emissions Measurement Attributes:
- One analyser measures multiple gases
- No requirement for extractive sample handling systems
- Auto-verification facilities
- Measurement of exhaust from residual and distillate fuel combustion
- High sensitivity at low levels
- User friendly display and secure recording of data from up to 6 analysers
- Multiple data outputs
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More27th May 2024 - Direct Air Carbon Capture & Storage (DACCS)
A government-funded report cautions that the UK must allocate up to £30 billion towards establishing a network of large-scale air purification systems aimed at extracting CO2 from the atmosphere to achieve net zero emissions. These 'direct air carbon capture systems' would have the capacity to extract up to 48 million tonnes of CO2 annually, subsequently injecting it into decommissioned oil and gas reservoirs beneath the North Sea or Irish Sea. The report, authored by Energy Systems Catapult (a government-backed organisation fostering innovation) asserts that without such an initiative, the UK will fail to meet its goal of achieving net zero emissions by 2050.
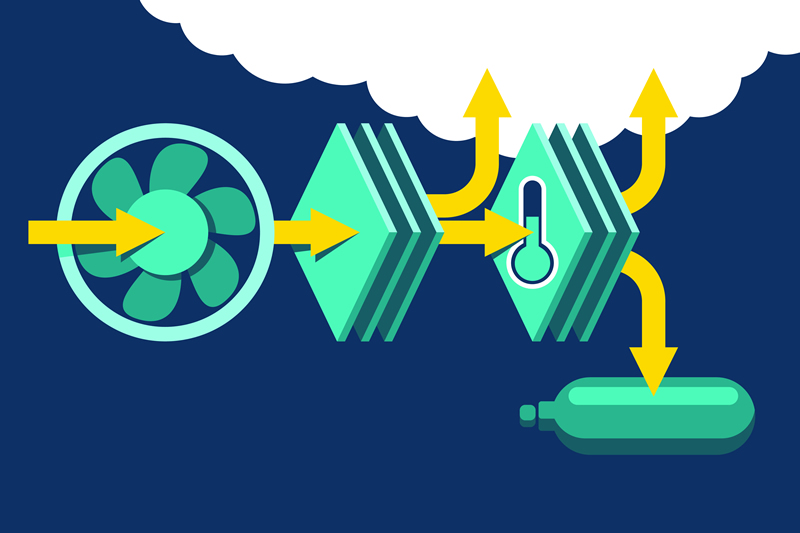
Direct Air Carbon Capture and Storage (DACCS) systems are technologies designed to remove carbon dioxide (CO2) directly from the atmosphere and then store it in geological formations underground or in other long-term storage facilities. Unlike traditional carbon capture and storage (CCS) systems, which capture CO2 emissions from industrial sources like power plants or factories, DACCS systems capture CO2 directly from ambient air.
DACCS typically involves several steps:
- Air Capture: DACCS systems use chemical processes or sorbents to capture CO2 directly from the air. This captured CO2 is then concentrated for storage.
- Carbon Dioxide Separation: The captured CO2 is separated from the air and concentrated into a pure stream of CO2.
- Storage: The concentrated CO2 is then transported to storage sites, typically deep underground, where it is injected into geological formations such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs, saline aquifers, or other suitable geological formations. The CO2 is stored securely to prevent its release into the atmosphere.
DACCS systems offer potential benefits in terms of flexibility and scalability since they can be deployed in various locations, regardless of the source of CO2 emissions. They can also potentially remove CO2 emissions from sectors where reducing emissions at the source is challenging, such as aviation or agriculture. However, DACCS technologies are still in the early stages of development and deployment, and they currently face challenges related to energy consumption, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. Despite these challenges, DACCS systems represent a promising avenue for addressing climate change by removing CO2 directly from the atmosphere.
The landscape for DACCS is being formed over the next few years and these are exciting times for all involved within this groundbreaking sector.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More20th May 2024 - Spotlight On The New Emission Control Area In Canadian Arctic Waters
The benefits of establishing an Emission Control Area (ECA) in Canadian Arctic waters support measures that would not only diminish harmful air emissions from ships, leading to improved air quality for northern communities, but also yield positive outcomes for marine and terrestrial ecosystems and wildlife. Furthermore, it would play a role in mitigating climate-forcing black carbon pollution in the Arctic. The recently announced ECAs in Canadian Arctic waters is poised to make substantial strides in reducing ship-related air pollution in the Arctic region.
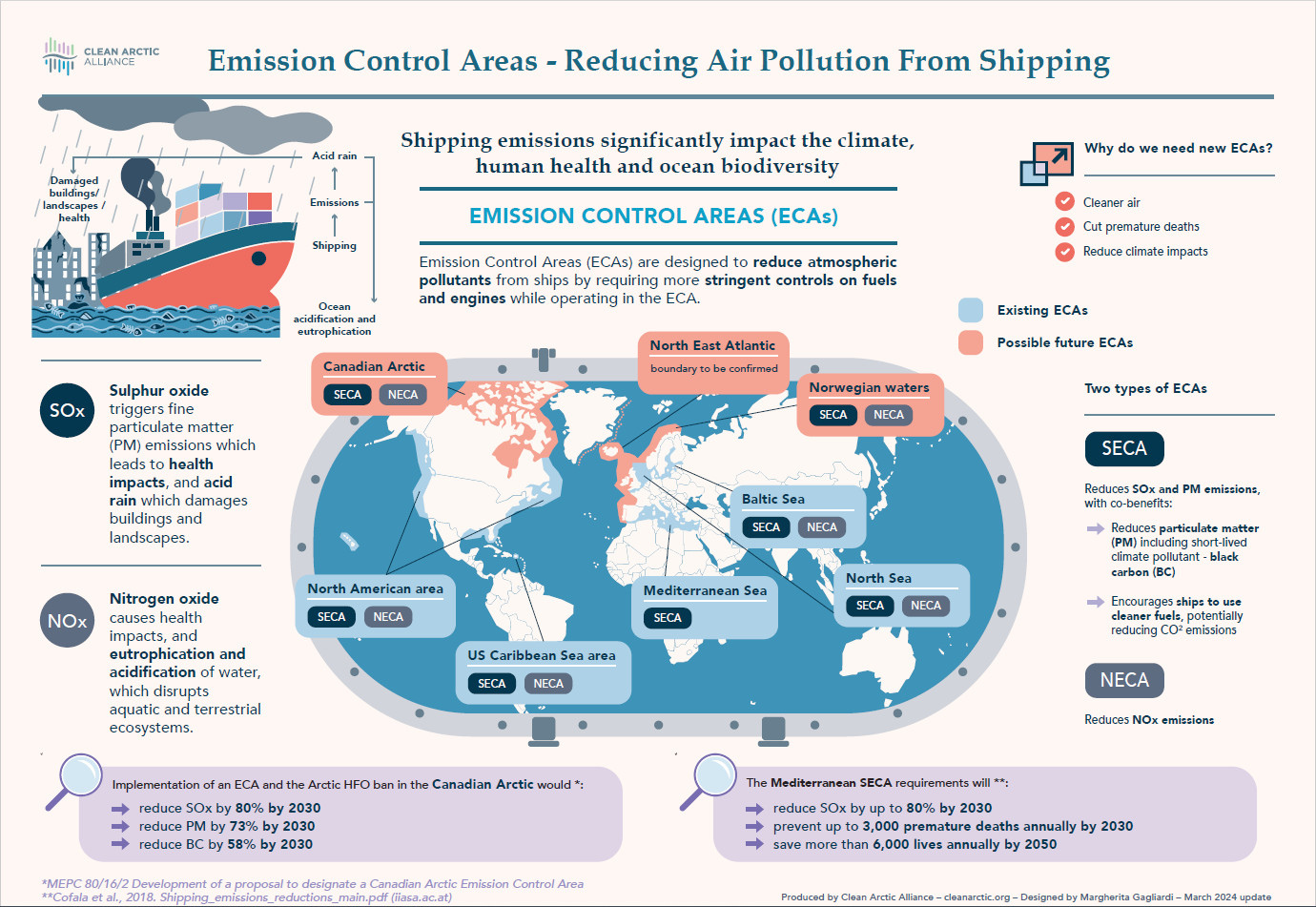
The Emission Control Areas (ECAs) proposed by Canada and Norway, sanctioned by member states of the International Maritime Organisation (IMO), will bolster environmental safeguards in Canadian Arctic waters and the Norwegian Sea. These measures aim to curtail emissions of sulphur oxides (SOx), particulate matter, and nitrogen oxides (NOx) stemming from international shipping activities.
“The creation of Emission Control Areas in the Arctic will set an important precedent for protection of our climate and our ocean,” said Sian Prior, Lead Advisor to the Clean Arctic Alliance. “The proposal for a Canadian Arctic waters ECA includes a welcome and clear reference to the fact that the use of scrubbers as an alternative compliance mechanism will not provide the same benefits in terms of reducing black carbon emissions. Black carbon constitutes 20% of the shipping sector’s global climate impact, and it is five times more potent a climate disruptor when emitted in the Arctic region from sources such as shipping,” Prior concluded.
“The creation of these two new Emission Control Areas will set an important precedent for protection of our climate and our ocean, and particularly the Arctic”, said Dr Sian Prior, Lead Advisor to the Clean Arctic Alliance. “We hope that the designation of ECAs in Canadian Arctic Waters and the Norwegian Sea will drive broad positive change on reducing shipping climate pollutants, especially if the shipping sector complies with the designation by switching to low-sulphur distillate fuels or other cleaner non-fossil fuels. In addition, moving to cleaner fuels will reduce emissions of SOx and particulate matter leading to co-benefits with reductions in black carbon (BC) emissions, provided that cleaner ECA-compliant fuels – and, in particular, distillates – are used."
“The creation of an ECA in Canadian Arctic waters will reduce polluting air emissions from ships, improve air quality for northern populations, deliver benefits to both marine and terrestrial habitats and wildlife and also contribute to a reduction in climate-forcing black carbon pollution in the Arctic”, continued Prior. “The Norwegian Sea ECA will reduce impacts on human health and contribute to reduced deposition of nitrogen and sulphur along the Norwegian coast, including a 58% reduction in particulate matter, such as black carbon, by 2030 compared with 2020. Both ECAs will significantly reduce air pollution from ships in the Arctic.”
“The designation of ECAs in the Canadian Arctic waters and the Norwegian Sea highlights the need for continued work on a possible creation of an ECA in the North-East Atlantic Ocean as referred to at MEPC 80 last summer”, said Carolina Silva, Shipping & Ocean Policy Officer at Zero. “These ECAs will significantly expand the socio-economic, environmental and health benefits for a large number of coastal communities, as well as marine and coastal habitats and wildlife along the North-East Atlantic region, and will also have the co-benefit of reducing black carbon emissions from shipping further south which can still impact the Arctic.”
“ECAs remain one of the most efficient tools at IMO Member States’ disposal to tackle air pollution from ships and are particularly relevant for sensitive ecosystems like the Arctic, therefore, it is important that proposals for new ECAs are as effective and environmentally sound as possible, to ensure their full potential is realised”, continued Silva. “To this end, the positive show of support for Norway’s proposal, which rectifies a problem in the existing ECA regulations whereby a loophole allows ships to delay the implementation of the most stringent NOx reduction requirements, is a good first step in the right direction. Now the IMO must urgently address the fundamental shortcomings of the NOx regulation to prevent further delay of the most stringent requirements in other regions, and to maximise the potential emissions reductions from establishing new ECAs.”
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More13th May 2024 - Carbon Capture Markets To Increase Up To 2030 & Beyond
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is emerging as a crucial technology for climate mitigation. Prominent analyses by the IEA, IPCC, and the Energy Transition Commission (ETC) all project that by 2050, large-scale deployment of CCS in the gigatonne range will be necessary. However, despite its pivotal role, current deployment levels fall well short of what is necessary to fully realise the technology's potential. Both governments and the private sector face significant challenges in financing and scaling CCS projects.

A carbon capture market refers to an economic system where entities can buy and sell carbon capture and storage (CCS) services or carbon credits. Carbon capture involves capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial processes or power generation facilities before they are released into the atmosphere. These captured emissions are then typically transported to storage sites, such as geological formations underground, where they are securely stored, preventing them from contributing to climate change.
In a carbon capture market, companies that emit CO2 can purchase carbon capture services or carbon credits from other entities that have implemented carbon capture technologies and reduced their emissions. This creates a financial incentive for industries to invest in carbon capture technologies and reduce their carbon footprint.
Carbon capture markets can be part of broader carbon trading systems, such as cap-and-trade programs, where a cap is placed on total emissions and companies can buy and sell permits to emit CO2 within that cap. Alternatively, carbon capture markets can operate independently, allowing companies to voluntarily offset their emissions by purchasing carbon capture services or credits.
Overall, carbon capture markets play a crucial role in incentivising the deployment of carbon capture technologies and helping to mitigate climate change by reducing CO2 emissions. The UK is looking to be a global leader in CCS with other G20 nations all looking to implement significant investment in both public and private sector projects.
The European Union pioneered the world's inaugural international Emissions Trading System (ETS) in 2005. Subsequently, in 2021, China introduced the world’s largest ETS, projected to encompass approximately one-seventh of global carbon emissions resulting from fossil fuel combustion. Numerous additional national and subnational ETS initiatives are currently operational or in various stages of development.
There are generally two main categories of carbon markets: compliance and voluntary. Compliance markets are established in response to national, regional, or international policies or regulations. Voluntary carbon markets, whether domestic or international, involve the issuance, purchase, and sale of carbon credits on a voluntary basis. Currently, the majority of voluntary carbon credits are supplied by private entities or governments that implement carbon projects or programs certified by carbon standards, resulting in emissions reductions and/or removals. Protea has a complete section on its website found at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/carbon-capture-and-storage-ccs offering more information on our range of CCS solutions.
Demand for these credits comes from individuals seeking to offset their carbon footprints, corporations with sustainability objectives, and other entities looking to trade credits for potential profit.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More7th May 2024 - Two New Emission Control Areas (ECAs) Support A Global Carbon Emissions Levy in the Shipping Sector
Two fresh Emission Control Areas (ECAs) have garnered support from the International Maritime Organisation's Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC 81), marking a significant step towards implementing a global carbon emissions tax within the shipping industry. MEPC 81, convened recently in London, greenlit the establishment of two distinct ECAs: one in Canadian Arctic Waters targeting nitrogen oxides, sulphur oxides, and particulate matter, and another in the Norwegian Sea addressing nitrogen oxides and sulphur oxides. These proposals are now poised for submission to MEPC 82 for final adoption.

Dr. Sian Prior, Lead Advisor to the Clean Arctic Alliance, hailed the creation of these ECAs as a landmark decision for safeguarding the climate and ocean, especially in the vulnerable Arctic region. She expressed hope that this move would catalyse a widespread shift towards cleaner shipping practices, emphasising the potential of low-sulphur distillate fuels and other non-fossil alternatives to curb shipping-related climate pollutants.
In addition to curbing emissions of sulphur oxides and particulate matter, transitioning to cleaner fuels is expected to yield collateral benefits, including reductions in black carbon emissions, provided vessels opt for compliant fuels within the ECAs, particularly distillates.M
Alongside the approval of the ECAs, MEPC 81 also endorsed several other initiatives:
- Approved new guidelines for the safe transport of plastic pellets in freight containers, encompassing stowage, packaging, and accurate transport/cargo documentation.
- Provisionally supported a draft action plan aimed at mitigating underwater noise stemming from commercial shipping, with plans for further deliberation and final endorsement at MEPC 82.
- Gave the nod to an updated roadmap for crafting guidelines pertaining to alternative fuels, including hydrogen and ammonia, as well as low flash-point fuels, and mandatory protocols for methyl/ethyl alcohols.
- Sanctioned a list of provisions and instruments slated for revision and/or development under the Ballast Water Management Convention, and endorsed interim guidance regarding the application of the convention to vessels navigating in challenging water quality conditions. Additionally, approved guidance for the temporary storage of treated sewage and/or grey water in ballast water tanks.
There is a drive to move to other zones across the globe whereby a global carbon emissions tax in the shipping sector becomes a reality. Protea has a complete section focused on marine emissions found at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More29th April 2024 - UK's First Waste To Energy Carbon Capture Pilot Plant Unveiled
Enfinium, a waste-to-energy operator based in the UK, has unveiled plans to inject £800 million into a carbon capture and storage (CCS) venture at its facility in West Yorkshire. Teaming up with green technology firm Hitachi Zosen Inova, Enfinium intends to set up the UK’s maiden energy-from-waste carbon capture pilot at its Ferrybridge-1 plant in West Yorkshire.

Upon becoming operational by 2030, the CCS technology installed at Enfinium’s Ferrybridge 1 and 2 facilities will have the capacity to capture approximately 1.2 million tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2) annually. This figure encompasses over 600,000 tonnes of durable, high-quality carbon removals. This achievement would be akin to eliminating the carbon emissions of every household in Manchester from the atmosphere. With CCS integration, Ferrybridge is poised to emerge as one of Europe's most substantial carbon removal initiatives.
The technology supplied by HZI will manifest as a scaled-down, containerized iteration of CCS technology adaptable for commercial deployment at energy-from-waste facilities. This unit is slated to capture up to one tonne of CO2 per day from Enfinium’s operations at the Ferrybridge-1 site in West Yorkshire. The trial is slated to run for a minimum of 12 months, with operational commencement slated for July 2024.
This pioneering pilot marks a significant achievement for HZI, heralding the commencement of Europe's first mobilized effort of its kind. It signifies a pivotal milestone for HZI, aiming to bolster its esteemed standing in the energy-from-waste and renewable sectors by introducing novel decarbonisation solutions to its clientele.
The pilot initiative seeks to showcase the application of carbon capture technology at energy-from-waste facilities to extract CO2 from the atmosphere. Through this endeavor, Enfinium aims to evaluate various amine solvents and gather authentic performance data, including CO2 capture rate, energy consumption, and solvent degradation.
This pilot initiative forms part of Enfinium’s broader vision to spearhead an investment totaling up to £800 million in Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) at its Ferrybridge 1 & 2 facilities. Once operational, these combined facilities are projected to capture over 1.2 million tonnes of CO2 annually. With the integration of CCS technology, the UK's largest energy-from-waste site is poised to transition into one of Europe's premier carbon removal initiatives.
Enfinium is a leading UK energy from waste operator with four operational sites in the UK, in West Yorkshire, Kent and Flintshire, and two in construction. Enfinium diverts 2.3 million tonnes of non recyclable waste from climate-damaging landfill, putting it to good use by turning it into home grown energy, enough to power 500,000 UK homes. Enfinium’s ambition is to transform its facilities into local 'decarbonisation hubs' powered by the millions of tonnes of non recyclable waste the UK will produce for decades to come. Using existing energy from waste infrastructure, enfinium could contribute to heat networks, produce electrolytic hydrogen, or use carbon capture technology to provide durable, high quality carbon removals which will be critical for the UK to achieve net zero by 2050.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More22nd April 2024 - Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Clean Ports Program In Focus
Earlier this year the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced a 3$ billion zero emission transition project. Established under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), the "Clean Ports" Program aims to help ports transition to zero-emissions operations, reduce diesel pollution and engage with the local community. The funding is open as a competitive bidding based process spread across a number of critera. 100% of the 3$ billion allocation is to be assigned by the middle of 2024.

What can the funding be used for?
Under the Zero-Emission Technology Deployment Competition, eligible expenses encompass:
- Procurement and deployment of new eligible battery-electric or hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, vessels, powertrains, or other mobile equipment designed for zero emissions.
- Establishment of zero-emission infrastructure such as fuelling stations to support equipment purchased with grant funding.
Activities eligible for support under the Climate and Air Quality Planning Competition include:
- Mandatory emissions inventorying and accounting practices.
- Stakeholder collaboration and communication, with a focus on communities situated near the port.
- Identification of resiliency measures.
- Analysis of strategies and setting goals.
This program, a component of President Biden’s Investing in America agenda, features two grant competitions. The Zero-Emission Technology Deployment Competition will allocate nearly $2.8 billion to finance zero-emission port equipment and infrastructure, including cargo handling machinery, vessels, and electric charging infrastructure. The Climate and Air Quality Planning Competition will provide approximately $150 million for planning efforts at ports aimed at reducing emissions and involving local communities.
EPA Administrator Michael S. Regan highlighted the program's significance in creating jobs, reducing air pollution, and advancing environmental justice.
"Our nation’s ports are among the busiest in the world, helping us to create good jobs here in America, move goods, and grow our economy,” Regan said. “Today’s historic funding announcement reflects President Biden’s vision of growing our economy while ensuring America leads in creating globally competitive solutions of the future. Today we’re making $3 billion available to install cleaner and more efficient technologies while cutting air pollution to protect the people who work at and live near ports."
The US represents a substantial component in global shipping and marine emissions with some of the busiest ports in the world. Ports are a vital part of a nation's maritime transportation system. The United States has more than 300 ports operated by states, counties, municipalities, and private corporations. Water transport was the dominant mode of transport for the US in 2021. That year, imports to the country amounting to the weight of 671 million short tons were transported by ships. Goods exported by ships from the US weighed 918 million short tons in 2021.
Protea partners with a valued distributor for US installations being Delta Instrument LLC. Delta Instrument supplies a variety of equipment to the process control industry selling and servicing Biogas Analysers, Calorimeters, Emission Analysers, Dew Point Measurement and Oxygen Analysers. Engineered solutions to problem measurements are a Delta Instrument specialty. Please contact us for all your analyser requirements.
Protea produces a range of analysers capable of measuring a full range of components on-line in the aggressive environments often encountered in today's emission measurement industry. Protea analysers include many advanced features and they have already achieved wide acceptance in a large number of applications. In addition to economies from their ability to measure several components in one operation, ease of installation and maintenance, the instruments are able to analyse problem applications such as, NOx, SOx,, NH3,, CO2,, CO with a high degree of accuracy and repeatability.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture Read More17th April 2024 - Wet Gas Calibrator for CEMS
Protea has released our new, improved wet gas calibrator for field calibration of CEMS. The atmosFieldCAL is a portable device that allows for wet or humidified calibration gas to be generated on-site to validate AMS/CEMS or P-AMS.

For commissioning or annual linearities (QAL2/AST) of water vapour measurements, atmosFIeldCAL can validate Protea or other manufacturers CEMS, either in-situ or extractive types. Cross-sensitivity to water can be assessed quickly on-site. The calibrator allows for single or dual gas inputs. With two gases, a check or span gas applied at the same time as the water, so cross interference at zero and span points can be assessed. As well as water vapour, solutions of HCl/NH3/HF can be used to validate CEMS measuring these gases, such as Protea’s atmosFIR and P2000 CEMs.
The atmosFieldCAL’s compact, backpack size is ideal for validating portable emissions equipment (P-AMS) on site too, such as Protea’s portable atmosFIRt FTIR. Mobile emissions test data can be validated with water vapour checks before and after data collection. The atmosFieldCAL can be provided with ISO 17025 calibration.
Please contact Protea for more information.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More17th April 2024 - Analyzer Tech Conference, Galveston TX
Protea’s products are being demonstrated at the Analyzer Tech Conference at Galveston Island Convention Center April 15– 19, 2024 https://www.analyzertechconference.org/

Please stop by Booth 313 and ask Delta Instrument LLC if there are any process, emissions or portable monitoring needs we can support with using our range of analytical technologies.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More15th April 2024 - Carbon Capture Storage Association Spring Budget Assessment
The Carbon Capture & Storage Association (CCSA) is the lead European association accelerating the commercial deployment of carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS) through advocacy and collaboration. CCUS is an essential solution to reach net zero emissions. CCUS plays a vital role in reducing emissions from industries such as steel, cement, chemicals and refining. CCUS is one of the very few methods which can remove CO2 from the atmosphere at an industrial scale.

Although the Government had previously promised backing for UK carbon capture, Ruth Herbert, Chief Executive of the Carbon Capture and Storage Association (CCSA), contends that the mark has been overlooked regarding carbon capture, utilisation, and storage (CCUS) projects. Following the Chancellor's Announcement on the Clean Energy Reset, Ruth Herbert, CEO of the CCSA, issued a statement expressing her views.
"Today’s budget was a missed opportunity for the Government to put in place a longer-term revenue support envelope for the next wave of projects – to provide the level of certainty they need to move forward," she said.
In last year's Budget, there was a pledge to allocate £20 billion ($25.5 billion) towards expanding CCS (Carbon Capture and Storage) projects throughout the UK, scheduled to be implemented over a span of 20 years. The government announced that this funding would facilitate the advancement of CCS endeavours in North Wales, the North West of England, and the East Coast. However, Herbert asserts that the funding has not yet reached the projects in dire need of it, despite looming deadlines.
"The UK’s CCUS industry is still waiting for the funding announced in last year’s Spring budget to be committed to projects, with final investment decisions for projects in the North West and North East of England needed in the next few months."
Without this, the UK risks losing the opportunity to attract around £30bn ($38bn) of private investment into UK CCUS by 2030, which would create and protect tens of thousands of jobs and transform industrial regions across the UK."
The CCSA offers a UK Carbon Capture Project Pipeline map on their website displaying information on identified carbon dioxide (CO2) capture projects in the UK, including, where disclosed:
- Estimated location
- The projected CO2 capture per year (MtCO2/yr) of these projects once operational
- The type of project, by sector and by anticipated government support package (where relevant)
- The project’s engagement with the Government cluster sequencing programme (where relevant)
CCSA objectives are stated as:
- Advance carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS) in the UK
- Promote CCUS internationally
Protea’s multi-gas FTIR technology is ideally suited to new processes involving carbon reduction, such as Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS).
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More10th April 2024 - The Protea Team Exhibiting At Sea Japan 2024
Protea are exhibiting at Sea Japan 2024, located at the Tokyo Big Sight East Hall 1 - 3, 135-0063 Tokyo, Koto City, Ariake, 3-chome-10-1 at booth 1J-09. Come and visit our booth to discuss shipping and marine emissions monitoring technologies.




Protea manufactures an extensive range of gas analysers for use in both Continuous Emission and Process Monitoring. This enables Protea to select the product best suited to the application without compromise. Protea operates from two modern facilities incorporating application development, production and after sales support. Our customers are supported by a worldwide partner company network employing factory trained service personnel backed up by our service team. Come and visit our booth 1J-09 to discuss our extensive range of products and expertise.
#SeaJapan #Protea #EmissionsMonitoring #CEMS #FTIR #GasAnalysers #ShippingEmissions #CarbonCapture
Read More8th April 2024 - Two Major British Carbon Capture Projects Unveiled
Two large Carbon Capture, Usage and Storage facilities have been recently granted planning permission with full backing by the UK Government. One project is located near Hull in East Yorkshire and the other near Middlesbrough in Teesside.

H2H Saltend
Equinor’s 600-megawatt (MW) low carbon blue hydrogen production plant, H2H Saltend, with carbon capture technology, has been granted planning permission by the East Riding of Yorkshire Council. Located in the Saltend Chemicals Park in Hull, the 600MW project will replace an existing steam methane reforming unit (which produces grey hydrogen from fossil gas) with a high-efficiency autothermal methane reformer (ATR) and CCS technology that Equinor claims will capture “at least” 95% of CO2 emissions.
The hydrogen produced at Saltend will be used to meet both existing and new demand within the industrial park and nearby area, with many processes that currently run on gas switched to run on H2 instead. This includes a plan to blend hydrogen into the gas-fired Triton Power Station, owned by Equinor and utility SSE Thermal, located within the chemicals plant.
The East Coast Cluster, of which H2H Saltend is just one project, aims to store CO2 from power plants which directly feed in their emissions, including Keadby 3 Carbon Capture Power Station, owned by Equinor and SSE, and Drax’s biomass-fired plant. The decision on H2H Saltend comes a month after a 1GW project at Stanlow refinery, linked to the HyNet cluster, became the first to secure planning consent. Construction work on the Stanlow refinery is expected to start this year.
The full 600MW of H2H Saltend has been granted planning permission, while the HyNet project is set to be built in two phases: with the first 350MW phase given full planning consent by local authorities, and the second 750MW preliminary consent. H2H Saltend becomes the third carbon capture project in the Humber region to secure planning permission, following the Drax BECCS project and Keadby Carbon Capture Power Station.
Net Zero Teesside Power (NZT Power)
Aims to be one of the world’s first commercial scale gas-fired power stations with carbon capture, has received development consent from the UK Government. Development consent includes onshore CO2 gathering and transport infrastructure operated by the Northern Endurance Partnership (NEP). NZT Power, which aims to take a final investment decision in September 2024 or before, could generate up to 860 megawatts of low carbon electricity.
The planned Net Zero Teesside Power project, which aims to be one of the world’s first commercial scale gas-fired power stations with carbon capture, took another step forward after receiving development consent from the Secretary of State for Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (DESNZ) following a recommendation from the Planning Inspectorate (PINS).
Consent was granted following a joint application between NZT Power and the Northern Endurance Partnership. NZT Power is a combined-cycle gas turbine electricity generating station with an abated capacity of up to 860 megawatts output with carbon dioxide (CO2) capture plant. The NEP project includes a CO2 gathering network on Teesside to transport captured CO2 from industrial emitters; a CO2 gathering/booster station to receive the captured CO2 from the gathering network and from NZT Power and the onshore section of a CO2 transport pipeline for the onward transport of the captured Net CO2 to the offshore Endurance store.
Ian Hunter, Managing Director, NZT Power, said: “The granting of a Development Consent Order is an important step towards the development of the UK’s first full-scale integrated power and carbon capture project. We thank the planning inspectorate and the Secretary of State for their work during this process and look forward to taking the project forward to a planned final investment decision in September 2024 or before”.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) could be key in the reduction in Carbon Dioxide (CO2) from industrial processes. Protea’s range of gas analysers have been used both in research into emerging technologies for CCS, but will also play an important role in the regulatory emissions monitoring from installations of CCS. Carbon Storage Protea’s atmosFIR FTIR gas analyser has proven a valuable tool in research into the effective storage of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) in the North Sea.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More2nd April 2024 - Protea Exhibiting At Sea Japan 2024
Protea will be exhibiting at Sea Japan 2024 located at the Tokyo Big Sight East Hall 1 - 3, 135-0063 Tokyo, Koto City, Ariake, 3-chome-10-1 at booth 1J-09. Since 1994, Sea Japan has been held under various themes that match the trends of the time and industry needs. Sea Japan 2024, its 15th edition will focus on clean energy and explore the various options for the industry. The event is taking place from Wednesday 10th April to Friday 12th April 2024.

Reasons you should visit Sea Japan / Offshore & Port Tech
The enormous challenge facing the maritime industry is to discover new energy sources to operate ships in order to achieve carbon neutrality. Which fuel, whether hydrogen, ammonia, LNG, electricity, or something else, will lead the industry towards this goal? How can the industry work to improve efficiency and ensure safety in order to commercialise this new energy source? At Sea Japan 2024 you will find the products, technologies and concepts that hold the key to solving this challenge.
There is a shortage of human resources not only within the maritime industry but in all industries around the world. This is driving the quest for technologies that will be used in the future to compensate for the shortage of manpower both aboard ship and ashore. Sea Japan 2024 will showcase a wide range of technologies for increasing automation and efficiency in vessel operations.
Responding to the growing opportunities for the maritime industry in offshore energy and resource development as well as in the ports sector, “Offshore & Port Tech” has been launched alongside Sea Japan 2024. The expansion and development of marine related resources such as offshore wind, tidal energy, sub-sea mining and aquaculture can only be achieved by calling upon the time-proven technologies, products and services of the shipbuilding, marine engineering and shipping industries. Offshore & Port Tech will explore the possibilities for technology repurposing and implementation, and the related new business opportunities.
A full program of conferences, seminars and workshops will be held alongside the exhibition. Seminars in the technical program will cover topics not only about clean energy but also DX, carbon neutral port and many others that industry professionals are currently facing. All sessions are free of charge, so don’t miss this opportunity to get up to date on the latest trends and developments in the maritime industry. The seminar programme has already been announced in February for you to be updated before your visit to the event.
Protea Ltd manufactures an extensive range of gas analysers for use in both Continuous Emission and Process Monitoring. This enables Protea to select the product best suited to the application without compromise. Protea operates from two modern facilities incorporating application development, production and after sales support. Our customers are supported by a worldwide partner company network employing factory trained service personnel backed up by our service team. Come and visit our booth 1J-09 to discuss our extensive range of products and expertise.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More25th March 2024 - Shipping Emissions CCS Trial Deemed A Success
A UK-based developer of carbon capture solutions has completed a successful trial of its carbon looping carbon capture technology on a commercial container ship, the Sounion Trader, owned by Lomar. Following this achievement, the company now aims to scale up the technology, with plans to initiate commercial operations by 2025.
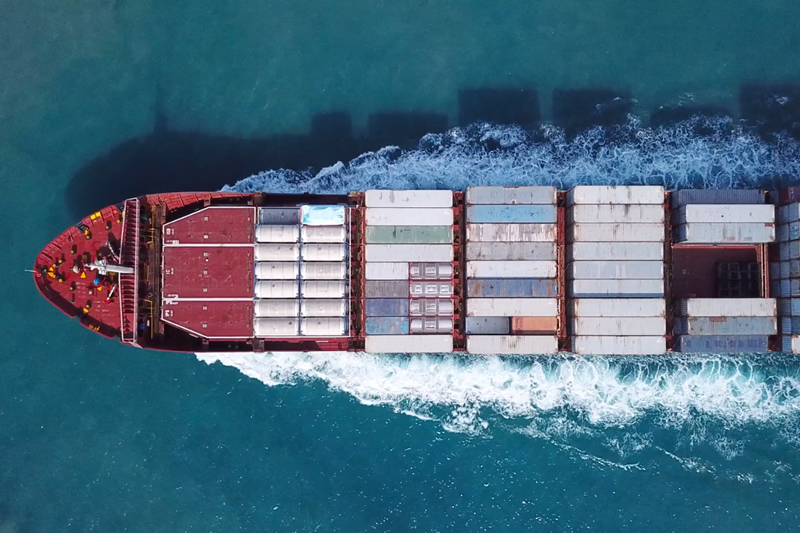

Seabound's system has the potential to capture up to 95% of a ship's CO2 emissions, converting them into solid calcium carbonate pebbles for reuse or sale upon unloading at port. Securing US$1.5 million in grant funding from the UK government's Clean Maritime Demonstration Competition Round 3, Seabound and Lomar facilitated part of the pilot project.
Installed on a 3200 TEU container ship, Seabound's compact carbon capture system demonstrated an impressive efficiency, capturing approximately 80% of CO2 and around 90% of sulfur emissions during the test. The Sounion Trader, a 240-meter-long container ship, underwent the trial in the Persian Gulf, showcasing one of the few ships actively working to reduce their carbon footprint by capturing and storing CO2 emissions onboard. However, accommodating large quantities of CO2 poses a challenge for shipping companies, considering the energy and space trade-offs with regular cargo.
During the trial, the prototype system successfully captured 1 tonne of CO2 per day. The Seabound team installed the system at a shipyard in Turkey and spent two months onboard the vessel, conducting tests to enhance carbon capture efficiency, which eventually reached 78%, with sulfur capture efficiency exceeding 90%.
With the pilot concluded, Seabound shifts its focus to developing full-scale carbon capture systems for commercial deployment starting from 2025. The prototype system, which underwent prior land-based trials, was installed on the vessel along with a container of calcium oxide, facilitating the conversion of CO2 into limestone for storage.
Following positive outcomes, the system has been disassembled and returned to Seabound's facilities in north London, preparing for a larger-scale trial. However, the challenge for all maritime carbon capture solutions remains the need for effective CO2 storage, whether for reuse, incorporation into larger transport systems, or sequestration. The volume of storage space is a critical factor determining the feasibility of CO2 capture solutions.
The landscape of carbon capture storage and emissions management/monitoring is changing rapidly both onshore and offshore.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More18th March 2024 - The Three Main Steps Of Carbon Capture & Storage
Protea has been running a number of articles on CCS during the year with a focus on the latest initiatives and activities around the globe. We thought we would revisit the principles of the process. Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is a process designed to capture carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions produced from industrial processes or power generation and prevent them from entering the atmosphere. The captured CO2 is then transported to a storage site, typically deep underground, where it is securely stored to prevent its release into the atmosphere.

Carbon dioxide (CO2) is naturally absorbed from the atmosphere by forests, plants, oceans, and soils. However, these natural processes are slow and are being undermined by deforestation, pesticide overuse, and pollution. Carbon capture and storage (CCS), also known as carbon sequestration, offers a way to prevent excess CO2 from entering the atmosphere. The CCS process generally involves three main steps:
- Capture: CO2 is captured from large point sources such as power plants or industrial facilities before it is released into the atmosphere. There are various capture technologies available, including post-combustion capture, pre-combustion capture, and oxy-fuel combustion, each suited to different types of emissions sources.
- Transport: Once captured, the CO2 is transported via pipelines, ships, or other means to a suitable storage site. Transportation methods vary depending on the distance between the capture site and storage location.
- Storage: The captured CO2 is injected deep underground into geological formations such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs, saline aquifers, or coal seams. These geological formations act as natural traps, securely storing the CO2 and preventing it from escaping back into the atmosphere over long periods of time.
CCS has the potential to play a crucial role in mitigating climate change by reducing CO2 emissions from industrial processes and power generation. It allows for the continued use of fossil fuels while minimising their environmental impact. Additionally, CCS can enable the removal of CO2 from the atmosphere, helping to offset emissions from sectors that are difficult to decarbonise, such as heavy industry and transportation.
However, CCS also faces challenges, including high costs, technical feasibility, and public acceptance. Continued research, development, and deployment of CCS technologies are essential to realising its full potential as a tool for combating climate change. Protea’s multi-gas FTIR technology is ideally suited to new processes involving carbon reduction, such as Carbon Capture and Storage and CCS Online Monitoring.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More11th March 2024 - EU Targets 50M Tonnes Per Year Of CO2 Storage By 2030
The European Union (EU) aims to achieve a storage capacity of 50 million tonnes per year of CO2 by 2030 as part of its strategy to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050, according to a new strategy released by the European Commission. This strategy emphasises the necessity of significantly increasing industrial carbon capture capacity to meet these goals.
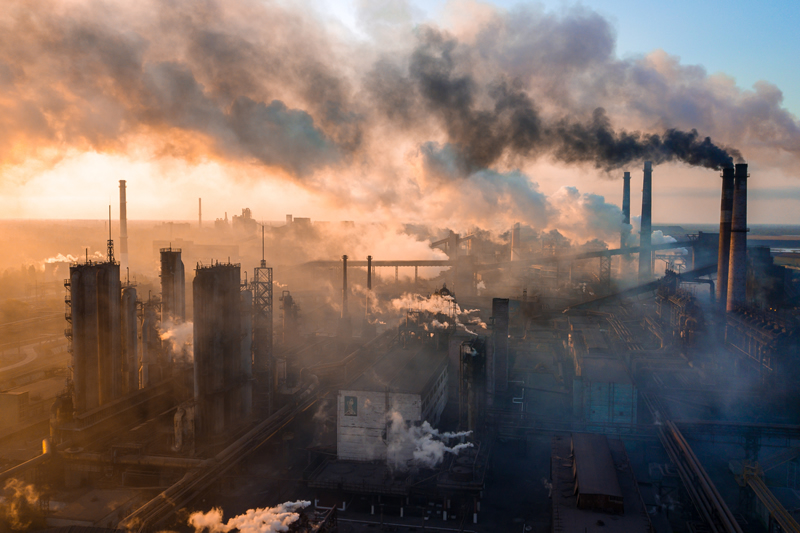

The Commission plans to establish a clear carbon accounting framework to encourage the utilization of captured CO2 as a resource in industrial processes, thereby reflecting the climate benefits of such utilisation. This initiative aims to drive the uptake of sustainable carbon in industrial sectors. To facilitate the implementation of industrial carbon management projects, the Commission outlines several key actions. These include:
- Investment and funding: The EU and Member States are encouraged to promote industrial carbon management projects under EU energy infrastructure programs and consider Important Projects of Common European Interest (IPCEIs). Additionally, the Commission will explore the possibility of supporting certain CO2 capture projects through market-based funding mechanisms such as competitive bidding auctions-as-a-service under the Innovation Fund.
- Research, innovation, and public awareness: The Commission plans to increase funding for research and innovation on industrial carbon management projects through existing instruments like Horizon Europe and the Innovation Fund. It will also support the establishment of a knowledge-sharing platform for carbon capture, use, and storage (CCUS) projects. Furthermore, the Commission aims to raise public awareness of these technologies and their benefits, engaging with local communities to discuss potential rewards.
- International cooperation:The Commission intends to expedite collaboration with international partners on industrial carbon management, focusing on harmonising reporting and accounting of carbon management activities. It also aims to ensure that international carbon pricing frameworks consider removals to address emissions in hard-to-abate sectors.
The EU is committed to achieving net-zero CO2 emissions by 2050. While significant emissions reductions will come from reducing current emission levels, technologies capable of capturing or removing CO2 directly from the atmosphere will also be essential. These technologies will target sectors with particularly challenging emissions reduction requirements, such as process emissions in cement production or waste-to-energy processes.
The Industrial Carbon Management Communication adopted by the Commission provides detailed insights into how these technologies can contribute to reducing emissions by 90% by 2040 and achieving climate neutrality by 2050. Protea is at the forefront of carbon capture technology with our range of FTIR technologies. Protea’s multi-gas FTIR technology is ideally suited to new processes involving carbon reduction, such as Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS).
4th March 2024 - CCS Growth Is Set To Continue With Challenges Ahead
The carbon capture and storage (CCS) market is anticipated to witness growth despite facing challenges in initiating significant momentum in 2024, according to global financial services provider ING. ING suggests that expectations for rapid expansion this year should be tempered, giving way to more pragmatic anticipation of steady progress in the emerging carbon capture sector.

One of the obstacles hindering the CCS market is the prevailing uncertainty stemming from various factors, including upcoming elections in the EU and US. CCS serves as a critical technology for facilitating the transition towards a net-zero economy, and while its growth is expected to gather momentum in 2024, overly optimistic projections of rapid advancement are likely to moderate. Additionally, elections in key markets such as the US and EU will further compound existing uncertainties.
Another challenge lies in the substantial cost associated with carbon capture technology, which remains a significant impediment to market expansion, hindering its growth rate necessary for mitigating the climate crisis. However, governments worldwide are increasingly demonstrating support for CCS solutions, with some anticipating an eightfold increase in carbon capture capacity by 2030, as reported by Bloomberg New Energy Finance.
Presently, the global carbon capture and storage effort captures and stores only a minute fraction – 0.1% – of global CO2 emissions. However, to effectively curb rising temperatures, this figure must escalate to 15% by mid-century. Efforts to decarbonize the global economy are approaching a critical juncture, evidenced by agreements reached at the COP28 climate conference to transition away from fossil fuels and triple investment in renewables. Nonetheless, renewables alone cannot achieve a net-zero economy, underscoring the indispensable role of carbon capture and storage in preventing CO2 emissions and mitigating global warming.
In 2024, CCS technologies are poised to gain further traction. More companies in hard-to-abate sectors are committing to decarbonization and recognizing CCS as a cost-effective technology for emission reduction, particularly in industries like steel or plastics production. Concurrently, government support for CCS is on the rise. Bloomberg New Energy Finance projects an eightfold increase in CCS capacity by 2030, contingent on the realization of all announced projects.
However, forecasting capacity growth in the nascent CCS market presents challenges, as not all project announcements carry the same weight. While numerous projects are in the pipeline, only a fraction have progressed to the final investment decision stage, with construction either underway or imminent.
Despite these challenges, ING views CCS as a promising market in the long term. Nonetheless, the company is attuned to real-world factors that will influence the market in 2024, including elections in the US, EU, and India, demand from major emitters for CCS, carbon pricing, and social acceptance. Protea has a complete Carbon Capture and Storage (CSS) section here at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/carbon-capture-and-storage-ccs for more information.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More26th February 2024 - Joint Venture Announced To Build Ship Based Carbon Capture Systems
Pooling their expertise, the joint venture endeavors to assist vessel owners in curbing CO2 emissions from both newbuild and existing ships. Shipboard CO2 capture holds tremendous promise as a technology, particularly in the North Sea, which is poised to witness a surge in CO2 shipping due to its proximity to densely populated regions of northern Europe. Bouman Industries and Conoship International, partners in the EverLoNG ship-based carbon capture project, have inked an agreement to establish a joint venture aimed at constructing ship-based carbon capture (SBCC) systems.

The EverLoNG project seeks to promote the adoption of SBCC by showcasing its effectiveness on LNG-fueled vessels and advancing it towards market readiness. According to the partners, incorporating a ship-based carbon capture system to capture CO2 from exhaust gases could potentially slash shipboard CO2 emissions by up to 95 percent. The captured CO2 can be cooled and stored onboard, with the possibility of being utilised onshore to produce synthetic methane.
Onboard carbon capture (OCC) encompasses a variety of technologies designed to capture carbon dioxide emissions emitted by ships during operation. In post-combustion systems, OCC involves the purification of exhaust gases to isolate CO2, which is then stored onboard in different forms including gas, liquid, or mineral for eventual offloading. In pre-combustion systems, carbon is separated from the fuel to produce hydrogen, which is then utilised in specialised energy conversion machinery.
The concept of onboard carbon capture is garnering increasing attention as a viable solution for reducing carbon emissions from ships. With the competition intensifying for green energy carriers like ammonia, hydrogen, and methanol both within the maritime sector and across other industries, the costs are expected to rise significantly. Onboard carbon capture presents an effective means of decarbonisation, enabling the continued use of established maritime fuels while mitigating environmental impact. Protea’s multi-gas FTIR technology is ideally suited to new processes involving carbon reduction, such as Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS).
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More22nd February 2024 - Protea At CEM India 2024 Booth 35
Members of the Protea team have enjoyed the last two days exhibiting at the Leela Ambience Convention Hotel in Delhi for CEM India. These CEM India events highlighted the benefits of CEMS such as quality control and process optimisation. It also offered help and solutions to process operators and end users to overcome the challenges of selecting the right technology, ensuring correct installation, proper calibration, and maintenance of their CEM systems.

The guidelines for continuous emission monitoring systems (CEMS) and continuous effluent quality monitoring systems (CEQMS) provide information on how suitable monitors are selected, installed and operated in order to demonstrate compliance. Continuous monitoring systems enable both compliance and enforcement of environmental regulations in India. Similar systems have been successful in Europe and the USA, and are being replicated by India and China. The aim of the CEM India conference and exhibition is to help process operators meet environmental objectives by providing guidelines, technical support and practicable solutions.

India is one of the world's fastest growing economies, The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) of India has taken an important step to adopt Continuous Emissions Monitoring Systems (CEMS) in India. The CPCB has initially directed plants in 17 categories of highly polluting industries to install CEMS for real time monitoring and compliance.

The main industries that have been targeted to install CEM Systems include Aluminium, Cement, Copper, Distilleries, Dying, Chlor Alkali, Fertilizers, Iron & Steel, Oil Refineries, Petrochemical plants, Pesticides, Pharmaceuticals, Power Plants, pulp and paper mills, sugar, Tanneries ,Zinc and the Copper industry. The Parameters for continuous monitoring include, Particulate matter, Fluoride, Ammonia, Sulphur Dioxide, NOx , Chlorine, HCL and Carbon Monoxide.
The CEM India conference follows on from the highly successful series of CEM events which have been held in Europe since 1997. CEM India will provide delegates and visitors in depth information on Indian regulation and policy, monitoring guidelines, calibration and quality control. There will be case study presentations from Industry as well as International speakers, Regulators and the Centre for Science and Environment on best practice , installation, procedures and data capture.
#cems2024 #protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More19th February 2024 - Protea Exhibiting At CEM India 2024
Protea will be at the Leela Ambience Convention Hotel, Delhi in India for CEM India at booth 35. Following on from the success of previous Emission monitoring events held in India the 3rd CEM India will take place in Delhi on the 20th-22nd February 2024. These CEM India events highlight the benefits of CEMS such as quality control and process optimisation but also offer help and solutions to process operators and end users to overcome the challenges of selecting the right technology, ensuring correct installation, proper calibration, and maintenance of their CEM systems.

India is one of the world's fastest growing economies. The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) of India has taken an important step to adopt Continuous Emissions Monitoring Systems (CEMS) in India. The CPCB has initially directed plants of highly polluting industries to install CEMS for real time monitoring and compliance. The guidelines for continuous emission monitoring systems (CEMS) and continuous effluent quality monitoring systems (CEQMS) provide information on how suitable monitors are selected, installed, and operated to demonstrate compliance. Continuous monitoring systems enable both compliance and enforcement of environmental regulations in India. Similar systems have been successful in Europe and the USA and are being replicated by India and China.
The aim of the CEM India conference and exhibition is to help process operators meet environmental objectives by providing guidelines, technical support, and practicable solutions. CEM delegates should enter at Gate no. 6 in Convention Tower. Protea’s range of gas analysers have been used both in research into emerging technologies for CCS, but will also play an important role in the regulatory emissions monitoring from installations of CCS.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More15th February 2024 - Distributor Training In South Africa With SI Analytics
A member of our training team recently delivered a training session which was held for a distributor located in South Africa. SI Analytics is a long-standing distributor partner whose staff members undertook training on the Protea P2000 and P5000 range with the training taking place from 22nd January 2024 to 26th January 2024.

Topics covered included P2000 Familiarisation, Infrared photometer principles, P2000 site service, Control Units and Analyser Software, P5000 Site Service and Troubleshooting and fault finding.







The Protea 2000 In-Situ Infra-red gas analyser connected to a Protea Control Unit forms the basis of a Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS). The Stack Mounted In-Situ analyser monitors the stack gas without the need for any sample handling equipment making it a cost effective solution to Continuous Emission Monitoring and Process applications.
The Protea 5000 is an ultra-violet (UV), continuous emission monitoring analyser, designed for in-situ analysis of gas-phase emission components. Using absorption spectroscopy, Protea 5000 stores and analyses the full UV spectrum and calculates the gas emission concentrations.
#sianalytics #protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More12th February 2024 - Protea Giving A Training Session At EUEC2024 In Dallas
Protea will be in attendance with one of our distributors Delta Instruments on booth 623 at EUEC2024 located at the Irving Convention Center in Dallas. We will also be providing a “must attend” training session for experts and operators of CEMs. This training session is part of "Track B" which includes EPA policy and procedures for accurate monitoring, reporting, and auditing of emissions pursuant to Part 75 of the Acid Rain Program & Clean Air Interstate Rule. This will be in Room Room 2 (Track B) Wednesday, February 14, 2024 covering CEMS, Emission Testing, Monitoring, Modeling, Remote Sensing. Come and visit the show and speak to one of the Protea team.

Victoria Brewster from Protea who is Product Leader of Spectroscopic Solutions, will be presenting and stated "The generation of electricity from municipal digesters and landfill is of increasing interest, as the biogas can allow for a form of renewable energy. Organosilicon compounds often find their way into land-fill or digester gases as siloxanes. Siloxanes are low-level hazards to the atmosphere in terms of their emissions, however when they are combusted in gas engines the hard silica that is produced is very harsh to the moving parts of the gas engine. Ultimately this increases maintenance cost and gives a lower energy output, making the generation of power less efficient."
Victoria went on to state "With this ever-growing market, the need for analysis of the siloxane content of the biogas pre-generator is important. A land-fill gas plant operator can determine the amount of siloxane removal of the pre-combustion feed gas. This enables a more cost-effective cleaning system to be employed. They can also determine whether an existing clean-up system is operating effectivelyThere is currently no standard method for gaseous siloxane measurement and to date no on-line gas process monitoring system. The usual method of gas analysis has involved the extraction of a sample gas, via bag or cylinder, and analysis off-plant. Sampling losses of siloxanes inevitably occur, as the sample can be adsorbed onto the sample container walls."
Protea has developed an analytical model for our atmosFIR FTIR gas analyser that allows speciation of siloxanes on-line. The full spectrum technique of FTIR also allows for the measurement of the main gas components, CH4 , CO2 , NH3 etc. providing real time, in-situ full gas composition analysis. In this paper we compare direct readings from a Protea FTIR with offline sampling methods. Comparisons have been made for siloxane calibration standards as well as real world gas data from both landfill and waste water.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More6th February 2024 - CCUS Vision Sets Out Plans for New Competitive Market in Carbon Capture, Usage and Storage
The UK government has recently revealed a bold new plan aimed at fostering a competitive carbon capture market, bolstered by an unprecedented £20 billion investment. This initiative, dubbed the CCUS Vision, outlines a roadmap for establishing a thriving UK carbon capture, usage, and storage market by 2035, thereby generating employment opportunities and advancing the nation's commitment to achieving net zero emissions.

Under the CCUS Vision, the UK aims to evolve from early-stage projects supported by government funding to a competitive market by 2035. This transition will empower UK enterprises to vie for the construction of carbon capture facilities and offer their services globally. Projections suggest that this endeavour could inject £5 billion annually into the economy by 2050, positioning the UK as a frontrunner in carbon capture technology while fulfilling its net zero objectives in a financially sustainable manner that alleviates the burden on taxpayers.
Carbon capture technology entails capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions before they are released into the atmosphere and securely storing them underground, utilising voids created by oil and gas extraction. The UK holds a strategic advantage in this regard, owing to its distinctive geology, skilled workforce, and robust infrastructure as an island nation. Moreover, the North Sea presents ample storage capacity for up to 78 billion tonnes of CO2.
This initiative represents the latest stride in advancing CCUS technologies, which aim to sequester 20-30 million tonnes of CO2 annually by 2030 and create 50,000 jobs by the same year, backed by a substantial £20 billion investment. Simultaneously, the government is facilitating the expansion of the HyNet Cluster in the North-West and Wales, inviting more companies to join and contribute to the region's growth, thereby fostering additional employment opportunities and investment.
Ruth Herbert, CEO, Carbon Capture and Storage Association said: "We welcome the CCUS Vision published today, setting out a long-term strategy for the UK’s CCUS industry to be able to store over 50Mt a year by 2035 to support the decarbonisation of domestic industries and take advantage of export opportunities. It is great to see CO2 transport by ship, road and rail will be enabled from 2025 onwards, which will also support longer-term cross-border CO2 transport solutions."
Protea’s atmosFIR FTIR gas analyser has proven a valuable tool in research into the effective storage of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) in the North Sea. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) could be key in the reduction in Carbon Dioxide (CO2) from industrial processes. Protea’s range of gas analysers have been used both in research into emerging technologies for CCS, but will also play an important role in the regulatory emissions monitoring from installations of CCS.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #carbon #capture
Read More29th January 2024 - China Aims To Build More Than Half The World's Cleaner-fuel Ships By 2025
China has outlined an ambitious target to manufacture over half of the world's cleaner-fuel-powered ships by 2025, as revealed in guidelines released by the industry ministry on Thursday. Although the guidelines did not specify the exact number of ships involved, they emphasised China's commitment to constructing more vessels propelled by lower-carbon fuels like methanol and liquefied natural gas. This initiative aligns with Beijing's broader aim to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060.

The document issued by the Chinese Ministry of Industry and Information Technology emphasises the need to implement innovation in ship engines, enhance the efficiency of traditional fuel and liquefied natural gas (LNG) marine engines, and progressively increase the widespread use of LNG in marine engines. Key enterprises have already made strides in reducing pollution and carbon emissions, with comprehensive energy consumption decreasing by 13.5% from 2020 levels, according to the guidelines. The environmental transformation of the shipping industry is slated for completion by 2030.
In 2023, China's shipyards constructed more than 50% of the world's ships. However, the shipbuilding landscape is on the brink of a significant shift, with fleet owners transitioning from oil-powered vessels to those utilising cleaner fuels in pursuit of the International Maritime Organisation's emission-free target by around 2050. With approval from a number of classification societies, backed up by MCERTS emissions and EX zone approvals, Protea’s Marine Emissions analysers meet the legislative requirements.
Beyond the target for manufacturing cleaner-fuel ships, China also intends to expedite research and design efforts for new ship types powered by liquefied ammonia, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. A unit of China State Shipbuilding Co. has already secured over $1 billion in contracts to construct methanol container ships for A.P. Moller-Maersk A/S, as reported recently.
This goal aligns with Beijing's broader strategy to future-proof its extensive industrial complex by focusing on sectors poised to gain prominence in the global effort to reduce emissions over the coming decades. China already holds a dominant position in the global production of solar panels, batteries, and electric vehicles.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More23rd January 2024 - Could Shipping Journeys Become Longer Due To Geopolitics?
Global shipping offers several pinch points or potential bottlenecks spread across the world's seas and oceans. There is potential for geopolitics to interrupt these recognised routes making journeys longer in both time and nautical distance. This in turn would have a major impact on not just cost, but also marine and shipping emissions.

As tankers, car-carriers, cruise ships and various merchant vessels navigate the Malacca Strait, the presence of unlit fishing boats weaving through shipping lanes at night makes it one of the world's most challenging sea areas to transit, even in times of peace. In the event of a major war in Asia, these challenges could escalate significantly, with hundreds of vessels hastily leaving international waters in the middle of the Strait, seeking potential safety within the national territorial waters of nearby neutral nations.
The Strait, positioned between Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Singapore, serves as the entry point from the Indian Ocean into the South China Sea, acting as a crucial maritime choke point for the transportation of goods manufactured in Asia to the rest of the world. It also plays a vital role in carrying a substantial portion of Asia's oil and gas, including three-quarters of China's supply.
Currently, the immediate threat to shipping in the region is relatively limited, though there are some areas of concern where shipping companies are taking action such especially around the Gulf of Aden, where Houthi militants have targeted multiple vessels since the start of the conflict across Gaza and Israel which is ongoing. In the Gulf of Aden, these attacks, along with attempted and successful hijackings by small boats, represent the most significant disruption to maritime trade since the peak of the Somali piracy crisis in 2011.
We also have the Black Sea conflict with Ukraine and Russia which is accessed via the Bosporus Strait. The potential for further conflict or geopolitical events globally is open to change very quickly with global powers seeking influence, territory and resources. As the word becomes smaller shipping distances could actually get longer. This would impact shipping and marine emissions significantly. Virtually all ships use liquid fossil fuels as the main energy source. Fuel grades range from distillate to residual. Distillate 'gas oil' contains little sulphur and is of low viscosity so needs no heating for combustion. Residual 'heavy fuel oil' is black in appearance, contains on average 2.7% sulphur and needs heating to over 120°C for combustion.
Recognised shipping routes include the following listed below:
- Strait of Hormuz between Oman and Iran at the entrance to the Persian Gulf
- Bab-el-Mandeb passage from the Arabian Sea to the Red Sea (Yemen and Socotra)
- Strait of Malacca and the Singapore Strait between Malaysia and Sumatra (Indonesia)
- Panama Canal and the Panama Pipeline connecting the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans
- Suez Canal and the Sumed Pipeline connecting the Red Sea and Mediterranean Sea (Egypt)
- Strait of Gibraltar along the Atlantic Ocean entering the Mediterranean Sea (Spain, Gibraltar and Morocco)
- Strait of Dover or English Channel separating the Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea (England and France)
- Strait of Magellan & Drake Passage (Chile)
- Beagle Channel (Chile and Argentina)
- The Cape of Good Hope (South Africa)
- Bering Strait (United States of America and Russia)
- Bosporus Strait linking the Black Sea (and oil coming from the Caspian Sea region) to the Mediterranean Sea (Turkey)
- Dardanelles Strait connecting the Sea of Marmara with the Aegean Sea (Turkey)
- Strait of Tartary along Sea of Japan and Sea of Okhotsk (Russia)
The impact of some of these choke points becoming closed would have a major impact on the IMO GHG strategy which states; The IMO remains committed to reducing GHG emissions from international shipping and, as a matter of urgency, aims to phase them out as soon as possible, while promoting, in the context of this Levels of ambition directing the 2023 IMO GHG Strategy are as follows:
- Carbon intensity of the ship to decline through further improvement of the energy efficiency for new ships - to review with the aim of strengthening the energy efficiency design requirements for ships.
- Carbon intensity of international shipping to decline - To reduce CO2 emissions per transport work, as an average across international shipping, by at least 40% by 2030, compared to 2008.
- Uptake of zero or near-zero GHG emission technologies, fuels and/or energy sources to increase - Uptake of zero or near-zero GHG emission technologies, fuels and/or energy sources to represent at least 5%, striving for 10%, of the energy used by international shipping by 2030.
- GHG emissions from international shipping to reach net zero - To peak GHG emissions from international shipping as soon as possible and to reach net-zero GHG emissions by or around, i.e. close to 2050, taking into account different national circumstances, whilst pursuing efforts towards phasing them out as called for in the Vision consistent with the long-term temperature goal set out in Article 2 of the Paris Agreement.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More15th January 2024 - LNG Fuel Bunkering Increases With New Emissions Rules
In just under 18 months, the Mediterranean is poised to implement stricter limits on maritime emissions. Market observers in the region are already anticipating that liquefied natural gas (LNG) will emerge as a favourable alternative to traditional and more polluting marine fuels.
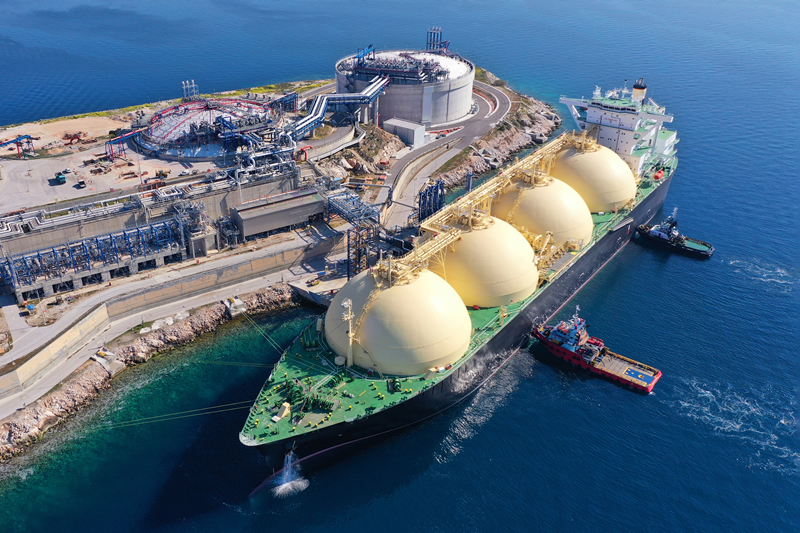

Late last year, the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) adopted new regulations designating the Mediterranean as an Emission Control Area (ECA) effective May 1, 2025. This move involves a reduction in the sulfur cap of marine fuels, earning praise from environmentalists but potentially leading to increased costs for traditional bunkering. According to maritime classification society DNV, compared to heavy fuel oil, the use of LNG could result in up to an 80% reduction in nitrogen oxide emissions, nearly eliminating sulfur oxide emissions and particulate matter.
With the Mediterranean transitioning into an ECA, Jason Stefanatos, Global Decarbonisation Director at DNV, anticipates heightened interest in LNG, noting changes in business cases for vessels compared to the past. This development aligns with the global expansion of LNG-fueled fleets, with LNG-fueled vessels holding the largest share in the alternative-fueled ship order book, as reported by DNV. Currently, there are 438 LNG ships in operation, with 97 on order. DNV predicts a significant increase, reaching 505 LNG ships in 2026.
While the majority of the existing 978 LNG-fueled ships operate globally, a noteworthy 19% exclusively operate in Europe, followed by Asia at 8% and America at 5%. In the Mediterranean, the port of Barcelona, recognised as a bunkering hub, witnessed LNG bunkering operations accounting for nearly 11% of total bunkering operations in 2021. Industry coalition group SEA-LNG data indicates approximately 16 LNG bunkering locations in the Mediterranean region.
The DNV observes a steady increase in LNG bunkering activities in the Mediterranean over the past year and anticipates further growth. Drawing parallels to the North Sea's ECA designation in 2015, suggesting a similar trend may unfold in the Mediterranean, despite recognising distinct conditions.
The ECA designation would render very low sulfur fuel (VSLFO) non-compliant as a shipping fuel in the Mediterranean. While marine gasoil (MGO) remains permissible under the new legislation, LNG is expected to be more competitively priced, according to trading sources. Regardless of fuel choice there needs to be an effective Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS). With our marine analysers installed on vessels all over the world, the ongoing service and support for the equipment is satisfied by our dedicated network working in and around major ports and installation locations.
The need to demonstrate environmental responsibility is key for today’s marine and offshore industries.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More8th January 2024 - Research Article Offers Impact Of Alternative Shipping Fuels
A recent study published in the online journal "Environments" assessed the environmental impact of eight alternative fuels in international shipping, comparing marginal and average emissions. The primary focus of the study was driven by global warming and environmental concerns, aiming to identify the most sustainable alternative among candidate fuels.

The research utilised life-cycle analysis (LCA) to evaluate the environmental impact of various fuels, emphasizing the importance of considering marginal emissions in predicting the effects of large-scale fuel transitions. The study compared marginal and average emissions for eight marine fuels, revealing non-intuitive results regarding biofuels. Despite significantly lower average emissions (19-73 kg CO2/MJ) compared to conventionally used fuel oils (169-175 kg CO2/MJ), biofuels exhibited equally or higher marginal greenhouse gas emissions (162-270 kg CO2/MJ propulsion). This discrepancy was attributed to the limited availability of climate-efficient biofuels, indicating that a large-scale shift to biofuels would not presently lead to substantial reductions in the shipping industry's climate impact. The study highlighted the following marine fuels:
- High-sulfur fuel oil
- Very-low-sulfur fuel oil
- Marine gas oil
- Liquified natural gas
- Biomethane
- Biomethanol
- Fossil methanol
- Hydro-treated vegetable oil
International shipping has grown significantly during the past three decades because of the globalisation of markets and the lower fuel consumption of shipping compared to other transportation options. Nowadays, more than 80% of all globally traded goods are transported via international shipping.
The study's findings indicate a potential risk due to the current higher demand for bio-based fuels compared to their supply. This situation raises concerns about the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of marginal biofuels, which are considerably higher than their average emissions. This consideration is crucial before embarking on a rapid, large-scale fuel switch, particularly in industries like shipping. Although biofuels have the potential to significantly reduce GHG emissions in shipping, achieving this requires a substantial reduction in marginal emissions from biofuel production, possibly through the use of more sustainable feedstocks.
The comprehensive Life Cycle Analysis (cLCA) suggests that substituting fossil oil products (VLSFO, MGO, and HSFO) with biofuels or LNG currently yields only limited positive climate impacts (e.g., with biomethane) or is directly counterproductive (as seen with biomethanol and HVO sourced from dedicated crops instead of residues). To meet the climate goals of the maritime industry, additional measures are essential. These include more climate-efficient biofuel production, the development of more energy-efficient ships, a reduction in shipping volumes, and the implementation of carbon capture techniques. In the long term, the adoption of climate-neutral electrochemical fuels, such as hydrogen and ammonia, is deemed crucial for achieving sustainability objectives. The paper reports marginal emissions values of:
- 169-220 kg CO2/MJ for Biofuels
- 162 kg CO2/MJ for Biomethane
- 180 kg CO2/MJ for Liquified natural gas
- 148-262 kg CO2/MJ Conventional bunkers
The full report can be found online at MDPI.com being created by Gustav Krantz, Christian Moretti, Miguel Brandão, Mikael Hedenqvist and Fritjof Nilsson and is available here https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3298/10/9/155.
The need to demonstrate environmental responsibility is key for today’s marine and offshore industries. Charterers and the public demand high standards of performance and reliability. Fuels and exhaust gas emissions are also the subject of international, regional and national controls. The most significant is IMO MARPOL Annex VI – Regulations for the Prevention of Air Pollution from Ships, which also applies to mobile offshore drilling units and other oil industry platforms.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More4th January 2024 - Ensure Your Fleet Adheres To EU ETS Standards
With the imminent inclusion of maritime emissions in the EU's Emission Trading System (ETS) from January 2024, the industry finds itself continuously adapting, having spent much of 2023 striving to meet the International Maritime Organisation's (IMO) CO2 requirements.

Starting January 1, 2024, all vessels exceeding 5,000 gross register tons (GRT) engaged in trade at EU ports will see their CO2 emissions contribute to the overall ETS cap, irrespective of their flag. The system encompasses 100% of emissions from intra-EU voyages and 50% of emissions related to loading or discharging outside the EU.
Consequently, shipping companies will need to acquire and surrender EU ETS emissions allowances (EUAs) for each tonne of reported CO2 (or CO2 equivalent) emissions. To facilitate a smoother transition, the initial phase-in period allows companies to surrender allowances for a portion of their emissions as outlined below:
- 2025: 40% of emissions reported in 2024
- 2026: 70% of emissions reported in 2025
- 2027 onwards: 100% of reported emissions
Operators are required to submit an annual emissions report, with data for a given year verified by an accredited verifier before March 31 of the following year. Once verified, operators must surrender the equivalent number of allowances by April 30 of that year.
EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS)
The EU ETS stands as a crucial element in the EU's strategy to combat climate change, serving as a key tool for cost-effectively reducing greenhouse gas emissions. As the world's first major carbon market, it remains the largest of its kind.
The Protea 2000 emissions monitoring system is approved for the analysis of exhaust gases from the engines and boilers of ships and offshore rigs. Robust and with proven reliability, up to six gases can be measured including SO2, CO2 and NOx. The Protea 2000 emissions monitoring system comprises up to 8 exhaust mounted analysers, each with automatic verification facilities. Emissions data from the entire system is securely managed and displayed at a dedicated Classification Society approved panel PC, with outputs to networks, control systems, and reporting facilities. Contact our expert sales and support team for more information on how you can manage and control shipping and marine emissions in line with the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS).
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More2023
20th December 2023 - Season's Greetings From Marine Emissions
Season’s greetings from all of us and we wish you a Merry Christmas and a Happy New Year. We are taking orders throughout December and will be operational offering support, products and services as normal. Our last working day before Christmas will be Friday 22nd December 2023, reopening on Tuesday 2nd January 2024. We would like to thank everyone involved with our company including our employees, customers, suppliers and people who have been involved in projects and related activities.

As a UK manufacturer of analysers using a range of technologies – IR, UV, FTIR, TDL and QMS – Protea can support the entire system from the analyser, software optimisation, systems automation and on-going service and support. Our core areas of expertise are for stack and marine emissions, where we are leading in the development of controlling global environmental emissions, pollution reduction and process improvement. Protea’s analysers can be applied to fixed applications, often in demanding environments, or portable monitoring tools to support environmental test laboratories and researchers.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More18th December 2023 - EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) Becomes Effective January 1st 2024
The EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) stands as a cornerstone of the European Union's strategy to combat climate change, serving as a pivotal tool to cost-effectively reduce greenhouse gas emissions. It was initially introduced in 2005 and is the world's largest carbon market, representing a significant global initiative to address climate change by reducing emissions through a cap-and-trade mechanism.

A recent expansion of the EU ETS occurred with the enactment of new legislation on June 5, 2023, extending its reach to the maritime transport sector, which was previously excluded. These new rules, set to come into effect on January 1, 2024, will have a substantial impact on the European shipping industry.
The EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) was originally established in 2005 as a market-driven approach to combat greenhouse gas emissions within the European Union. While it initially focused on energy-intensive sectors such as power generation and manufacturing, recent developments have incorporated shipping into the EU ETS. Key features of the EU Emissions Trading System:
• Imposes financial responsibility on polluters for their greenhouse gas emissions.
• Facilitates the reduction of emissions and generates revenue to support the EU's transition to a more environmentally friendly economy.
• Operates across all EU member states, as well as Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway (EEA-EFTA states).
• Encompasses emissions from approximately 10,000 facilities in the energy and manufacturing sectors, as well as aircraft operators within and departing from the EU, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom, amounting to around 40% of the EU's emissions.
• Will extend its coverage to emissions from maritime transport starting in 2024.
Through the EU ETS, the European Union has created a market-based mechanism that assigns a price to CO2 emissions, creating incentives for emissions reduction in the most cost-effective manner. The primary aim is to progressively decrease emissions in power generation and energy-intensive industries, such as iron production, aluminium manufacturing, cement production, glass manufacturing, cardboard production, and chemical industries. This system has contributed to reducing emissions from these sectors by approximately 35% between 2005 and 2021.
In December 2022, political negotiators reached a provisional agreement to extend the EU ETS to include the shipping industry. This agreement was subsequently ratified and published in the Official Journal of the European Union on May 16, 2023, officially bringing shipping activities within the scope of the ETS. As of 2024, ship operators will be obligated to monitor, report, and surrender allowances for each ton of CO2e they emit.
The UK Emission Trading Scheme (ETS) operates as a cap-and-trade system, restricting the overall level of greenhouse gas emissions. It establishes a carbon market with a price signal to encourage decarbonisation efforts. The UK ETS came into effect on January 1, 2021, replacing the UK's participation in the EU ETS, which was originally established in 2005.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More11th December 2023 - 5% Scalable Zero Emission Fuel (SZEF) Use By 2030 Progress Report
A recent analysis has revealed that the world is falling short of its goal to have zero-emission fuels represent 5% of international shipping fuels by 2030. This poses a significant challenge to the shipping industry's 2050 decarbonisation objective. Earlier efforts had proposed a crucial milestone known as the "2030 Breakthrough," aiming to achieve at least 5% utilisation of scalable zero emission fuel (SZEF) by 2030. This milestone was endorsed and further refined in the 2023 International Maritime Organization (IMO) GHG Strategy, which now aspires to reach "5%, with an aspiration for 10% utilisation of zero and near-zero GHG emission fuels by 2030" as a portion of the overall energy consumption in international shipping.

The assessment was introduced at the recent annual summit of the Global Maritime Forum. This disclosed that the current production of scalable zero-emissions fuel (SZEF) in the pipeline would only satisfy a quarter of the required fuel by 2030. The Global Maritime Forum, a non-profit international organisation serving the global maritime sector, brings together leaders from the maritime industry, policymakers, experts, NGO's, and other influential decision-makers.
Furthermore, the progress in delivering zero-emission vessels is also falling short of expectations. By the end of 2022, there were 24 ships capable of operating on SZEF, primarily methanol, with an additional 144 on order. However, the report, conducted by the UMAS consultancy, which includes experts from the University College London Energy Institute, finds that the current orders are only one-fifth of what is necessary to meet mid-term targets.
Kathryn Palmer, the shipping lead of the UN COP Climate Champions, emphasised that the current progress is insufficient in terms of scale and pace, stating, "We need to see demand and supply actors collaborate to implement specific solutions." It is worth noting that global shipping is responsible for approximately 3% of the world's greenhouse gas emissions stemming from human activities. In response to this, the International Maritime Organisation revised its greenhouse gas strategy this year, endorsing the 5% target while also encouraging the industry to strive for achieving 10% zero-emission energy in international shipping fuels by the end of the decade.
Meeting the demand for 5 to 10% of shipping fuel in 2030 would require about 5.3 million metric tons of hydrogen, 29.8 million metric tons of ammonia, or 28.1 million metric tons of methanol. It is estimated that the industry will need to invest approximately $40 billion annually in SZEF bunkering and production.
The Getting to Zero Coalition, a collaborative effort between the Global Maritime Forum and the World Economic Forum, was initiated at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in New York in 2019. This coalition brings together around 200 stakeholders from the shipping and fuels value chain. Its primary objective is to have economically viable Zero Emission Vessels operating on deep sea trade routes by 2030, supported by the necessary infrastructure for scalable zero-carbon energy sources, including production, distribution, storage, and bunkering.
The ultimate vision of the Getting to Zero Coalition is to achieve complete decarbonization of global shipping by 2050. In 2021, the Call to Action initiative was developed, involving more than 150 industry leaders and organisations, to urge governments and the global shipping industry to commit to full decarbonization of international shipping by 2050.
The key conclusion of the Global Maritime Forum report was stated as "Overall progress to reach the 5% by 2030 SZEF goal can be considered to have remained partially on track from last year. The past 12 months have seen significant developments in terms of international commitments at the IMO, national policy developments, industry announcements, and technological developments. However, in order to reach the 5% goal, significant progress remains necessary, especially in terms of concrete national policies turning the IMO’s level of ambition into specific economic and technical measures. There is also a need to turn growing appetite for zero carbon freight into concrete demand on the orderbook for SZEF vessels which can send the right signals to SZEF suppliers. The strong technological progress observed in recent years must continue to be capitalised on to ensure sufficient supply of SZEF in 2030, both in terms of expanding the announced pipeline of production and ensuring a sufficient proportion of announced capacity passes the final investment decision stage."
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More5th December 2023 - Protea Exhibiting At Marintec 2023 In China
Protea have a booth at the Marintec 2023 China this week. Our booth number is N3C2A-07. Come and visit the global leader in Continuous Emissions and Periodic Emissions Monitoring Systems. Protea has been at the forefront of emissions monitoring systems for many years, as both a manufacturer and a user of stack emissions equipment. The event is running from Tuesday 5th December through to Friday 8th December 2023 at the Shanghai New International Expo Centre (SNIEC) in China.


#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More4th December 2023 - Marine Emissions Analysers P2000 In-Situ CEM In Focus
The Protea 2000 emissions monitoring system is approved for the analysis of exhaust gases from the engines and boilers of ships and offshore rigs. Robust and with proven reliability, up to six gases can be measured including SO2, CO2 and NOx.

The Protea 2000 emissions monitoring system comprises up to 8 exhaust mounted analysers, each with automatic verification facilities. Emissions data from the entire system is securely managed and displayed at a dedicated Classification Society approved panel PC, with outputs to networks, control systems, and reporting facilities.
The advanced Protea 2000 analyser utilises an in-situ (inside the exhaust) sample cell so avoiding the need to extract gas. Importantly this avoids the use of costly, high maintenance sample handling systems, and enables analysis of an unmodified, truly representative gas sample.
Exhaust gases from the combustion of residual and distillate fuels can be analysed, so that compliance can be confirmed in port, in Emissions Control Areas and in international waters. The Protea 2000 includes highly effective sintered filters that prevent the ingress of particulate matter into the sample gas cell and a heater to prevent condensation and deposits where the exhaust is below its dew point. Construction materials are ideally suited to the marine environment.The analyser will automatically range change (capable of multiple ranges) in the event of a non-operational Exhaust Gas Cleaning Systems. This also allows monitoring of higher levels of SO2 when the vessel is outside an ECA area but still subject to the higher global emission level.
The measurement range of Protea 2000 analysers is such that compliance can be confirmed even when regulated emissions are at a very low level. Emissions after an exhaust gas scrubber, that are the equivalent of 0.1% sulphur fuel, are readily measured. Protea 2000 analyser solutions can be fitted to all sizes of exhaust and ATEX/IEC approved options are available for use in the hazardous areas typically found in offshore and tanker applications.
The Protea marine CEMS has been designed for minimal intervention with a high availability, in addition the systems operate a comprehensive diagnostic routine. Enhanced Customer Support - Recent upgrades include our new Automatic Field Data Collection (AFDC) module that uniquely allows the ship's engineer to automatically run a routine collecting all the relevant data from the analyser under the various states of operation. This can then be e-mailed to Protea’s customer support team who will analyse and determine any remedial action required. Protea will upgrade existing Procal supplied CEMS saving the ships operator time and expenses and increasing emission data availability. For more information on the P2000 shipping and Marine emissions analyser please contact us at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/contact.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More27th November 2023 - New Study Reveals High NOx Emissions From Tier II Vs Tier I Engines
A recent research paper published by the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) has brought attention to the concerning levels of nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions originating from ships. This research paper examined 615 real-world NOx emission samples from 545 ships plying the waters between the North Sea and the Baltic Sea in 2019. The measurements were collected through sensors attached to helicopters, which flew into the exhaust plumes of the vessels. The data encompassed a variety of engine age categories (tiers).

Surprisingly, the results revealed that newer Tier II engines exhibited higher NOx emission rates than their older Tier I counterparts. Additionally, the study found no significant distinction in emissions between unregulated Tier 0 engines and Tier II engines.
Of particular concern is the discovery that the highest average NOx emission rates were observed when main engines operated at loads below 25%, averaging 12 grams per kilowatt-hour (g/kWh) across all vessel types and engine tiers. As engine loads increased, emission rates decreased, with mean rates dropping to 8.1 g/kWh at loads exceeding 75%. This finding challenges the established assumptions regarding NOx test cycles for marine engines, highlighting that these engines tend to operate at lower engine loads rather than higher engine loads, as previously believed.
The study suggests that current NOx regulations may necessitate revision to effectively combat air pollution. Its authors urge the International Maritime Organization to consider implementing not-to-exceed (NTE) standards for both new and existing ships, with a particular focus on operations at low loads. Furthermore, the study underscores the importance of including a test point below the 25% load threshold in future regulations.
These findings underscore the imperative need for more robust measures to address ship emissions and safeguard air quality in coastal regions. Effectively dealing with NOx pollution from ships is essential in the ongoing endeavor to combat climate change and promote sustainable maritime practices.
Tier 1-3 Emission Standards
The nonroad engine regulations of 1998 were structured as a three-tiered progression. Each tier involved a phased implementation (based on horsepower rating) over several years. Tier 1 standards were phased in from 1996 to 2000. The more stringent Tier 2 standards became effective from 2001 to 2006, with even stricter Tier 3 standards being phased in from 2006 to 2008 (Tier 3 standards applied only to engines ranging from 37-560 kW).
Whilst the pace of change may have created uncertainty across all Tier engine classifications (Tiers I, II, & III) pushing the boundaries for some technologies, the Protea 2000 emissions monitoring system has been proven in long-term service onboard ship as a robust and reliable method of confirming compliance with emissions regulations.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More20th November 2023 - Future Fuel Types For Shipping & Cargo Vessels Being Commissioned
There are an estimated 60,000 cargo ships worldwide, and this number is continually changing as new vessels are constructed and older ones are retired. Cargo ships can be categorised based on their design, size, and the type of cargo they transport. Fuel type is also going to a categorisation that will become more important moving forward.

Ships powered by oil and diesel face challenges in transitioning to green fuels. To achieve a greener fleet, the approximately 60,000 ships in operation worldwide will need significant upgrades or replacements by 2050. Retrofitting existing vessels to run on methanol and ammonia is possible but costly, with expenses ranging from $5 million to $15 million per ship, irrespective of their size. For older vessels, this investment may not be economically viable given their remaining service life.
Three future fuel options for shipping vessels are emerging being methanol, ammonia, and hydrogen. Container shipping lines like Maersk, Evergreen, CMA CGM, and COSCO are ordering ships capable of burning both methanol and methane. Maersk, for instance, received its first dual-fuel vessel that operates on green methanol and fuel oil and completed a voyage from South Korea to Denmark with cargo in August 2023.
The world's first ammonia-fuel ready vessel, the ABS-classed Suezmax tanker "Kriti Future", has been delivered to new owners in Greece. MSC Cruises has also ordered two hydrogen-ready vessels for 2028. While these orders inspire optimism about decarbonisation, they represent a small fraction of the global fleet.
Transitioning to green fuels will necessitate the development of pipelines, storage tanks, and port refueling stations. In particular, green hydrogen, a crucial component for other green fuels, demands substantial investment for storage in specialized containers at temperatures around -253°C. The shipping industry has yet to reach a consensus on its fuel of the future, and it is likely that multiple options will be necessary due to the limited supply of renewable energy.
The positive aspect is that decarbonizing international shipping will have broader benefits beyond the industry itself. It will accelerate investments in renewable energy and offer sun-rich emerging economies the opportunity to produce cost-effective green hydrogen.
The shift of the shipping industry from bunker fuel to cleaner fuels is an essential component of achieving net zero greenhouse gas emissions targets by 2050. Achieving net zero carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions by 2050 aligns with efforts to limit the long-term global temperature increase to 1.5°C. This requires a profound transformation in how we generate, transport, and consume energy.
Protea will play a critical role in this transition, particularly in shipping and marine emissions monitoring. The Protea 2000 In-Situ Infra-red gas analyser, in conjunction with a Protea Control Unit, forms the foundation of a Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS).
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More13th November 2023 - Long Term Emissions Monitoring Compliance With Protea
Despite recent efforts by the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) to enforce, strengthen and tighten requirements for reducing CO2 emissions, both the United Nations and the European Union are yet to mandate the use of precise and exact real time data. Currently the process can include unreliable calculations when it comes to the logging of marine and shipping emissions.

Over 95 percent of modern vessels currently utilise internal-combustion engines (ICE's) fueled by a range of petroleum products, including heavy fuel oil (HFO), marine gas oil (MGO), and marine diesel oil (MDO). Technology is available to provide a more accurate understanding when discussing ship emissions of Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Nitrogen Oxides (NOx), Sulfur Oxides (SOx) content in fossil fuel exhaust gases, and harmful particulate matter. This practice has been established on land for many years, but the need to demonstrate environmental responsibility is key for today’s marine and offshore industries.
Advanced equipment from Protea is available for precise measurements of CO2 and harmful particle emissions from ships. The technology is readily accessible, and it primarily involves shipping companies making modest investments in this equipment to demonstrate compliance with emission limits. Currently, shipping companies rely on calculating their emissions, but these calculations are known to be imprecise and can underestimate emissions. The Protea 2000 emissions monitoring system has been proven in long-term service onboard ships as a robust and reliable method of confirming compliance with emissions regulations.
Shipping firms frequently note the widespread incorporation of efficiency measures, yet only a limited number have initiated efforts to embrace novel fuels and alternative power systems. In the coming years, shipping is likely to migrate to a mixture of fuel types, blended with new technologies rather than a single fuel type. This will introduce challenges in accurately calculating emissions, particularly with the use of pilot fuels in the ignition process, which can lead to calculation inaccuracies but can be readily measured. Additionally, upcoming fuels like biofuel can be lacking in uniform composition, making accurate calculation harder and more difficult. They can be accurately measured to provide an exact representation.
If shipping companies do not voluntarily adopt this equipment on cargo ships, cruise ships, ferries, and other vessel types, policymakers should consider the necessity of requiring documented emissions rather than relying on calculated estimates. Replacing variable unreliable calculations with solid real time data, will significantly bolster the industry's credibility and contribute to climate benefits. While decision-making in international forums may move slowly, it highlights the need to take the initiative across all sectors involved with shipping and marine emissions.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More6th November 2023 - European Maritime Industry Gears Up For Emission Fees
Beginning in January 2023, the shipping sector became a part of the European Union's Emissions Trading System, leading to substantial emission-related costs for ships transporting various goods in and out of the EU. This marks the world's first extensive carbon charge initiative for international shipping and aligns with the EU's environmental agenda to combat climate change. However, while these fees are significant, they may not be potent enough to trigger an immediate transition to cleaner marine fuels.

The maritime industry will integrate with the EU's Emissions Trading System, imposing carbon emission expenses on large vessels, potentially running into hundreds of millions of dollars for some major freight companies.
To illustrate how this system operates: A ship transporting 5,000 standard-sized containers between the EU and Asia in a year generates around 40,000 tons of CO2. Since a portion of these emissions occurs outside of Europe, only half of them require coverage. Consequently, costs will be incurred for 20,000 tons of CO2, along with an additional 2,500 tons while the ship is in European ports. In the first year, 40% of qualifying emissions will be subject to charges. Using a carbon price of 90 euros per ton, this would amount to €810,000.
By 2025, when 70% of emissions must be accounted for, these costs will rise to 1.4 million, and by 2026, when all emissions are chargeable (assuming a 90-euro carbon price), they will reach 2 million. Additionally, the EU will enforce the FuelEU Maritime regulation in 2025, which is designed to encourage shippers to adopt cleaner fuels. This regulation establishes maximum limits on the annual greenhouse gas intensity of energy used by vessels, with increasingly stringent targets over time.
Shipping and Marine emissions are very much in the spotlight and will be at the forefront of all involved with the sector from global manufacturers, ship builders, cargo handling, operators and governments. This will make emissions monitoring even more vital as a key element across aspects of reporting of greenhouse gas emissions. The Protea range of systems available are designed to provide accurate, ongoing and real time measurement of all emissions relating to a vessel's propulsion and power generation system.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More30th October 2023 - Shipping Is Targeting Zero Emissions With A New Industry Coalition
The maritime industry is making significant strides towards achieving zero emissions. The Zero Emission Maritime Buyers Alliance (ZEMBA), a non-profit organization consisting of major retail brands, has initiated a Request for Proposals (RfP) for the transportation of 600,000 twenty-foot containers (TEUs) over a three-year period using ocean vessels powered by zero-emission fuels.

ZEMBA's inaugural tender has garnered support from over 20 members, including industry giants like Amazon, IKEA, Nike, and others. Shipping is among the challenging sectors where decarbonization is imperative, and ZEMBA's coalition is introducing innovative procurement methods with the backing of leading global companies.
Over the course of three years, ZEMBA aims to assist its member companies in reducing nearly 1 million tons of carbon emissions. The ZEMBA RfP is designed to solicit bids for shipping services from individual carriers or consortiums that achieve a minimum 90% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional fossil fuels throughout their lifecycle. The choice of fuel will also address safety and land use concerns, particularly those related to biogenic substances.
Through this initiative, ZEMBA expects to help its member companies reduce almost 1 million metric tonnes of carbon emissions, equivalent to removing 215,000 cars from the road. The delivery of shipping services powered by cleaner fuels is anticipated by 2025.
Given the global reach of the maritime shipping sector and the multitude of companies relying on ocean transport, cargo owners cannot drive the demand for zero-emission solutions on their own. Initiatives like ZEMBA and the First Movers Coalition within the maritime decarbonization space allow cargo owners of various sizes to accelerate action and benefit from economies of scale.
ZEMBA stands out as the sole buyers' alliance in the maritime sector dedicated to expediting the commercial deployment of zero-emission shipping. By committing to ZE solutions through advanced market agreements, ZEMBA members will gain early access to zero-emission shipping services not currently available, instilling confidence among private sector stakeholders and policymakers that there is sufficient demand for zero-emission solutions to drive additional investment and regulatory action at the global, regional, and domestic levels.
The Zero Emission Maritime Buyers Alliance (ZEMBA) represents a groundbreaking consortium in the maritime industry, committed to hastening the adoption of zero-emission shipping, fostering economies of scale, and empowering cargo owners to achieve emissions reductions that surpass what any single freight buyer could achieve independently. Through consolidated demand and a competitive forward procurement process, ZEMBA members will access zero-emission shipping services ahead of the curve and encourage other participants in the maritime value chain to invest further, knowing that substantial demand for zero-emission solutions is present.
Protea has been at the forefront of emissions monitoring systems for 20 years, as both a manufacturer and a user of stack emissions equipment. We fully embrace industry leading shipping and marine emissions initiatives.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More24th October 2023 - Kormarine 2023 In Pictures
Protea are exhibiting at Kormarine 2023. The exhibition is proving to be a great success being held in Bexco (Busan Exhibition & Convention Center) Busan between 24th October 2023 to 27th October 2023. Protea are exhibiting at POD 12 on the UK Pavilion, side 1C61 offering the latest in Continuous Emissions and Periodic Emissions Monitoring Systems.





Korea is holding its title for being one of the leading countries in the shipbuilding industry. According to Clarksons Research, 62% of high value-added vessel orders in the first half of 2022 occurred in Korean shipyards. Since its first event in 1980, KORMARINE has written the history of the shipbuilding and maritime industries with our exhibitors. And now, we are sailing with global leading companies. Protea has been at the forefront of emissions monitoring systems for 20 years, as both a manufacturer and a user of stack emissions equipment.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #kormarine2023
Read More23rd October 2023 - Distributor Service Training Event By Protea
In October Protea held a Service Training Event for some of our Distributors Service Engineers to learn more about our products. The attendees visited Protea Peterborough and Middlewich within the week and studied topics such as Servicing of the P2000/AtmosIR/FTIR.





#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More16th October 2023 - Protea Exhibiting At Kormarine 2023 In South Korea
Protea are exhibiting at Kormarine 2023. The exhibition will be held in Bexco (Busan Exhibition & Convention Center) Busan on 24th October 2023 to 27th October 2023, showing the very best of the Korean ship building and construction industry covering machinery, engineering and boat construction. Protea will be exhibiting at POD 12 on the UK Pavilion, side 1C61 offering the latest in Continuous Emissions and Periodic Emissions Monitoring Systems.

Korea is holding its title for being one of the leading countries in the shipbuilding industry. According to Clarksons Research, 62% of high value-added vessel orders in the first half of 2022 occurred in Korean shipyards. Since its first event in 1980, KORMARINE has written the history of the shipbuilding and maritime industries with our exhibitors. And now, we are sailing with global leading companies. Protea has been at the forefront of emissions monitoring systems for 20 years, as both a manufacture and a user of stack emissions equipment.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #kormarine2023
Read More11th October 2023 - Shipping Emissions 20% Higher Than 10 Years Ago
According to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development's "Review of Maritime Transport 2023," international shipping's greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2023 were 20% higher than they were a decade earlier. Overall, the shipping industry accounts for over 80% of global trade volume and nearly 3% of worldwide greenhouse gas emissions. Despite a dip of 0.4% in global maritime shipping volumes in 2022 due to disruptions caused by COVID-19, the report anticipates a 2.4% growth in 2023.

Containerized trade, which saw a 3.7% decline in 2022, is expected to rebound with a 1.2% growth in 2023, followed by further expansion of 3% between 2024 and 2028. In contrast, oil and gas trade volumes exhibited strong growth in 2022, and tanker freight rates experienced a significant upturn driven by geopolitical events. Rebeca Grynspan, Secretary-General of UNCTAD, emphasised the urgency of decarbonizing maritime transport while ensuring economic growth. Striking a balance between environmental sustainability, regulatory compliance, and economic imperatives is essential for a prosperous, equitable, and resilient future for the industry.
Ship owners are grappling with the challenge of renewing their fleets amid uncertainty regarding technology and regulatory frameworks. Port terminals face similar dilemmas, particularly in making investment decisions. As the transition to alternative fuels is still in its early stages, a substantial 98.8% of the global fleet continues to rely on conventional fuels such as heavy fuel oil, light fuel oil, and diesel/gas oil.
Only 1.2% of vessels use alternative fuels, primarily liquified natural gas (LNG), with lesser adoption of battery/hybrid, liquified petroleum gas (LPG), and methanol. However, progress is underway, as 21% of vessels currently on order are designed to operate on alternative fuels, with LNG being the most prominent choice.
Breaking down the vessels on order and under construction by fuel type, LNG constitutes 52.1%, battery/hybrid accounts for 39.9%, LPG represents 5.5%, methanol makes up 3.4%, and hydrogen is at 0.3%. In terms of active tonnage, nearly 6% of the active fleet runs on alternative fuels, mainly LNG, and one-third of the tonnage on order is designed for alternative fuel use. It's worth noting that while LNG has a lower carbon footprint than heavy fuel oils, it remains a fossil fuel and faces challenges like methane emissions. Batteries are better suited for vessels operating shorter distances, according to the report.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More3rd October 2023 - UNCTAD Report Calls For Decarbonised Shipping
The United Nations has issued a call for swift decarbonisation of the shipping industry, cautioning that the cost could exceed $100 billion annually, as emissions from the sector continue to rise. The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) has released its "Review of Maritime Transport 2023" ahead of World Maritime Day on 28 September 2023, advocating for an equitable and just transition towards a decarbonised shipping industry.

UNCTAD underscores the urgent need for cleaner fuel options, digital solutions, and a fair transition to address the ongoing carbon emissions and regulatory uncertainties in the shipping sector. With the shipping industry responsible for more than 80% of the world's trade volume and nearly 3% of global greenhouse gas emissions, which have surged by 20% in a mere decade, the situation demands immediate action.
Rebeca Grynspan, Secretary-General of UNCTAD, emphasizes, "Maritime transport must decarbonize without delay, while sustaining economic growth. Striking a balance between environmental sustainability, regulatory compliance, and economic imperatives is crucial for a prosperous, fair, and resilient future for maritime transport." UNCTAD also expresses concerns about the aging global shipping fleet; as of the beginning of 2023, commercial vessels were, on average, 22.2 years old, marking a two-year increase from a decade ago. Over half of the world's fleet is now over 15 years old, underlining the growing need for continuous emissions monitoring systems, in which Protea is a global leader.
In preparation for the United Nations climate conference (COP28) in November of this year, UNCTAD will advocate for a transition to cleaner fuels in the shipping industry, emphasizing the necessity of an environmentally effective, procedurally equitable, socially just, technologically inclusive, and globally equitable strategy.
UNCTAD, an intergovernmental organization within the United Nations Secretariat, champions the interests of developing countries in global trade. Established in 1964 by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA), it reports to both the UNGA and the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC). Comprising 195 member states, UNCTAD collaborates with non-governmental organisations worldwide, with its permanent secretariat headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
UNCTAD's primary goal is to formulate policies encompassing all facets of development, including trade, aid, transportation, finance, and technology. It was founded in response to concerns among developing nations that existing international institutions such as GATT (now replaced by the World Trade Organisation), the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the World Bank were ill-equipped to address the specific challenges of developing countries. UNCTAD was conceived as a platform where developing nations could discuss and tackle issues related to their economic development.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More27th September 2023 - Protea Distributor Sales Conference
Protea Distributor Sales Conference held at the Hyatt Regency Barcelona Tower, Barcelona, Spain. All key distributors attended to familiarise themselves with New / Upgraded Instruments and Software.

The training covered topics such as Protea FIR, FID, upgraded P2000, atmosIR and atmosFieldCal to maintain the existing installed base and new analysers. The Protea Team looks forward to meeting with you all again soon.




#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #cem2023
Read More26th September 2023 - CEM Barcelona 2023 In Pictures
Protea Exhibited at CEM Emissions Monitoring Barcelona 2023 and here we present our exhibition Stand and activity from the distributor sales conference which took place the day before the exhibition. The event was held on Wednesday 20th to Friday 22nd September 2023 in Barcelona, Spain. This CEM event was the place to go for emissions monitoring solutions. The CEM 2023 conference was held in Hyatt Regency Barcelona Tower, Barcelona, Spain.

In 2023 the CEM event was celebrating its 25th Anniversary, CEM first started in the United Kingdom in 1997 and has been held in The Netherlands, Denmark, France, Switzerland, Italy, The Czech Republic, Turkey, Portugal, India and Hungary. In 2022 the conference, due to covid, was held virtually, attracting delegates from all over the world, building on this success CEM 2023 was held on the 20th - 22nd September in Barcelona. Past visitors and delegates to the CEM events have come from a range of industries around the world that have a common goal and the need to monitor emissions from their plants or processes. For the 2023 event the Scientific Committee expanded the conference program to now include the pressing issues of achieving Net Zero Emissions.






#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine #cem2023
Read More22nd September 2023 - Commercial Shipping Powered By Wind
Cargill, the largest private company in the United States and the world's leading agricultural shipping firm, has embarked on its inaugural voyage utilising specialised sails partially powered by wind. The primary objective is to investigate how wind propulsion can contribute to the reduction of energy consumption and carbon emissions in cargo ships and the broader maritime sector.

With a global annual transportation of 225 million tons of dry bulk cargo across more than six hundred vessels, Cargill aims to explore innovative solutions for sustainability. In pursuit of this goal, one of its cargo ships has been retrofitted with WindWings sails designed to curtail fuel consumption and consequently decrease carbon emissions associated with shipping. The vessel in question has been outfitted with two WindWings sails, each towering at a height of 37.5 meters (123 feet). Constructed from materials similar to those found in wind turbines, these sturdy sails can be integrated onto cargo ship decks, offering a feasible option for older vessels to enhance their environmental performance. The ship's inaugural journey will take a route from China to Brazil.
This pioneering project is a collaborative effort involving BAR Technologies (the developer of the sails), Cargill Ocean Transportation, Mitsubishi Corporation, and Yara Marine. Jan Dieleman, President of Cargill, underscores the challenges of decarbonising the maritime industry and the significance of innovation in propelling the sector forward. According to BAR Technologies, these expansive sails have the potential to reduce the ship's fuel consumption by approximately 20%. Cargill perceives this maiden voyage as a prospect to assess whether reverting to traditional wind-assisted propulsion could be a viable direction for the future of maritime cargo transportation.
Should the trial prove successful, Cargill intends to install WindWings on ten additional ships. The appeal of wind energy, described by Jan Dieleman as "free," offers an attractive incentive for this transition. He emphasises that while no single solution can entirely decarbonize the industry, wind-assisted propulsion technology holds promise in contributing to this effort.
The Pyxis Ocean joins a limited fleet of very few large commercial ships employing some form of wind-assisted propulsion. Despite over 110,000 new-build order vessels, fewer than 100 currently integrate wind-assisted technology. However, if more shipowners, operators, and charterers opt to harness renewable energy for their fleets, it could significantly impact cleaning up the environmentally taxing shipping sector. Protea views the integration of renewable energy systems as a positive stride, as saving one ton of marine fossil fuel usage is equivalent to mitigating around three tons of carbon dioxide emissions.
Addressing carbon emissions on a broad scale within the shipping sector demands intricate implementation and substantial investment. Throughout this process, Cargill expresses its commitment to catalysing change, leveraging its central position in the value chain to drive positive transformations. By making significant investments in wind-assisted propulsion and green methanol fuel, Cargill demonstrates a willingness to share risks with commercial partners and recognises that the commercial value of these technologies can pave the way for widespread adoption.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More18th September 2023 - Showcase For A Green Shipping Programme
Norway has taken decisive strides towards establishing itself as a global frontrunner in efficient and environmentally-conscious shipping, epitomised by its Green Shipping Programme. This dynamic collaboration between the public and private sectors is wholly dedicated to advancing Norway's maritime strategies and objectives. Originally introduced as the Green Coastal Shipping Program in January 2015, this comprehensive initiative involved the participation of 16 private companies, various organisations, and two government ministries.

In 2019, the program underwent a name change, becoming the Green Shipping Programme (GSP), a shift that underlined its aspirations for global impact and its unwavering commitment to devising feasible solutions for efficient and eco-friendly shipping in alignment with both national and international climate targets.
At its core, the Green Shipping Programme (GSP), functioning as a public-private partnership, is designed to propel the Norwegian government's maritime strategies and plans forward. The program's overarching vision revolves around fostering and bolstering Norway's endeavor to establish itself as a global benchmark for the most efficient and environmentally-friendly shipping practices. Originally inaugurated in January 2015 under the moniker "the Green Coastal Shipping Program," In the spring of 2019, the program underwent a name transformation, rebranding itself as the Green Shipping Programme to express its international ambitions more explicitly.
By the spring of 2023, the program had expanded to include over 108 private companies and organisations, along with 12 public observers. Funding for the Green Shipping Programme is derived partially from public allocations within the Norwegian State budget and partly from contributions by its member entities. One of its primary goals is to be a global leader, providing the world's most efficient and environmentally-conscious shipping practices among all nations. As indicated, this program was initiated in 2015 and is now in its eighth year of operation.
A previous news article that we published provided insights into a single facet of the program, which has now been embraced by the European Union as a significant directive, particularly focusing on shore-to-ship power systems. We elaborated on some of the advantages of this initiative in our earlier news piece.
In April 2018, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) adopted a strategy aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions from international shipping. This strategy established an ambition of reducing emissions by at least 50% by 2050 compared to 2008 levels. The overarching vision is to ultimately phase out greenhouse gas emissions from the industry as expeditiously as possible within this century. The revised strategy for 2023 now sets an even more ambitious goal of achieving net-zero emissions from ships "by or around, i.e. close to, 2050." This represents a significant enhancement in ambition compared to the initial 2018 strategy, which targeted a 50% reduction in emissions within the same timeframe. Protea is well-positioned to support these objectives with our suite of shipping emissions management technologies.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More12th September 2023 - Shipping Emissions Reduced Using Shore To Ship Power Systems
The European Union is on an inspirational journey advocating for the integration of shore-to-ship power systems within the shipping and maritime sector. With a resolute commitment to a more eco-friendly and sustainable future, the EU has taken definitive measures to counter the adverse impacts of greenhouse gas emissions. Drawing inspiration from the momentous Paris Agreement, the EU has established ambitious targets to curtail carbon emissions, initiating a transformative odyssey across various domains.

Acknowledging the environmental challenges posed by sea vessels during their port sojourns, the EU recognises the detrimental effects of conventional diesel generators. In response, the EU has taken a leading role in promoting widespread implementation of shore-to-ship power systems, revolutionizing port operations and heralding a new era of sustainability.
The EU actively champions ecologically responsible solutions, ranging from promoting electric vehicle usage on land to revolutionising the maritime field. By placing pollution reduction at the forefront and embracing inventive strategies, the EU has embarked on a remarkable path that champions the adoption of shore-to-ship power systems in the maritime realm.
These cutting-edge systems facilitate vessels in seamlessly discontinuing their diesel generators upon docking, transitioning to electricity sourced from the port's power infrastructure. This ingenious approach not only eradicates harmful emissions but also substantially diminishes noise and vibrations in port vicinities, providing tangible advantages to nearby communities and marine ecosystems.
By enabling ships to connect to cleaner power sources during their stationary phases, the EU actively mitigates the environmental impact of the maritime sector, converting ports into thriving hubs of sustainability and advancement. The European Union has established ambitious targets through its Climate Law, aiming for a minimum 55% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030, with the ultimate objective of achieving climate neutrality by 2050. Within the maritime domain, around 6% to 7% of CO2 emissions arise during port stays within the European Economic Area.
This underscores the imperative to strongly promote sustainability in shipping and ensure that port services adopt eco-conscious practices while also establishing infrastructure for alternative fuels. Simultaneously, it's pivotal for key maritime and inland ports located along the trans-European transport network (TEN-T) to adapt to their critical role as strategic multimodal nodes and hubs for clean energy.
The Norwegian government stands out as a pioneer in shore-to-ship power systems, exemplified by the creation of the Green Shipping Program. A visionary initiative placing significant emphasis on the indispensable role of shore-to-ship power in achieving emission reduction goals. This program is dedicated to fostering the advancement and adoption of sustainable maritime solutions, with a specific focus on the development and integration of shore power infrastructure. By prioritising this innovative technology, the program strives to contribute to a more verdant and environmentally conscious future for the shipping industry.
The need to demonstrate environmental responsibility is key for today’s marine and offshore industries. Charterers and the public demand high standards of performance and reliability. Fuels and exhaust gas emissions are also the subject of international, regional and national controls.Protea is at the forefront of shipping emissions management, control and reduction. We have a full section on our website dedicated to shipping and marine emissions at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More4th September 2023 - Marine Scrubber Control In Focus
Protea’s marine emissions analyser plays an important role in the operation and control of on-board emissions scrubbers. With regulations as laid out in the IMO publication MARPOL Annex VI, control of SO2 emissions from vessels is critical for operators. To reduce emissions, Sea Water Scrubber Flue Gas Desulphurisation (SWS FGD) is operated in both Open Loop and Closed Loop modes.
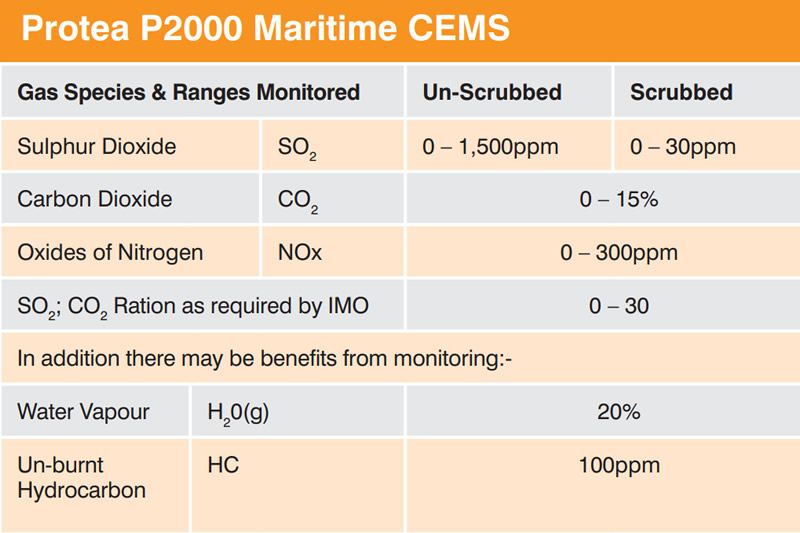
Protea works closely with scrubber manufacturers and suppliers and partnership with our analyser can give vessel operators the peace of mind that the scrubber is operating effectively. The ability for the emissions analyser to also measure non-scrubbed emissions, under fuel switching operation, give the flexibility of operation for vessels. With the Protea P2000 marine emissions analyser installed, the reduction of SO2 emissions can clearly be demonstrated, and scrubber operation controlled to ensure efficiency. The P2000 marine emissions system is:
- Certified by the UK Maritime and Coastguard Agency
- Marpol 73/78 Annex VI Reg 13 of the NOx Technical Code
- Meets or exceeds requirements of IACS E10
- Also meets or exceeds relevant parts of IEC 60945
- US EPA 40 cfr Part 60 & 75 Compliant
- Certified to MCERTS Std (EN 14181)
- Approved by Classification Society
The need to demonstrate environmental responsibility is key for today’s marine and offshore industries. Charterers and the public demand high standards of performance and reliability. Fuels and exhaust gas emissions are also the subject of international, regional and national controls. The most significant is IMO MARPOL Annex VI - Regulations for the Prevention of Air Pollution from Ships, which also applies to mobile offshore drilling units and other oil industry platforms. More information can be found at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine-scrubber-control.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More29th August 2023 - Maritime Biofuel Test Yields 20% Emission Reductions
In its most recent assessment, the Global Centre for Maritime Decarbonisation (GCMD) has successfully achieved a noteworthy 20% decrease in emissions through trials involving maritime biofuels. The specific blend under scrutiny consisted of a 30% composition of hydrotreated vegetable oil biofuel, combined with 70% marine gas oil. GCMD's investigation centred on a dual-fuel liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) vessel, which exhibited the emission reduction when utilising the vegetable oil-infused biofuel in contrast to conventional very low sulfur fuel oil (VLSFO).

The Global Centre for Maritime Decarbonisation has been diligently conducting a series of tests using diverse biofuel combinations in the maritime shipping sector, all aimed at curtailing CO2 emissions. In the latest instance, this biofuel mixture was employed in the third of five supply chain bunkering trials, involving a substantial 200 million tons of the biofuel amalgam. Notably, the hydrotreated vegetable oil (HVO) component, constituting 30% of the blend, was entirely derived from waste and residues. This HVO was ingeniously incorporated into the trial as part of the blended fuel, synergising with marine gas oil provided by GoodFuels. The blended concoction served as the pivotal fuel for the LPG propulsion system.
These pilot tests of biofuel blends are oriented toward enabling maritime vessels to adhere to the updated regulations laid out by the International Maritime Organisation (IMO). The significance of these trials lies in their contribution to the joint efforts of the fuel and shipping sectors in formulating eco-friendly fuels, in line with the International Maritime Organisation's ambitious decarbonization objectives for 2030 and 2050.
Notably, in June, the IMO revisited its strategy for curbing greenhouse gas emissions, instating more stringent targets. The immediate objective is a 20–30% reduction in net emissions from maritime operations by 2030, followed by an even more ambitious 70–80% reduction target by 2040. In light of this, the GCMD emphasises that the recent testing, along with the previous two trials, ought to instill a greater sense of confidence among fuel consumers regarding their capacity to meet these revised stipulations.
Dr. Sanjay Kuttan, Chief Technical Officer at GCMD, elucidated, "This pilot initiative serves as a demonstration of how diverse tracing methods can safeguard the legitimacy and quantity of sustainable biofuels within the supply chain. Furthermore, employing a biofuel blend in conjunction with LPG emerges as a viable route for maritime vessels to attain the newly revised IMO benchmark for decarbonisation by 2030."
In the following months, GCMD is slated to execute the final two supply chain trials. These assessments are being conducted at the Port of Vlissingen in Flushing, the Netherlands. The gains in operational efficiency and the concurrent reduction in emissions are indeed a welcome outcome of these endeavors. Protea have a range of Marine and Shipping Emissions Analysers and Control Units and Scrubber Control Systems all providing a combined Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS). Our Marine and Shipping Emissions Monitoring systems are also backed by global approvals which can be viewed at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine-approvals.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More21st August 2023 - The EU Emission Trading System & Shipping In Focus
Emission trading schemes (ETS) are increasingly being seen as tools that governments and regulators can employ to combat pollution from international shipping. The central concept behind an ETS is to establish a market mechanism that enforces the "polluter pays" principle. Polluters are required to pay for the environmental and social costs of pollution, including cleanup expenses and potentially research into pollution-reducing technologies. Naturally, raising the cost of pollution provides an incentive to decrease its generation. Protea is a global lead on shipping and marine emissions monitoring systems with a full global support team across the whole of the EU. We are well placed to provide Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS) to the shipping industry with our range of products and solutions.

The interest in extending current domestic emission trading programs to encompass international shipping has been growing. In the European Union (EU), a consensus has been reached on the application of the EU's emission trading system to the shipping industry starting from 2024. Ship owners and charterers need to begin contemplating how they will adhere to these requirements.
At the national level, governments can impose taxes on pollution sources at the point of production or sale, as seen with products like petrol. The intention is for these taxes to offset the expenses associated with managing pollution and encourage reduced consumption. However, the challenge with international shipping is that if only a few governments implement such taxes on bunker fuel, buyers are likely to adjust their strategies to avoid bunkering at the taxed ports. To make a sales tax on bunker fuel effective, major bunkering ports worldwide would need to collaborate and uniformly tax bunker fuel. Given the unlikelihood of such global cooperation in the near future, governments are now considering imposing charges on emissions rather than fuel sales.
Emission trading schemes (ETS) are increasingly being seen as tools that governments and regulators can employ to combat pollution from international shipping. The central concept behind an ETS is to establish a market mechanism that enforces the "polluter pays" principle. Polluters are required to pay for the environmental and social costs of pollution, including cleanup expenses and potentially research into pollution-reducing technologies. Naturally, raising the cost of pollution provides an incentive to decrease its generation.
Consequently, there is a growing interest in expanding existing emission trading schemes to encompass international shipping, including initiatives in the EU, China, and Japan. The core concept of an ETS involves a limited number of emission permits being traded on the market. Emitters must purchase and surrender enough allowances to cover their emissions. The price of these allowances will fluctuate based on supply and demand dynamics, motivating emitters to find cost-effective ways to reduce emissions.
The European Union Emission Trading Scheme, initiated in 2005, operates as a "cap and trade" system. CO2 emitters in specific sectors are required to buy allowances to cover their carbon emissions during designated trading periods. The quantity of allowances available at any given time is fixed, generally decreasing annually to drive emissions reduction within the EU. The implementation of this scheme in the shipping industry has been under deliberation for a while. However, a consensus seems to have emerged among the European Parliament, the Council of Ministers, and the European Commission on key features:
- The system encompasses carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide emissions. Application to all vessels over 5,000 gross tons operating within EU waters, regardless of their flag.
- Commencement date of January 1, 2024 (moved from January 1, 2023).
- Phased implementation: 40% coverage in 2024, 70% in 2025, and 100% in 2026.
- Inclusion of all intra-EU voyage emissions.
- Coverage of 50% of EU-bound and outbound voyage emissions.
- The "shipping company" (defined as owner, manager, or bareboat charterer) is responsible for surrendering allowances.
- A deadline of April 30 for surrendering allowances for the preceding calendar year (e.g., April 30, 2025, for 2024 emissions).
- Non-compliance can result in penalties and expulsion orders.
Another area of discussion involves determining emissions during voyages into or out of the EU, and the potential for operators to evade full application of the EU ETS. For instance, if a vessel stops at an intermediary port just outside the EU shortly after leaving EU waters, the outbound voyage may be calculated as shorter than one from/to the actual next loading port. Although this issue is anticipated to be addressed in the implemented scheme, it currently requires further consideration.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More13th August 2023 - Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC 80) Recap
During the recent 2023 MEPC 80 session, the IMO strategy concerning the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions from ships was approved. This version of the strategy incorporates more ambitious goals for addressing detrimental emissions. Protea is at the forefront of Shipping and Marine emissions monitoring with our P2000 range of Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMS) specifically designed for stack exhaust power units.

The need to demonstrate environmental responsibility is key for today’s marine and offshore industries. The updated IMO GHG Strategy encompasses a heightened collective aspiration to achieve nearly zero greenhouse gas emissions from global shipping around 2050. This entails a pledge to promote the adoption of alternative fuels with minimal or zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2030, and it also outlines approximate progress checkpoints for 2030 and 2040.
A key element from the recent MOEC 80 session was clarification on Tackling climate change - cutting GHG emissions from ships. During the 80th session of the International Maritime Organization's Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC 80), an updated GHG Strategy was embraced. This revised approach strives to substantially diminish greenhouse gas emissions originating from worldwide maritime activities. The fresh objectives encompass a 20% emissions decrease by 2030, a 70% decrease by 2040 (in comparison to 2008 levels), and the overarching aim of attaining emissions neutrality by 2050. Anticipated to be enforceable around the middle of 2027, these novel regulations hold importance for ship proprietors, managers, equipment producers, and fuel providers.
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has established worldwide guidelines pertaining to energy efficiency for vessels (further information can be found here). Furthermore, IMO remains actively engaged in implementing tangible measures to guarantee that global maritime transportation contributes proportionately to combating climate change.
Following extensive negotiations spanning multiple months, the 80th session of the Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC 80) concluded by endorsing the 2023 IMO Strategy for Mitigating Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Ships. This revised strategy sets more ambitious goals to address detrimental emissions effectively.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More8th August 2023 - Shipping Industry Debates LNG Versus Fuel Oil
The shipping industry plays a significant role in global trade, accounting for 80-90 percent of merchandise trade volume. However, it also contributes heavily to greenhouse gas emissions, burning of fuel each year, resulting in one billion tonnes of CO2 emissions, which make up about 3 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions. Large ocean-going container ships, tankers, and bulk carriers are responsible for the majority of these pollutants as they transport goods worldwide. Efforts are being made to address this issue, but the implementation of measures is crucial.

In recent times, there has been a shift towards alternative fuels in the shipping industry, with a substantial number of new ships being ordered to run on methanol and methane, particularly in the form of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG). While this might seem promising, it is important to consider the full impact of these fuels over their entire lifecycle.
At first glance, methanol and methane appear attractive alternatives as they contain less carbon than traditional oil-based fuels and are relatively cost-effective. However, when accounting for all greenhouse gases (GHG's) emitted during fuel production and consumption, the picture changes. Methanol produced from fossil natural gas emits vast amounts of CO2 during its manufacturing process. When combined with exhaust emissions from the ship's engine, the overall environmental impact of methanol turns out to be worse than conventional fuel by approximately 20%. To achieve significant GHG reductions, ship operators using methanol-powered ships would need to explore alternatives to fossil-based methanol, which are currently limited.
One potential option is capturing and sequestering CO2 emissions during production. However, such projects require time to scale up and significant investment, which will be justifiable only if greener methanol commands a premium price in the market. This is contingent on a proper accounting of upstream emissions in regulations.
In July 2023, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) adopted a revised GHG reduction strategy, with member states discussing proposals for ambitious targets to phase out lifecycle GHG emissions by 2030, 2040, and 2050. The majority of member states support the shipping industry's goal of achieving zero lifecycle GHG emissions by 2050, aligning with the 1.5°C warming limit and avoiding out-of-sector offsets. Potential measures to support these targets include a technical element like a GHG fuel standard that gradually increases over time and considers lifecycle GHG emissions, along with an economic element like GHG pricing.
Regarding LNG, it does produce significantly lower amounts of CO2, soot, dust, particulates, sulphur dioxide, mercury, and other harmful compounds compared to coal and oil. Nonetheless, it still emits CO2, which contributes to greenhouse gas effects. To address emissions monitoring, the Protea P2000 emissions monitoring system is approved for analysing exhaust gases from ship engines and boilers. It can measure up to six gases, including SO2, CO2, and NOx, providing valuable data for emissions management.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers #shipping #marine
Read More4th August 2023 - Protea Exhibiting at CEM Emissions Monitoring Barcelona 2023
Protea will be exhibiting at CEM Emissions Monitoring 2023 held in September this year. Dates of the event are Wednesday 20th to Friday 22nd September 2023 in Barcelona, Spain. Our booth number is 48 for this CEM event, which is the place to go for emissions monitoring solutions. The CEM 2023 conference will be held in Hyatt Regency Barcelona Tower, Barcelona, Spain. Come and visit Protea by registering for your tickets at https://www.ilmexhibitions.com/cem/registration/.

CEM is an International Conference and Exhibition dedicated to Emission Monitoring. Delegates and Visitors will gain valuable insights into the latest regulation, technologies and best practices in monitoring and measuring industrial emissions. The 15th CEM conference and exhibition will take place in Barcelona, Spain in September 2023. Find out more about at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/protea-exhibitions.
In 2023 the CEM event will be celebrating its 25th Anniversary, CEM first started in the United Kingdom in 1997 and has been held in The Netherlands, Denmark, France, Switzerland, Italy, The Czech Republic, Turkey, Portugal, India and Hungary. In 2022 the conference due to covid was held virtually attracting delegates from all over the world, building on this success we are now pleased to announce that CEM will be held Live on the 20th - 22nd September in Barcelona. Past visitors and delegates to the CEM events have come from a range of industries around the world that have a common goal and the need to monitor emissions from their plants or processes. For the 2023 event the Scientific Committee has expanded the conference program to now include the pressing issues of achieving Net Zero Emissions.
Visitors and delegates to the CEM events come from a range of industries around the world that have a common goal and the need to monitor emissions from their plants or processes. The Live Barcelona CEM event will encourage visitors and delegates network with industry influencers, speakers and leading CEM equipment and service suppliers all in one place at one time, this means visitors and delegates will get the best advice available on regulation, equipment, new products and new technologies on the market now and in the future.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers
Read More1st August 2023 - Goals For Greenhouse Gas Cuts Agreed With Shipping Emissions Levy Delayed
The imposition of a greenhouse gas emissions levy on international shipping to fund climate action has been postponed, but governments have reached agreements on greenhouse gas reduction goals. The conclusion of recent talks among 175 governments at the International Maritime Organization (IMO) received criticism from campaigners, who consider the agreement insufficient to decarbonize the sector.

Under the agreement, international shipping aims to reduce the carbon intensity by 40% by 2030, compared to 2008 levels. Carbon intensity refers to emissions produced per cargo and distance travelled. Additionally, governments have committed to cutting total emissions from international shipping by at least 20% by 2030, with an ambition to achieve 30% cuts by that date. The IMO has set a target of reaching net-zero emissions "close to" 2050. However, campaigners had hoped for a more ambitious goal, advocating for a 50% reduction by 2030 and a clear commitment to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 at the latest.
The agreement also includes measures to encourage the adoption of clean technologies in shipping. By 2030, at least 5% of the energy used for international shipping should be zero carbon or near-zero carbon, with an ambition to reach 10% by that date.
Critics argue that these targets fall short of what is required to limit global heating to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, as per the Paris Agreement's goal. They contend that at the current rate, international shipping is projected to exceed its 1.5 degrees Celsius carbon budget by around 2032 under this agreement. Campaigners expressed disappointment at the outcome of the talks, viewing it as a missed historic opportunity to align the shipping industry with the Paris Agreement's temperature goal of 1.5 degrees Celsius. They stress the urgency of continued efforts to decarbonize international shipping in a fair and equitable manner as soon as possible.
Shipping currently contributes about 3% of global greenhouse gas emissions, and without substantial intervention, this figure is expected to rise significantly due to the growing demand for shipping services, resulting in emissions accelerating faster than many other sectors. Whilst the pace of change has created uncertainty and appears to have pushed the boundaries for some technologies, the Protea 2000 emissions monitoring system has been proven in long-term service onboard ship as a robust and reliable method of confirming compliance with emissions regulations. Find out more about at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine-emissions-analysers
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers
Read More24th July 2023 - Shipping Emissions In Europe Up To 3 Year High & Returns To Pre-Pandemic Levels
Europe's shipping industry experienced a concerning rise in CO2 emissions, reaching a three-year high in the previous year as it approached pre-pandemic activity levels. The analysis conducted by Transport & Environment (T&E) revealed that container and cargo vessels were the primary contributors to these emissions.

According to T&E, vessels that visited European ports in 2022 emitted nearly 130 million tons of carbon dioxide (CO2). Additionally, the resumption of leisure travel led to an increase in cruise vessel emissions, which amounted to six million tons in 2022.
The most significant trend observed in cargo shipping in 2022 was the surge in LNG shipments, which rose by 58%. The imposition of stricter sanctions on Russia's oil prompted Europe to boost LNG imports, resulting in a considerable increase in seaborne emissions.
Jacob Armstrong, the shipping manager associated with T&E, highlighted that shipping firms in Europe now rank alongside airlines and coal plants as major polluters. The largest ocean liner company in the world, MSC, was primarily responsible for the rise in Europe's shipping CO2 emissions, emitting around 10.2 million tons of CO2 in the previous year. CMA CGM, Maersk, COSCO, and Hapag-Lloyd also featured among the top shipping emitters in the region.
Armstrong emphasized that unless more stringent regulations are implemented, shipping firms will continue to neglect investments in efficiency and environmentally-friendly fuels. However, some positive steps have been taken, as leading ocean container carriers like Maersk and CMA CGM have ordered green methanol-fueled ships to be integrated into their fleets starting from early 2024.
The analysis also revealed that cruise vessel emissions nearly doubled from 2021 levels due to the resumption of international travel. The MSC Grandiosa was identified as the most polluting vessel of 2022, emitting over 130,000 tons of CO2, equivalent to the emissions of a small town. Inadequate port electrification was cited as a contributing factor to the rise in shipping emissions, with carbon pollution, nitrogen oxide (NOx), sulfur oxide (SOx), and suspended particulate matter (PM 2.5) increasing slightly at ports last year. The report recommended greater shore-side electrification as a solution to this issue.
The Protea 2000 emissions monitoring system comprises up to 8 exhaust mounted analysers, each with automatic verification facilities. Emissions data from the entire system is securely managed and displayed at a dedicated Classification Society approved panel PC, with outputs to networks, control systems, and reporting facilities.
To ensure accountability, it is crucial to monitor European shipping emissions and establish stricter regulations to compel shipping firms to invest in efficiency and green fuels. Without such measures, the industry risks irreversible damage to the environment. The European Federation for Transport and Environment, commonly referred to as Transport & Environment (T&E), is a European umbrella for non-governmental organisations working in the field of transport and the environment, promoting sustainable transport in Europe.
Find out more at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine-emissions-analysers.
#protea #marine #shipping #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers
Read More18th July 2023 - Marine Emissions Analysers In Focus
This month, representatives from 175 shipping nations convened in London, under the supervision of the International Maritime Organisation (IMO), a United Nations body. Their objective is to negotiate a revised timetable for achieving complete decarbonisation of the shipping industry. The Protea 2000 emissions monitoring system is approved for the analysis of exhaust gases from the engines and boilers of ships and offshore rigs. Robust and with proven reliability, up to six gases can be measured including SO2, CO2 and NOx.

Advocates are pushing for a more stringent goal, aiming for a 50% reduction by 2030 and a new target of net-zero emissions by 2050. Some proponents go even further, proposing a faster timeline for achieving full decarbonization by 2040. "If member states can successfully accomplish this, they will align the shipping sector with the temperature objectives of the Paris Agreement and foster investments in green technologies that will fundamentally reshape the industry," stated Kerrlene Wills, the Director for Ocean and Climate at the UN Climate Foundation.
Enhanced Customer Support - Recent upgrades include our new Automatic Field Data Collection (AFDC) module that uniquely allows the ship's engineer to automatically run a routine collecting all the relevant data from the analyser under the various states of operation. This can then be e-mailed to Protea’s customer support team who will analyse and determine any remedial action required. Protea will upgrade existing Procal supplied CEMS saving the ships operator time and expenses and increasing emission data availability.
Find out more at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/marine-emissions-analysers.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers
Read More17th July 2023 - ISO 9001:2015 Re-certification Complete
Protea has a renewed ISO 9001:2015 certificate following our successful recertification audit on our Quality Management System by TÜV Rheinland.
Our joint-factory management system approval shows Protea’s commitment in delivering high quality gas analyser products and associated services to our Global customer base.

6th June 2023 - Come & Visit The Protea Booth at Nor-Shipping 2023
Protea will be exhibiting at Nor-Shipping 2023 from Tuesday 6th to Friday 9th June 2023 in Oslo, Norway. Our booth number is D05-12C for Nor-Shipping. Come and visit Protea by registering for your tickets at https://nor-shipping.com/exhibition/



Nor-Shipping is the optimum arena for Ocean Solutions. This is where the business of the ocean comes to life. Come and visit the Protea team to learn more and find out what to do at Nor-Shipping and to get the best Nor-Shipping experience. Nor-Shipping is the meeting place for globally leading maritime players, technology innovators, investors, and all the stakeholders interested in realising ocean opportunities. An international arena for building cross industry partnership, business and sustainable ocean development. Nor-Shipping is Your Arena for Ocean Solutions.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers
Read More1st June 2023 - Protea Exhibiting at Nor-Shipping 2023
Protea will be exhibiting at Nor-Shipping 2023 held in June this year. Dates of the event are Tuesday 6th to Friday 9th June 2023 in Oslo, Norway. Our booth number is D05-12C for Nor-Shipping which is an optimum arena for Ocean Solutions. This is where the business of the ocean comes to life. Come and visit the Protea team to learn more and find out what to do at Nor-Shipping and to get the best Nor-Shipping experience. Come and visit Protea by registering for your tickets at https://nor-shipping.com/exhibition/.

Nor-Shipping is the meeting place for globally leading maritime players, technology innovators, investors, and all the stakeholders interested in realising ocean opportunities. An international arena for building cross industry partnership, business and sustainable ocean development. Nor-Shipping is Your Arena for Ocean Solutions.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers
Read More5th May 2023 - Asian Distributor Conference & Sea Asia Exhibition 2023
Protea's Commercial Director Karen Canham and Sales & Marketing Director Chris Daw were at the Sea Asia Exhibition 2023 last week where we also invited our Distributors in the region for training.

Sea Asia enjoys strong support from government agencies and key trade associations, firmly establishing itself in the marketplace as the leading platform for both the global and local maritime and offshore communities to explore business, network and unveil new products and services. The 3-day conference and exhibition promises to provide a plethora of diverse marine products and services, with good networking opportunities.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers


 Read More
Read More 3rd May 2023 - Marine Emissions Analyser Control Units In The Spotlight
Protea’s P2000 marine emissions analyser is operated via our dedicated Marine Emissions Analyser Control Unit. With the P2000 analyser being installed in-situ in the Exhaust Gas Cleaning Systems, or insulated exhaust duct, this can be some distance away from the system controller. The Marine Emissions Analyser Control Unit utilises a high grade marine-approved Panel PC.

The Marine Emissions Analyser Control Unit operated both as a display, data logger and a data transmission system. Gas concentrations from each of the stack mounted analysers on the vessel are displayed. In addition, the Control Unit will log the data and retransmits it to a supervisory system. The main screen, one for each analyser, displays the concentrations of each gas. Protea’s emission systems also report the SO2:CO2 ratio, along with any additional information such as process pressure, analyser and sample temperatures.
A dedicated diagnostics routine runs through a self-check on the emissions systems, applying check gas if available, and provides a diagnostic summary file. This can be sent to Protea’s support team if needed. Features include:
- Control of multiple marine emission analysers
- Monitor Accurately Required Emission Levels
- SO2:CO2 ratio reporting
- Minimal System Maintenance
- Compliant with Relevant International Standard
- Certified For Marine Installation
- Global Commissioning & Service Capability
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers
Read More19th April 2023 - Protea Distributor Attending The Analyzer Technology Conference
One of our strategic global partners is in attendance at the 2023 Analyzer Technology Conference held at the Galveston Island Convention Center in Texas, USA. The event is running from April 17th to April 21st 2023. Come and visit Delta Instrument LLC at booth 607.

The vendor hall is open Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday. on March 23rd 2023. The team from Delta Instruments were in attendance along with other vendors. In keeping with a long tradition of in-person technical conferences and symposia, the Houston Analysis Committee is holding a conference and exposition focusing on analysis and measurement in the chemical processing industries. In the tradition of similar technical conferences, this event will highlight relevant, new technical papers related to grab sampling, sample handling systems, data analysis and process analyzers such as gas chromatographs, spectrometers and analytical sensors.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers
Read More2nd April 2023 - Protea Exhibiting At UK Pavilion At Sea Asia 2023
Protea will be exhibiting at the UK Pavilion at Sea Asia. Dates of the event are Tuesday 25th to Thursday 27th April 2023 in Marina Bay Sands, Singapore. Our booth number is B2-A21 for Asia's Anchor Maritime and Offshore Event. Sea Asia, a premier maritime conference and exhibition, will return to Marina Bay Sands in Singapore April 2023. The show will be held in conjunction with Singapore Maritime Week 2023, which brings together leading Shipowners, Offshore Operators, Ship-managers and Shipyard procurement teams from around the globe.
Come and visit Protea by registering for your tickets at https://registration.mvents.asia/SA2023/RegistrationAttendeesEntry

Sea Asia enjoys strong support from government agencies and key trade associations, firmly establishing itself in the marketplace as the leading platform for both the global and local maritime and offshore communities to explore business, network and unveil new products and services. The 3-day conference and exhibition promises to provide a plethora of diverse marine products and services, with good networking opportunities.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers
Read More29th March 2023 - Protea Distributor Exhibits At M+R Exhibition In Antwerp
Strategic Protea partner Ankersmid, recently exhibited at the 2023 M+R Exhibition in Antwerp 22nd March to 23 March 2023 at the Expo centre. This was the the place to be for every professional player in industrial maintenance, shutdown technology, asset management and production reliability own technology, asset management and production reliability. The show was well attended and Protea provided support for CEMS solutions which are found around the world across a number of applications.

In the process industry it is of vital importance to be able to continuously monitor the production via the correct instrumentation. In order to optimally manage the increasing complexity of installations and to manage unforeseen circumstances in the process, you have to make use of the technological best of the best. All important developments in the field of process instrumentation were gathered on 22 and 23 March in Antwerp Expo during M+R 2023, the largest Benelux event on this theme.

#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers
Read More1st March 2023 - Residual Gas Analysers In The Spotlight
For both research and industrial applications, Protea’s Residual Gas Analyser (RGA) products can be supplied in 100amu, 200amu and 300amu versions with smallest size and highest performance on the market.
The ProtaR Residual Gas Analyser (RGA) from Protea represents the smallest footprint electronics and maximum performance for value of any RGA on the market. Protea’s ProtaR RGA is a compact, stable and robustly designed Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer (QMS) instrument incorporating all the latest Quadrupole technology. ProtaR is a useful analytical tool for testing and residual gas analysis in leak testing, semiconductor, coating and process applications, being able to detect and measure almost all gases with low detection limits and fast response.
A mass spectrometer measures the mass-to-charge ratio of the molecules in a sample and by collecting and analysing the mass spectrum we can identify and quantify which molecules are present. The QMS within ProtaR contains a mass filter that is made up of 4 parallel circular rods, hence the name quadrupole.
- Very quick (millisecond) response time
- Detects almost any gas
- Low maintenance costs, with corrosion resistance inlets
- Advanced chemometrics for multi-gas quantification
Applications include Vacuum Furnaces, Semiconductor Processes, Metallurgy, Research and Development, Vacuum Process and Integration with existing vacuum systems.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #ftir #gas #analysers
Read More14th February 2023 - Bio360 Expo Exhibition 2023 In Pictures
Protea recently exhibited at Bio360 Expo located within the Exponantes le Parc des Expositions in Hall XXL in Nantes, France. Bio365 2023 was also an international meeting place for people and organisations who are engaged in and committed to accelerating the biotransition. The Bio360 Expo comprised a large exhibition, comprehensive international conference programmes with simultaneous translation, study tours, the innovation competition, and much more. The Protea team would like to thank everyone we had contact with and look forward to seeing you and working with you again during the year.

Protea Ltd is the world's leading supplier of both fixed and transportable analysers to monitor Impurities in Biogas & Biomethane. Siloxanes are low-level hazards to the atmosphere in terms of their emissions, however when they are combusted in gas engines the hard silica that is produced is very harsh to the moving parts of the gas engine. Ultimately this increases maintenance cost and gives a lower energy output, making the generation of power less efficient.



#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #marine #bio360
Read More1st February 2023 - Bio360 Expo - Dates Wednesday 8th to Thursday 9th February 2023 in Nantes, France
Come and visit Protea at stand E40 for Bio360 Expo at the Exponantes le Parc des Expositions in Hall XXL located in Nantes, France. Bio365 is also an international meeting place for people and organisations who are engaged in and committed to accelerating the biotransition. Bio360 Expo comprises a large exhibition, a comprehensive international conference programme with simultaneous translation, study tours, the innovation competition, and more besides.

Because time is so short and there is so little room for trial and error, the imperative to knowledge share and collaborate could not be more pressing. Through its international exhibition and conference programme, Bio360 Expo does all in its power to be a platform where 1+1=3, where innovative collaborations are conceived, where success builds on success, enabling us to get there quicker. A crossroads for the worlds of agriculture, forestry and wood, public bodies and decision makers, bioindustry players, energy, research institutions, associations and pan-industry bodies, journalism, finance, legal. Bio360 Expo is the place that strives to bring all this together and to serve the transition to a new bioage where future generations can continue to thrive, sustainably.
Protea Ltd is the world's leading supplier of both fixed and transportable analysers to monitor Impurities in Biogas & Biomethane. Siloxanes are low-level hazards to the atmosphere in terms of their emissions, however when they are combusted in gas engines the hard silica that is produced is very harsh to the moving parts of the gas engine. Ultimately this increases maintenance cost and gives a lower energy output, making the generation of power less efficient.
With this ever-growing market, the need for analysis of the siloxane content of the biogas pre-generator is important. A land-fill gas plant operator can determine the amount of siloxane removal of the pre-combustion feed gas. This enables a more cost-effective cleaning system to be employed. They can also determine whether an existing clean up system is operating effectively. To visit the show please register at https://www.bio360expo.com/Login?aid=1183.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #marine
Read More6th January 2023 - Exhibitions List Announced For 2023
A new year presents new opportunities for our business to network and exchange exciting innovations across a global platform. Our exhibitions list for 2023 has been announced and it consists of some excellent locations with world class facilities. We will be at Bio360 Expo in France, UK Pavilion Group at Sea Asia in Singapore, Nor-Shipping in Norway and CEM in Spain and look forward to meeting you during the year.

Bio360 Expo - Dates Wednesday 8th to Thursday 9th February 2023 in Nantes, France
Bio360 Expo is an international meeting place for people and organisations who are engaged in and committed to accelerating the biotransition. Because time is so short and there is so little room for trial and error, the imperative to knowledge share and collaborate could not be more pressing. Through its international exhibition and conference programme, Bio360 Expo does all in its power to be a platform where 1+1=3, where innovative collaborations are conceived, where success builds on success, enabling us to get there quicker. A crossroads for the worlds of agriculture, forestry and wood, public bodies and decision makers, bioindustry players, energy, research institutions, associations and pan-industry bodies, journalism, finance, legal … Bio360 Expo is the place that strives to bring all this together and to serve the transition to a new bioage where future generations can continue to thrive, sustainably.
UK Pavilion at Sea Asia - Dates Tuesday 25th to Thursday 27th April 2023 in Marina Bay Sands, Singapore
Sea Asia, a premier maritime conference and exhibition and Asia's Anchor Maritime and Offshore Event, will return to Marina Bay Sands in Singapore April 2023. The show will be held in conjunction with Singapore Maritime Week 2023, which brings together leading Shipowners, Offshore Operators, Ship-managers and Shipyard procurement teams from around the globe. Sea Asia enjoys strong support from government agencies and key trade associations, firmly establishing itself in the marketplace as the leading platform for both the global and local maritime and offshore communities to explore business, network and unveil new products and services. The 3-day conference and exhibition promises to provide a plethora of diverse marine products and services, with good networking opportunities.
Nor-Shipping - Dates Tuesday 6th to Friday 9th June 2023 in Oslo, Norway
Nor-Shipping is the meeting place for globally leading maritime players, technology innovators, investors, and all the stakeholders interested in realising ocean opportunities. An international arena for building cross industry partnership, business and sustainable ocean development. Nor-Shipping is Your Arena for Ocean Solutions. This is where the business of the ocean comes to life. Here you can learn more and find out what to do at Nor-Shipping and to get the best Nor-Shipping experience.
CEM - Dates Wednesday 20th to Friday 22nd September 2023 in Barcelona, Spain
CEM is an International Conference and Exhibition dedicated to Emission Monitoring. Delegates and Visitors will gain valuable insights into the latest regulation, technologies and best practices in monitoring and measuring industrial emissions. The 15th CEM conference and exhibition will take place in Barcelona Spain in September 2023. In 2023 the CEM event will be celebrating its 25th Anniversary, CEM first started in the United Kingdom in 1997 and has been held in The Netherlands, Denmark, France, Switzerland, Italy, The Czech Republic, Turkey, Portugal, India and Hungary. In 2022 the conference due to covid was held virtually attracting delegates from all over the world, building on this success we are now pleased to announce that CEM will be held Live on the 20th - 22nd September in Barcelona. Past visitors and delegates to the CEM events have come from a range of industries around the world that have a common goal and the need to monitor emissions from their plants or processes. For the 2023 event the Scientific Committee has expanded the conference program to now include the pressing issues of achieving Net Zero Emissions.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #marine
Read More2022
8th December 2022 - Seasons Greetings From Protea
Season’s greetings from all of us and we wish you a Merry Christmas and a Happy New Year. We are taking orders throughout December and will be operational offering emissions monitoring systems and services as normal. Our last working day before Christmas will be Friday 23rd December 2022, reopening on Tuesday 3rd January 2023. We would like to thank everyone involved with our company including our employees, customers, suppliers and people who have been involved in projects and related activities.

We manufacture a range of extractive and in-situ analysers, applying the technologies of IR, FTIR, UV, TDL and Mass Spectrometry (QMS) in portable and fixed gas measurement systems. In particular, we are specialists in the design, manufacture and supply of Continuous Emission Monitoring (CEMS) and process analyser systems. As a flexible and agile manufacturer, we also offer custom equipment, requiring a high level of R&D; new developments feed into our core products and markets. We look forward to working with you in 2023.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #marine
Read More1st November 2022 - Emissions Consulting In The Spotlight
Protea’s range of gas analysers are used in emissions monitoring as both fixed, Continuous Emissions Monitoring (CEM) systems or as portable stack emissions testers. Protea can provide consultancy service on the best implementation of our equipment or 3rd party equipment that may complement Protea’s equipment to give the customer the full capability for their emissions monitoring requirements. Find out more at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/emissions-consulting

Consultancy across Continuous Emissions Monitoring (CEM) covers the following areas:
- Emissions analyser selection
- Dust analysis
- IED requirements, including MCPD
- Agriculture and livestock emissions testing
- Instrumental and manual stack testing
- Emissions Reporting Software (DAS)
- Permit issues
- Implementation of Standard Reference Methods (SRM)
- Process and procedures for management of in-house stack testing
- MCERTS training
Our consultancy services are backed-up with our in-house emissions analyser rental department, and our service department who can support non-Protea equipment.
#protea #emissions #monitoring #cems #marine
Read More6th October 2022 - Protea Ltd - Product Portfolio
Protea Ltd based in the UK with two state of the art manufacturing units in Middlewich and Peterborough.
The company design, manufacture and support a comprehensive range of advanced Continuous Emission Monitoring & Process analysers and systems. Protea’s technologies include Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR), In-Situ IR and Extractive Photometers, In-Situ UV and Extractive Spectrophotometers, TDL, Mass Spectrometers, FID Analyser. This enables Protea to offer the most suitable technology to meet the customers specification.
In addition to manufacturing analysers Protea have developed a modular CEMS / AMS solution comprising of all the necessary elements to monitor and report in compliance with the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED).
To complement Protea’s range of gas blenders, the portable atmosFieldCal capable of humidifying certified test gas and calibration solutions has been developed. The units mini evaporator mounted on an umbilical can be connected directly to the analyser or sample probe hot ports, enabling for example humidified Hydrogen Chloride to be to be introduced into the AMS.
To see our Product Portfolio, click on the image below or here.

23rd September 2022 - Protea at the AQE Air Quality and Emissions Monitoring Exhibition October 2022
Protea would like to invite you to join us at the AQE Air Quality and Emissions Monitoring exhibition and conference on the 12th & 13th October. Protea will be exhibiting on stand B1.
Please come and see us to discuss your product and service requirements or for a technical demonstration and catch up.

AQE is free to attend, there are over 100 hours’ worth of presentations on regulation, testing methods and training plus there are free lunches and onsite parking! Your AQE visitor badge will also give you access to the Co-located WWEM Water monitoring show.
To gain Fast Track entry please register today, we look forward to seeing you at the show.
Read More5th September 2022 - Process Monitoring & Online Solutions
Process monitoring is key for operators to understand, improve and implement efficiency savings. With the ability to measure any gas in the most demanding of applications, Protea can help to deliver those savings. Find out more about our online systems at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/online-solutions where the full range of online solutions is presented below:

Online solutions cover these applications below:
- Nitric Acid Plant Process Control - The P2000 emissions analyser measures Oxides of Nitrogen for process control purposes, typically upstream of the N2O abatement reactor where typical pressures can be as high as 10 bar
- Siloxanes Analysis - Protea can offer online siloxanes analysis using our atmosFIR gas analysers. This allows the real time measurement of siloxanes on plant
- Syngas - The composition of fuel gas is important in order to determine calorific value and also to detect any unwanted contaminants in the gas. Online analysis is important in order to give real-time and direct action on issues
- TO Multi-Stream Bypass System - Commonly, activated carbon beds are used as abatement systems on plant with emissions being reduced by adsorption onto the bed
- Liquid TiCL4 Vanadium Oxychloride Monitor - The chloride process of titanium dioxide (TiO2) pigment manufacture first converts titanium-containing ores to TiCl4 via a carbochlorination reaction
- VOC Analyser - As well as standard methods for VOC such as FID, Protea’s FTIR gas analysers can provide real-time speciated VOC measurements for hundreds of organic species in process and emissions applications
- Multipoint Gas Analysis Solutions - Protea’s FTIR, TDL and QMS analysers are available with control for multiple sample points. A multiple sample point or multi-stream solution can enable cost savings by allowing one analyser to make sequential measurements from many different sample points
19th July 2022 - AIR-IQ Spectral Search

Protea’s patented algorithm for spectral identification is now available within our PAS platform. The AIR-IQ plug-in offers a unique and powerful searching tool to enable users of our spectroscopic instrumentation (FTIR and Mass Spectrometer) to identify unknown gases in their sample, being able to then add to the analysis method quickly and easily.
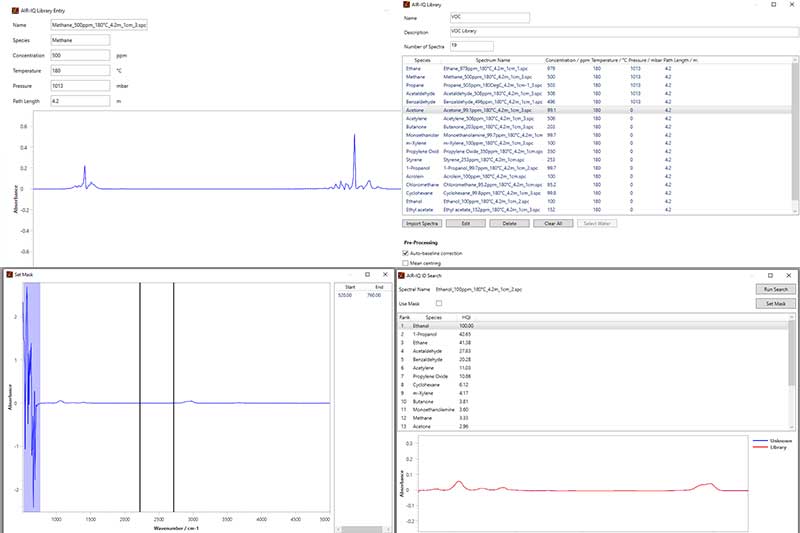
Built upon decades of experience of analysing complex gas matrices from FTIR emissions and process data, AIR-IQ offers features such as:
- Library management of qualitative and quantitative spectra
- Spectral file recognition: auto-read gas names, temperatures, pressures and pathlength - makes adding new calibration references quicker
- Spectral search window masking and pre-processing steps, including water subtraction
- Subtraction of identified gases and re-analysis: iterative approach to qualifying all gases in sample spectrum means ALL unknows can be identified one after the other.
- Identified gases are seamlessly added into the current analysis method. This can be done as “ interference only”, meaning re-calibration is not required and existing methods can be corrected quickly without generating new references.
Please contact Protea for more information on AIR-IQ, if you are a new or existing customer.
Read More18th June 2022 - Distributor Training
Now that we are open for travel and meeting again, it is great to be able to welcome our Distributors and end users back to Protea for training courses. This month we have entertained our friends from Poland, Finland, Canada and Singapore to both Protea factories in the UK.
Training courses covering service, support and advanced data analysis of FTIR spectra have been carried out.


 Read More
Read More 25th May 2022 - FAT Testing Facility
Protea’s dedicated factory for extractive emissions monitoring equipment integration and testing has given us the increased capacity for our gas analyser system deliveries. This allows both for our MCERTS approved Continuous Emissions Monitoring systems and our customised process and research systems to be tested alongside each other.
Both analyser systems on show here use the same core atmosFIR FTIR gas analyser. Whilst one needs to measure regulatory emissions from incineration process, the other is measuring very high concentrations using in-built dynamic dilution of the sample for an academic research centre. Protea can deliver repeatable, standardised and approved products for regulatory requirements. Or we can push our FTIR technology to the limits with challenging gas mixtures require hardware and software customisation.
 Read More
Read More 12th May 2022 - Ethylene Oxide Monitoring
The atmosFIR FTIR gas monitoring system from Protea has been successfully installed measuring low levels of Ethylene Oxide emissions from sterilisation facility. Working together with the supplier of the emissions purification technology, Protea’s FTIR gas analyser can monitor the very low emissions produced post-purification to confirm emissions are below the stringent limit values and that the abatement process is working effectively. A measurement range of 0 – 5ppm of Ethylene Oxide was delivered, with a lower detectable limit of 20ppb.

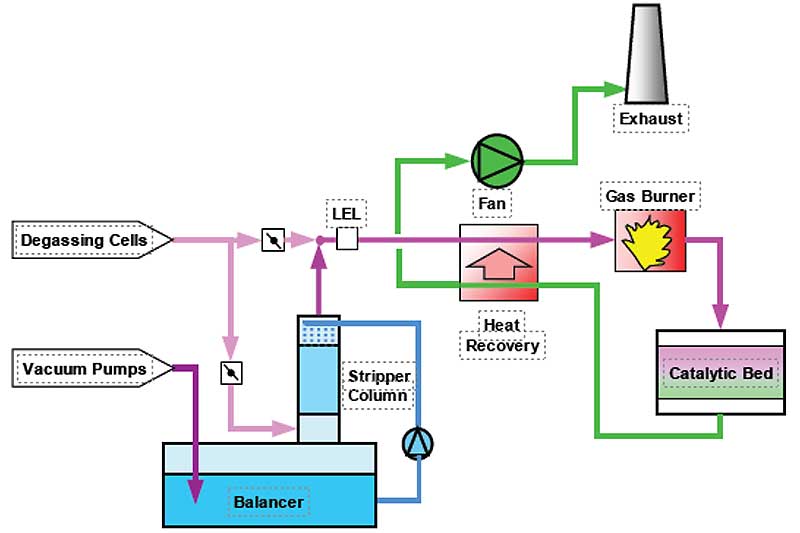
The atmosFIR system delivered is the same configuration as our MCERTS approved emissions system for combustion incineration processes, but with a lower operating sample temperature. The benefit of FTIR as a solution is, not only that it can deliver the measurement accuracy for Ethylene Oxide itself, but FTIR allows for the addition of other gases or interference correction should there be any other gases within the sterilisation and abatement process in the future.
| Component | Range 1 | LDL | Units | % of Range | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethylene Oxide C2H4O | 0-5 | 0.02 | ppm | 0.38 | Pass |
 Read More
Read More 4th May 2022 - CCS Online Monitoring Now Available
Protea’s multi-gas FTIR technology is ideally suited to new processes involving carbon reduction, such as Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS). Protea have supplied a multi-stream gas monitoring system that has enabled measurement of up to 5 gas streams around a CCS plant. This includes high concentration CO2 streams, with up to 100% CO2 being measured.

Our FTIR technology can simultaneously detect low level impurities aldehydes and other solvents as well as measure the high CO2 background. The uniqueness of Protea’s chemometric software and hardware connectivity allows for a complete, different gas calibration to be loaded on multiple streams. So other gas streams can measure very low CO2, <100ppm. Find out more about CCS Online Monitoring at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/css-emissions.
Read More6th April 2022 - The Largest Benelux Event For Process Instrumentation
Protea Distributor Ankersmid recently exhibited at the M + R 2022 event for the industrial process industry at the Antwerp Expo. In the process industry it is of vital importance to be able to continuously monitor the production via the correct instrumentation. In order to optimally manage the increasing complexity of installations and to manage unforeseen circumstances in the process, you have to make use of the technological best of the best. The P2000 In-Situ Continuous Emissions Monitoring System was presented at the show.

Ankersmid Sales Manager, Serge Rottiers stated “Now that the corona vicissitudes are finally over, our company has been given the opportunity to exhibit the devices of our suppliers at the M+R fair in Antwerp. Expectations were high, because both suppliers and customers were happy to finally have face-to-face contact again. The pandemic has made good use of new communication options such as Teams, Zoom and so on, but nothing beats a real personal conversation and the opportunity to see a device in real life. The new expo demo version and the UV-led upgrade of the P2000 were positively received and open up new opportunities for future applications."

 Read More
Read More 4th April 2022 - Meeting Marine Emissions Challenges
Protea have been featured in the latest edition of Clean Shipping International, demonstrating how our advanced patented in-situ CEMS solutions are benefiting the global reduction in marine emissions.
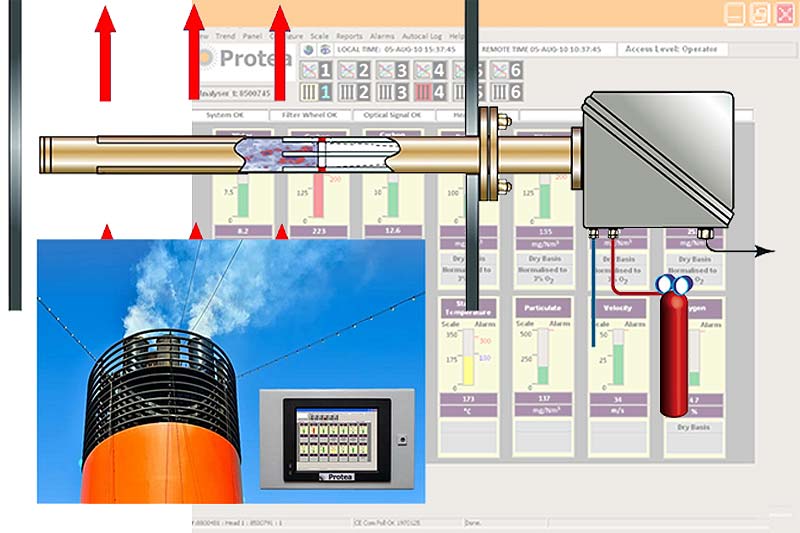
The In-Situ P2000 analyser offers a unique approach to monitoring exhaust emissions monitoring is an ideal solution for the marine industry to enable compliance with IMO regulations. The analyser is fitted directly to the exhaust with the gas monitored within the exhaust duct. An In-Situ technique, unlike extractive systems, does not require sample preparation components. Our P2000 analyser is certified by several Classification Societies as an analyser system suitable to monitor Sulphur Dioxide and Carbon Dioxide and report the SO2:CO2 ratio.
The P2000 was first installed on early Exhaust Gas Cleaning Systems (EGCS) in 2010 and since 2010 several hundred instruments have been installed on several classes of vessels, both on scrubbed and un-scrubbed applications.
In 2018 Protea made a series of product improvements, working with users and marine industry specialist the outcome of the evaluation identified three main areas which would benefit from improvements.
The solutions employed in the latest P2000 are:
- Patented UV/IR hybrid technology capable of monitoring lower levels of SO2 in a background of high water vapour
- Capable of monitoring post scrubber (EGCS) with liquid phase water vapour carry over
- Enhanced support features to enable vessels engineers to identify and rectify performance issues
Protea operates an extensive worldwide network of factory trained sales & service partners strategically located to support the marine industry. We would like to thank and recognise the input from our valued marine engineer users, whose expertise and feedback has gone into improving our products in this demanding market.
Read more here www.cleanshippinginternational.com/csi-magazine-spring-2022/
Read More1st April 2022 - CCS Carbon Capture and Storage
Protea’s atmosFIR FTIR gas analyser has proven a valuable tool in research into the effective storage of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) in the North Sea. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is a key technology to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial processes in a feasible, substantial, and timely manner. For geological CO2 storage to be safe and reliable, robust strategies for CO2 leakage detection, quantification and management are crucial.

The STEMM-CCS (Strategies for Environmental Monitoring of Marine Carbon Capture and Storage) project aimed to provide techniques and understanding to enable and inform cost-effective monitoring of CCS sites in the marine environment. A controlled CO2 release experiment was carried out in the central North Sea, designed to mimic an unintended emission of CO2 from a subsurface CO2 storage site to the seafloor.

Protea’s model atmosFIR FTIR gas analyser was used on board the RRS James Cook to measure the molar fractions of CO2, SF6, C3F8 and CH4 in the discrete gas samples collected during the release experiment. The FTIR was equipped with a custom-made sample injection system allowing reference gases to be injected. Find out more at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/carbon-storage
Read More23rd March 2022 - Protea At The 2022 Asia Pacific Maritime Exhibition
Protea recently exhibited at the 2022 Asia Pacific Maritime Exhibition in Singapore. The exhibition was very good, and we made some interesting contacts. From the exhibitor side it was international, with visitors being about 95% from Singapore. It was very good for networking, everyone was very delighted to meet people in an exhibition setting for the first time in two years.

The 2022 Asia Pacific Maritime (APM) at Marina Bay Sands in Singapore is a biennial exhibition in the globally important market of Singapore. The Singapore market is very strong and influential with yards, owners and management companies all based locally. This exhibition drew in visitors from the surrounding region so expect to see attendees from Vietnam, Indonesia and Malaysia. It is particularly strong in showcasing the latest marine equipment, products and services as well as incorporating workboat and offshore technology and services.



 Read More
Read More 8th February 2022 - APM Asia Pacific Maritime Exhibition In Singapore 16/03/22 - 18/03/22
Protea will be attending the APM exhibition in Singapore. Come and visit our stand at booth number E-K07 to discuss customer focused solutions for process, emission and environmental monitoring applications. Asia Pacific Maritime (APM) is at the centre of maritime conversation. Held in Singapore, it is the arena where the global maritime industry convenes every two years to forge partnerships and discover business opportunities.

Singapore provides an anchorage for APM to bring together key decision makers, whilst capitalising on its key role on the global stage as a leading Maritime Nation and trade linkages to the Asian markets. As the industry discusses new possibilities and change, it is now more imperative than ever for the community to embark on achieving real results and make real progress.
Read More10th January 2022 - First CEM Event For 2022 Is At Krakow In Poland 02/03/22 - 04/03/22
The first CEM Emissions Monitoring event of 2022 is in Krakow, Poland at the start of March. Protea are booked in attendance at stand 28. CEM the continuous emissions monitoring conference and exhibition started in the United Kingdom started in 1997 and has been held in The Netherlands, Denmark, France, Switzerland, Italy, The Czech Republic, Turkey, Portugal, India and Hungary. Poland was chosen as the ideal location for 2022 due to its economic strength which has been growing steadily over the past 27 years which is a record high in the EU and the most impressive performance in Central Europe.

Topics covered at this event include dust measurement at low concentrations, Emission regulation and future monitoring challenges, Fence line monitoring & measurement of fugitive/diffuse emissions, Gaseous species at low concentrations (HCl, HF, NH3, SO3, CH4, N2O, CHOH & TOC), Greenhouse Gases, Hydrogen in flue gas, Innovative Measurement Technology, Industrial Case Studies (Power industry, Cement industry, Metal industry, Chemical Industry, Glass industry, Minerals and Mining, Waste Management and Incineration), Mercury and Trace Metals, Standards and Quality (Including Measurement Uncertainty and Limits of Detection).
Read More2021
3rd November 2021 - Lowest NO and NO2 MCERTS emissions analyser
Protea’s atmosFIR FTIR emissions analyser now has the lowest certified NO and NO2 range of any FTIR analyser and is one of the lowest range NO/NO2 instruments of any technology on the market. With global emissions limiters becoming lower, measurement technology needs to be suitable for the lower ELVs. atmosFIR can offer a NO range of 0-80mg/m3 and NO2 range of 0-50mg/m3. Older FTIR technology limited by resolution often achieve only 0-200mg/m3 range for NO2 for example.
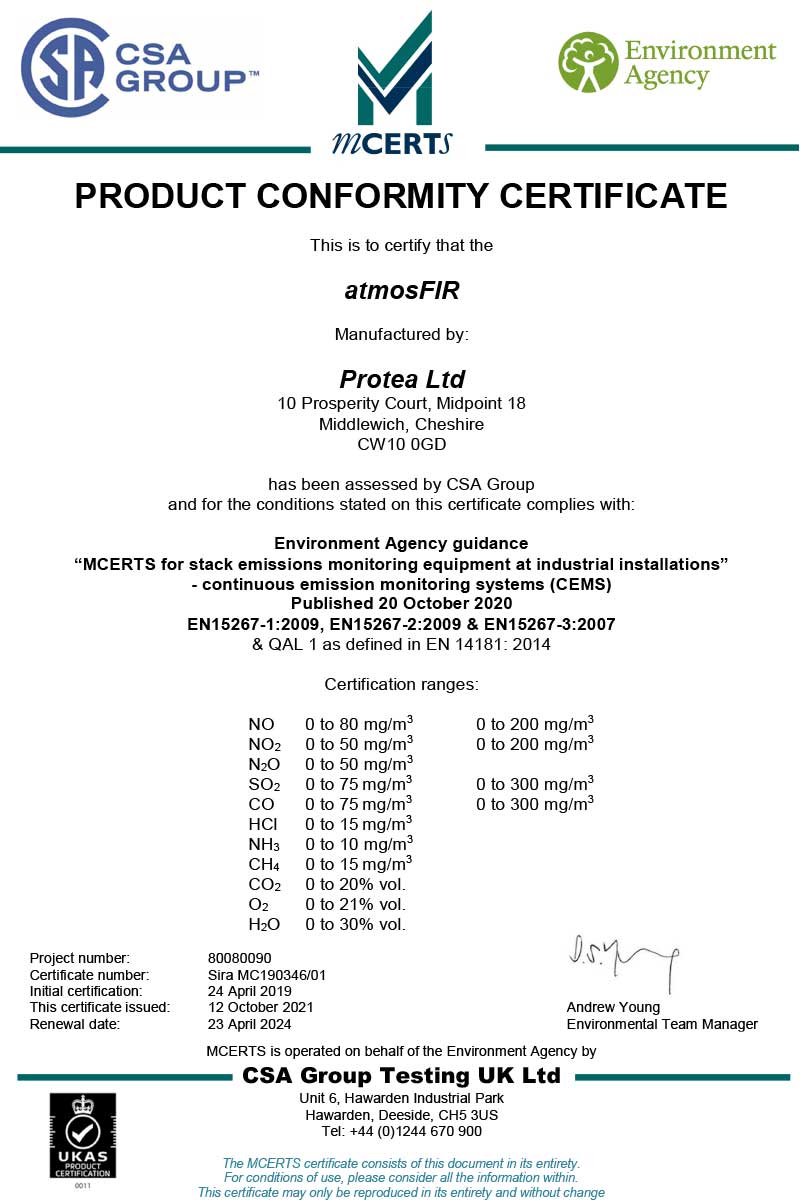
This increases the potential for using the atmosFIR (available in portable as well as CEM versions) to low-NOx emissions plant emissions testing. Added to this the power of FTIR in measuring hundreds of gases with one instrument, atmosFIR is the proven future-proof technology for emissions monitoring.
Protea can also announce our NH3 (ammonia) MCERTS range has been improve to 0-10mg/m3.
Read More11th October 2021 - Differences between CEN/TS 17337:2019 and TGN M22 for Portable FTIR Emissions Testing
Protea and the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) have recently completed a Measurement 4 Recovery (M4R) project to produce an Industry Transition Document (ITD) that concisely lays out the changes required of stack testing organisations transitioning from TGN M22 to CEN/TS 17337.

Currently, UK stack emissions laboratories are moving from following TGN M22 to CEN/TS 17337 for reporting of industrial emission measurements using portable FTIR gas analysers, such as the Protea atmosFIR. This change is not without some complexities. In order to implement the new measurement method, the laboratory has to know what changes in sampling apparatus are required, for example, and how the new standard requires them to process, QA/QC check and report results from their FTIR. Protea’s FTIR analysers and software are fully compliant with the requirements of the new standard.
As one of the leading manufacturers of FTIR for stack testing organisations Protea have always provided significant support to our user base. This document benefits not only the customers we support, but also many other stakeholders in the emissions community, from laboratory assessors, to regulators and plant operators who are receiving the reported data from portable FTIR analysers.
Read More8th October 2021 - GPS Enabled Gas Analysers
Protea’s range of FTIR, TDL and Mass Spectrometer gas analysers are now available with optional GPS module. For portable gas analysers used across various locations and sites, geotagging data can be a requirement of reporting. Protea’s FTIR gas analysers in particular now write the longitude and latitude of the location the spectrum was acquired to the spectrum file itself. This gives a permanent record of where the raw data was collected.
 Read More
Read More 7th September 2021 - Applied Technologies Through Innovation
With over 20 years' experience of process and emissions measurements, Protea is a world leader in getting the most from a range of technologies and can measure any gas. With complimentary measurement technology and measurement automation, Protea can design and supply the complete solution. This section gives a brief introduction to the various technologies that Protea uses.

Protea can also provide specific customer-focussed training courses on the technology if required. Click here www.protea.ltd.uk/innovation for more information about our innovation with FTIR Gas Analysers, IR Gas Analysers, UV Gas Analysers, FID Total VOC, TDL Gas Analysers, Hazardous Area Gas Analysers & Zirconia Sensors.
Read More7th June 2021 - The First P300 Extractive Gas Analyser Shipped
Protea has recently manufactured and shipped its very first P300 Extractive Gas Analyser. Monitoring percent levels of HCl, HF and SO2 the unit will monitor high levels of corrosive toxic gases in a hazardous area.

All sample “wetted” components are manufactured from Monel, the zero / calibration valves are pneumatically actuated. The sample cell has a purged containment element, if for any reason the window seals fail the process gas will be discharged to a safe vent. In the event of the pressure exceeding 6 bar(g) or a power failure the process sample gas is isolated and the cell purged with instrument air. The cell was pressure tested to 12Bar(g)
The Protea 300 is a multi-component configurable gas and liquid analyser certified for use in hazardous area. Applications in BioGas, Bio Methane, Natural Gas and many applications in refineries. More information on the P300 is found here www.protea.ltd.uk/p300-extractive-gas-analyser
Read More15th April 2021 - Multistream Gas Analysis Solutions From Protea
Protea’s FTIR, TDL and QMS analysers are available with measurement from multiple sample points using standard modular equipment for cost-effective bespoke solutions.
A multiple sample point or multistream solution can enable cost savings by allowing one emissions analyser to make sequential measurements from many different sample points. Multistream systems from Protea use tried and proven components and features. The modular aspect of our designs means a multistream solution can begin with a low number of points and additional pieces of hardware added in time to build an expanded solution in the future.
- Inlet and Outlet for emission abatement efficiency
- Multi-stack CEMs with standby systems
- High dust CEMs with dual sample system switchover
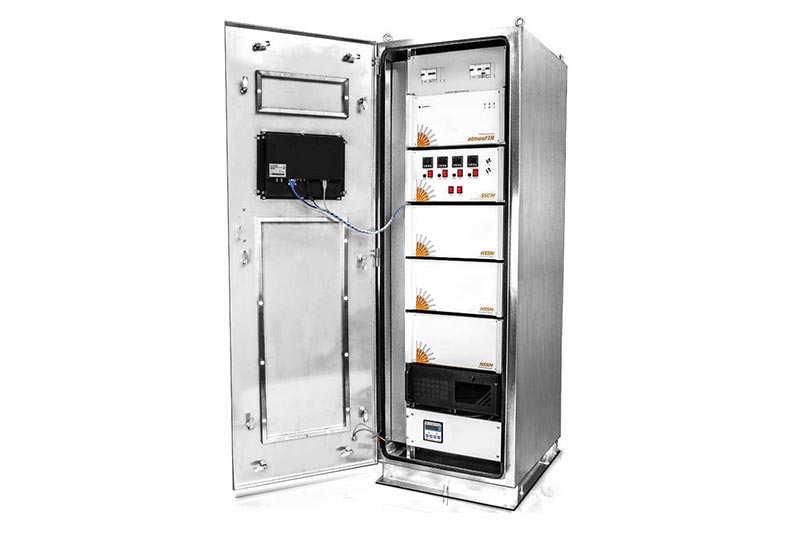

Multistream Benefits
- Separate analyser calibration file for each sample point
- A different set of gases and ranges can be measured from each sample point so one FTIR can do the job of hundreds of sensors
- Separate configuration file for each sample point
- Variable measurement times configured for each stream, some points can be quick measurements (2-5 seconds), some longer (1-2 minutes)
- Pauses can be configured in the sequence, to allow gases to condition in the sampling system and the analyser
- By-pass pump can be provided and controlled by the software. This allows non-sampled positions to be flushed with sample ready for measurement, ensuring quick response time
- Span gas checks per stream, allowing each point to have response time and to check for leaks
- Heated multiple sample point systems available up to 12 streams, with 12 heated probe alarms and 12 heated line alarms with heated valve manifolds
- Sequence easily built in PAS-Pro software – no programming or PLC programme updating needed
- Separate log file for data for each stream - easy for operator to sort data and report values
- Separate OPC and Modbus data outputs for each stream
12th April 2021 - Emissions Sampling Equipment
As part of our delivery of portable or fixed emissions analysers, Protea will supply the most suitable sampling equipment for making accuracte, repeatable emissions. We can happily provide consultation and support in supplying you with sampling equipment for use with other emissions gas analysers.
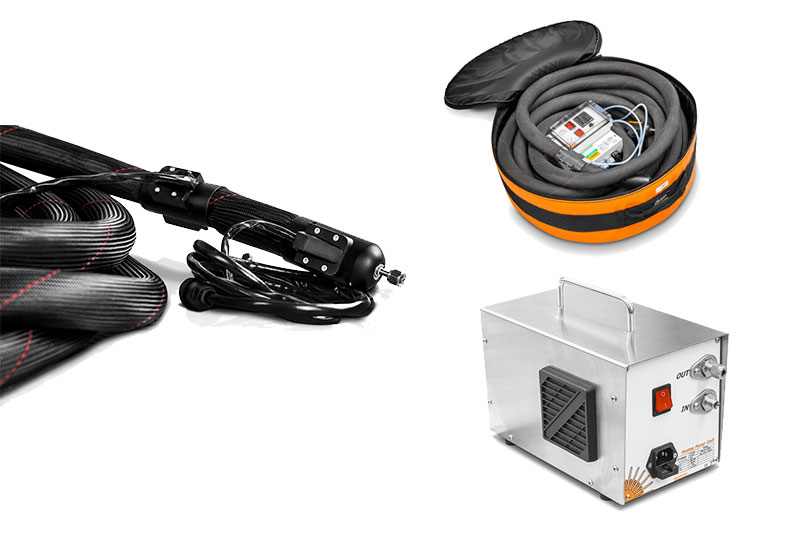

- Heated lines of any length and material
- EX/ATEX sample lines and probes
- Heated sample probes with best selection of filter and probe materials
- Sample conditioning systems
- Sample flow control
8th March 2021 - CEM Integration by Protea
Protea can quickly and cost-effectively provide gas analyser integration support for your project.
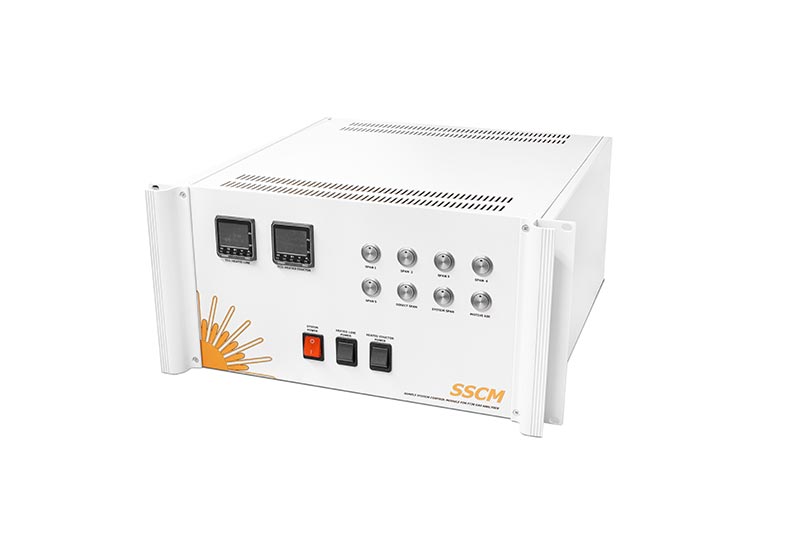

Protea’s own extractive emissions analysers use a modular concept for CEM design and build. This not provides engineering benefits for our own manufactured analysers, but also allows for Protea to support the integration of 3rd part instruments cost-effectively. As a UK-based expert on gas analysers and CEMS, Protea can integrate and customise analyser operation for a range of process and emissions applications.
Our Sampling System Control Module (SSCM) product is a PLC-based CEM control unit that can manage features such as:
- Heated Line Alarms
- Heated Probe Alarms
- Multiple Span Gases
- Span Direct/Probe
- Sampling control, including pump integration
- Blow-Back/Back-Purge
- By-Pass Sampling Control
 Read More
Read More 5th March 2021 - Emissions Analyser Software Features
Protea’s range of portable and fixed emissions gas analysers implement unique features to benefit emissions gas testing. Our PAS and PAS-Pro software offers the following features that make compliance with emissions testing standards easier as the software will dynamically calculate the required test results on-site:
- T90 response time results for span/check gases recorded live
- Span drift results and pass/fail recorded live
- Drift correction calculation within software
- Repeatability on zero and span results calculated live
- Lower Detection Limit (LDL) calculator
- FTIR residual analysis carried out live
- Emissions Limit Value (ELV) exceedance warning on-screen
- FTIR residual test as per M22, CEN/TS 17337 and other standards
- Raw and Dry/O2 corrected values logged in real-time
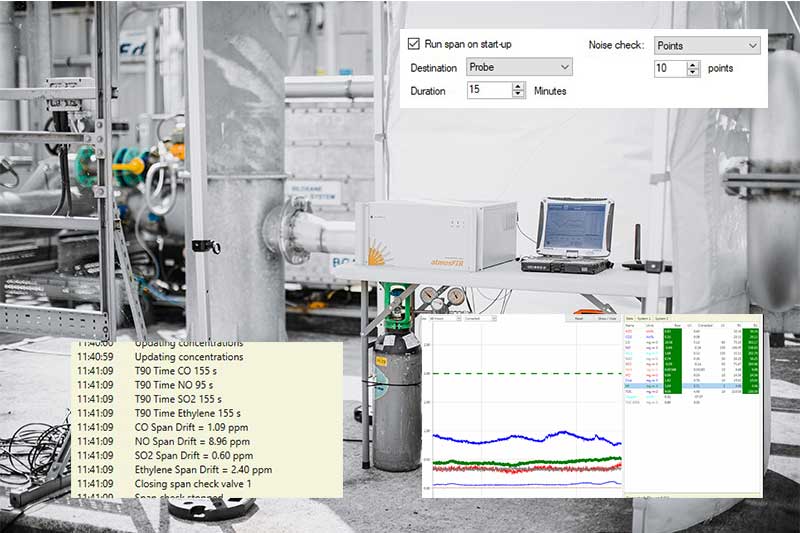 Read More
Read More 2nd February 2021 - Hazardous Area Gas Analysers For Zone 1 & 2
Protea can provide gas analysers for installation in Hazardous area - Zone 1 and Zone 2. Protea is certified as a manufacturer of ATEX equipment as per Directive 2014/34/EU. For installation of gas analysers in Hazardous area, Protea can provide fully certified analysers and systems. As a manufacturer accredited under Directive 2014/34/EU our P2000 and P300 in-situ and extractive IR gas analysers have a history of installation in applications such as refinery monitoring. The atmosFIR EX is a complete multi-gas FTIR analyser Zone 1 and Zone 2 approved installation, that can provide emissions or process measurements for multiple sample points. Protea can also provide Hazardous area sampling lines and probes to give a complete solution.

ATEX FTIR Gas Analyser
atmosFIR EX is an ATEX certified gas analyser system for measurement of industrial gases in a Zone 1 or Zone 2 area, providing a complete EX certified gas measurement system that meets both the sampling of non-flammable and flammable gases, utilizing Protea’s multigas atmosFIR FTIR gas analyser platform.
P300 Extractive Gas Analyser
The Protea 300 is a multi-component configurable gas and liquid analyser certified for use in hazardous area. Applications in BioGas, Bio Methane, Natural Gas and many applications in refineries.
P2000 In-situ CEM
The Protea 2000 is a multi-component configurable gas and liquid analyser certified for use in hazardous area. The only Hazardous Area approved Multi Component CEM analyser. The unit is certified EEx d (Flameproof) therefore no need for purge control equipment.
2020
5th November 2020 - Flame Ionisation Detector (FID) Total VOC Launched
Protea’s Flame Ionisation Detector (FID) analysers allow for Total VOC analysis from a range of emissions, process, exhaust and ambient air applications. Protea’s Flame Ionisation Detector (FID) analysers are used to give quick, accurate measurement of Total VOC concentration in a range of applications such as emissions and process control and offer MCERTS EN 15267-3 QAL1 certification. Find out more at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/fid-total-voc
Within the FID analyser chamber is a Hydrogen (H2) flame burning in an electrical field. The flame is fed by high purity fuel gas (atmosFID can use H2 gas or a H2/He mix) and a hydrocarbon (HC)-free combustion air. The sample gas to be analyzed is then also fed into this flame. The hydrocarbons within the sample gas are "cracked" in the flame and the resulting HC fragments are then ionized. An ion current in the order of 10-14A is generated in the electric field; this electric current is related to a DC amplifier and gives the detection of the HC content.
The measuring method requires that the measuring signal is proportional to the number of non-oxidized carbon atoms in the sample gas. Carbon atoms that are pre-oxidized are only partially measured. This phenomenon is expressed by the response factor (RF) of various hydrocarbons. Protea can provide a complete response factor list for the atmosFID.
Read More20th October 2020 - ISO 9001:2015 Certification Reissued
Protea is pleased to announce the successful re-certification of our Quality System under ISO 9001:2015. Protea’s scope covers the design, manufacture, supply and service of analysers for gas emissions, process control and research across our two UK factories.
 Read More
Read More 2nd September 2020 - Introducing BetaCap Capillary Gas Divider
Capillary technology offers an improvement in uncertainty of measurement of a gas dilution system over other technologies. The BetaCAP range of blenders offered by Protea has a set number of highly accurate capillaries – 30 or 60 as standard. The unit “switches” in the most suitable capillaries to generate the desired gas concentration, with fine-tuning of the gas delivery being made by pressure compensation.

The relative measuring uncertainty is low with this type of blender technology, as it is a function of the measured value of each capillary that is used not the instrument range, as is the case with sonic nozzle or MFC blenders. Blenders are offered in laboratory or field-ready packages, as well 19” rack configurations for installing alongside gas analysis equipment. Find out more at www.protea.ltd.uk/capillary-gas-divider
Read More3rd August 2020 - Introducing the atmosCAL MFC Gas Divider
The accurate calibration of gas analysers is critical, during factory build, routine service but also for on-going field assessment of analyser performance. Protea has developed the atmosCAL Gas Blender to enable dilution of high concentration gas cylinders over lower concentration ranges, in order to calibrate gas analysers - allowing characteristics such as absolute reading, repeatability, reproducibility, linearity and response time to be tested on analysers.

Using multiple Mass Flow Controller (MFC) technology, generating required gas concentration is as simple as typing into the touchscreen the desired concentration and choosing the flow rate. MFC technology operates on the principle of thermal mass, and different gases require compensation. The atmosCAL embedded software is pre-loaded with a range of compensation factors so the majority of gases can be used with the atmosCAL without adjustment. Find out more at https://www.protea.ltd.uk/atmoscal.
Read More10th March 2020 - Global Marine Support Network Expanded
With our marine analysers installed on vessels all over the world, the ongoing service and support for the equipment is satisfied by our dedicated network working in and around major ports and installation locations. Visit www.protea.ltd.uk/marine-support-network for more information.

Protea’s installed base of marine emissions analyser is supported and serviced by our dedicated Marine Support network operating globally. With the full support of our UK-based marine analyser service team, our support network is located in and around the major locations for installation, commissioning and readily available to provide on-vessel service when needed. Protea offer a worldwide service capability to the Marine Industry.
- Annual service of Protea and Procal supplied analysers
- Annual analyser verification and certification Protea and Procal supplied analysers
- Call out service of Protea and Procal supplied analysers
- Ship gaseous emission survey using the latest transportable analysers
All Protea and Distributor service personnel are of the highest professional standard, factory trained and routinely attend refresher courses to ensure that they are up to date with all aspects of the products and legislative requirements.
Read More1st March 2020 - Well-prepared Operators Have Ensured a Calm Switch to the IMO 2020 Sulphur Cap
In the past few years, the clarion call has been to delay the introduction of 0.5% low sulphur fuels as the dangers were many: not enough fuel, crew would be hard pressed to understand the changes from one fuel type to another, ships would break down in the middle of the ocean, and so on.

Quietly, the regulator, the International Maritime Organization (IMO), has maintained its line and finally, when the day of reckoning arrived, the anti-climax was deafening. Not that the introduction of the IMO 2020 sulphur cap has been all plain sailing — far from it. Shortages in some regions and the delays to vessels, of up to three weeks, in Singapore are testament to that.
However, as one bunker expert told Clean Shipping International: "The vessel operators were so well prepared that the transition has been very calm." Even the major issue in Singapore, which saw Pacific International Lines' ships stranded, was not a failure of the fuel supply, but rather the consequence of attempting to supply a number of fuel types with too few bunkering barges. Or, as the expert suggested, once barges had cleaned their tanks they were reticent to “dirty” them again by filling them with high-sulphur fuel again. While events such as these are unwelcome, they are not the catastrophic events that were sometimes alluded to in some shipping circles.
In fact, the conversation has very swiftly moved on to the greater impact of a faltering global economy, which has seen declines in demand for goods and consequent decline in demand for oil, pushing prices for oil downward with the knock-on effect of seeing the price of bunkers also falling.
Added to the general malaise is the coronavirus issue. This is having the effect of stalling parts of the industry with a number of China’s major cities in lock-down and backlogs of cargo building in ports around the world. This was definitely not on the menu when the IMO served up its sulphur cap regulation.
Cost is not the major issue for the shipping industry, however, but the spread between fuel types is significant, that is the price differential between very low sulphur fuel oil (VLSFO) and 380 heavy fuel oil (HFO).
On 7 January, bunker prices stood at US$401/tonne for HFO and $740 for VLSFO. By 10 January, that convergence had already begun with a spread of $326 between VLSFO and HFO, according to figures from the Sweden-based Marine Bunker Exchange (MABUX).
Today, the MABUX index shows a spread of $200/tonne, but the narrowing of the spread has stalled over the past few days. That is good news for shipowners that fitted exhaust gas cleaning systems (EGCS), which can offer cheaper freight rates to those owners that are still operating on VLSFO.
The spread is key for EGCS users to recoup the capital cost of the equipment used to clean the sulphur from exhaust gases, but the next deadline for the maritime industry is 1 March, when all ships that do not have an EGCS will be precluded from bunkering, or storing, HFO. It will herald the end of an era and, as with the nature of such things, the entry into a great new epoch.
For owners with open loop capabilities on their EGCS, the reports on the use of these scrubbers and the discharge of washwater will also be a key factor. However, the question will arise again at IMO at the next Marine Environment Protection Committee meeting, MEPC 75, which will convene for five days from 30 March.
Even so, Armageddon appears to be a long way off for the maritime sector. Its adaptability to new realities is legendary — and it will be tested to the full over the coming decade.
Read More10th February 2020 - Limiting Engine Power to Reduce CO2 From Existing Ships
As the International Maritime Organization works to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from international shipping, technical measures to limit engine power are among the ideas being considered to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) from the existing fleet. Engine power limitation (EPL) is a semi-permanent, overridable limit on a ship’s maximum power that could reduce fuel use and CO2 emissions if it reduces the operational speeds of affected vessels.
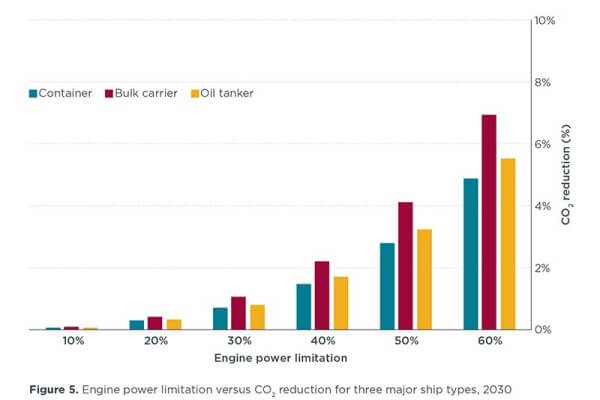
This study models the relationship between varying levels of EPL and CO2 emissions based on 2018 real-world ship operations. The authors find that CO2 reductions are not proportional to engine power reductions because ships are already operated well below their maximum speeds and therefore engine powers. EPL scenarios below 30% provide negligible cuts in CO2 for the 2018 fleet, while a 30% EPL is estimated to reduce CO2 by 2% for container ships and oil tankers, and 3% for bulk carriers. Larger, 50%+ EPL could more meaningfully reduce ship CO2 by 8%–19% depending on ship type and size.
Additionally and importantly, benefits diminish over time if EPL is not required for newer ships due to fleet turnover and growth. As illustrated in the figure below, by 2030, EPLs of 30% or less would reduce fuel use and CO2 emissions by 1% or less, while the maximum 60% EPL scenario would cut emissions by about 6%. By comparing a Base scenario with a High Speed scenario, the authors find that EPLs of 30%+ in 2030 could help lock in the fuel savings of existing slow steaming practices by constraining future speed increases.
Read More3rd January 2020 - Cleaner Air in 2020: 0.5% Sulphur Cap for Ships Enters Into Force Worldwide
From 1 January 2020, the maximum sulphur content of marine fuels is reduced to 0.5% (down from 3.5%) globally – reducing air pollution and protecting health and the environment. Sulphur Oxide (SOx) emissions from ships' combustion engines cause acid rain and generate fine dust that can lead to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, as well as reduced life expectancy.

Commissioner for Transport Adina Valean said: “Maritime transport is a global business, and reducing its emissions requires global solutions. The entry into force of the global sulphur cap is an important milestone for the entire maritime sector; it will contribute to further reduce emissions of harmful air pollutants, directly benefiting cities and communities around the globe, including important ones on our Southern European shores. It also shows that concerted effort from the EU and the IMO, together with strong commitment from the industry can deliver important benefits to the environment and the health of our citizens.”
Commissioner for the Environment, Oceans and Fisheries Virginijus Sinkevicius added: “The European Green Deal is set to deliver on a zero-pollution ambition for both climate neutrality and a toxic-free environment. This EU ambition protects our citizens' well-being, but also ensures healthy and clean environments, seas and oceans within a carbon-free and sustainable blue economy where all sides jointly engage, including maritime transport. We welcome low sulphur standards globally and in Emission Control Areas so that more EU coastal citizens can breathe clean air.”
EU's low sulphur approach as international example
Since 2012, the EU has taken firm action to reduce the sulphur content of marine fuels through the Sulphur Directive. In 2016, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) maintained 2020 as entry-into-force date of the global 0.5% sulphur cap.
Moreover, in some very fragile ecosystems such as the Baltic Sea and the North Sea – designated as ‘Sulphur Oxides Emissions Control Areas' (SECAs) – the maximum sulphur content has been reduced to 0.10%, already in 2015. Such stricter sulphur limits have more than halved sulphur dioxide concentrations around SECAs, bringing health benefits to people in coastal regions and ports, while the overall economic impacts on the sector remained minimal.
Next steps on sustainability in shipping
Based on the successful implementation of the Emission Control Area (ECA) limits, the introduction of the global sulphur limit is expected to bring similar results. The EU is also actively working in the context of the Barcelona Convention, on the possible future designation by the IMO of ECAs in other EU waters such as in the Mediterranean Sea.
The EU has striven for an active role in tackling maritime emissions more generally, both at home and globally. In 2018, the IMO agreed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from shipping by at least 50% by 2050. The EU and its Member States played an instrumental role in brokering and securing the deal for the sector, which currently represents 2-3% of global CO2 emissions. Discussions are already ongoing at the IMO to translate this deal into concrete measures.
To tackle plastic pollution within our oceans, the EU adopted new rules on port reception facilities, making sure that waste generated on-board ships or fished at sea is collected and treated in ports.
The EU is also working with the IMO to address concerns regarding discharge waters from after-treatment systems used by ships. The objective is to ensure full sustainability of those systems, possibly by setting stricter and uniform legislative requirements.
In addition, the European Green Deal, presented by the President of the Commission Ursula von der Leyen in December 2019, sets out further action to make shipping more sustainable such as the extension of the European emissions trading to the maritime sector.
Background
Maritime transport has a direct impact on air quality in many European coastal cities. Exhaust gases from ships are a significant source of air pollution, including through sulphur oxide emissions resulting from the burning of fuel oil. Sulphur oxides are harmful to the human respiratory system and make breathing difficult.
Ships traditionally use fuel oils for propulsion, which can have a sulphur content of up to 3.50 %. For comparison, the sulphur content of fuels used in trucks or passenger cars must not exceed 0.001 %. The 2012 Sulphur Directive which was revised in 2016, reduced SOx emissions by setting maximum sulphur content levels for marine fuels and incorporated new standards set by the International Maritime Organisation into EU law both inside regionally protected areas and outside of those.
Read More2019
7th November 2019 - Type Approval Certificate For Marine Automatic Devices & Equipment Japan
Protea has attained a further marine emissions approval accreditation to certify that the undernoted product (P2000) has been approved in accordance with the requirements specified in Chapter 1, Part 7 of 'Guidance for the Approval of Materials and Equipment for Marine Use' and the relevant Society's rules.

Nippon Kaiji Kyokai is a ship classification society. It is also known by the brand name “ClassNK” or often in the industry as just “NK”. It is a not for profit society dedicated to ensuring the safety of life and property at sea, and the prevention of pollution of the marine environment. ClassNK offers a broad range of services such as ship classification surveys, statutory surveys and certification on behalf of Flag States based on both international conventions, codes, national statutes, as well as ClassNK’s own rules and regulations.
They also include assessment and certification services of safety management systems of ship management companies as well as the quality systems of ship builders and related manufacturers as an independent third party. ClassNK also offers appraisal, consulting and supervisory services on both marine and non-marine related projects.
Read More4th September 2019 - Protea P2000 Product Focus
The Protea P2000 is an infra-red (IR), duct or stack-mounted Analyser, designed to provide In-Situ analysis of up to six gas-phase emission components.A typical system comprises of a stack mounted Analyser, an integral Calibration Module and a Control Unit with options which include a powerful In-Situ Heater anda stand-alone Analysis Software package. MCERTS Product Conformity Certificate is also available with the P2000 Series Continuous Emission Monitor With Protea Control Unit.

The P2000 uses the reflective beam principal to directly measure process gas as it enters the in situ sample cell. Unlike higher maintenance extractive systems, Protea’s patented, sintered metal technology removes the need for gas filtering or sample conditioning.The P2000 analyser requires very little maintenance and achieves a class-beating availability of over 98% in demanding applications.The Control Unit can support multiple analysers from the Protea range.
Read More6th March 2019 - New Marine Emissions Brochure Now Available
We have recently updated our Marine Emissions download focused on meeting the environmental challenges faced for global shipping and logistics activities. The most important gases in terms of emissions are currently sulphur oxides (SOx), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). Annex VI has a schedule for significant reductions in both over the next 10 years. Please contact us for your Marine Emissions requirements.
The need to demonstrate environmental responsibility is key for today’s marine and offshore industries. Charterers and the public demand high standards of performance and reliability. Fuels and exhaust gas emissions are also the subject of international, regional and national controls. The most significant is IMO MARPOL Annex VI - Regulations for the Prevention of Air Pollution from Ships, which also applies to mobile offshore drilling units and other oil industry platforms.
Read More11th January 2019 - Global Marine Emissions in the Spotlight
The need to demonstrate environmental responsibility is key for today’s marine and offshore industries. Charterers and the public demand high standards of performance and reliability. Fuels and exhaust gas emissions are also the subject of international, regional and national controls. The most significant is IMO MARPOL Annex VI - Regulations for the Prevention of Air Pollution from Ships, which also applies to mobile offshore drilling units and other oil industry platforms.

The Emissions Monitoring Solution from Protea is the P2000 emissions monitoring system is approved for the analysis of exhaust gases from the engines and boilers of ships and offshore rigs. Robust and with proven reliability, up to six gases can be measured including SO2, CO2 and NOx.
The Protea 2000 emissions monitoring system comprises up to 6 exhaust mounted analysers, each with automatic verification facilities. Emissions data from the entire system is securely managed and displayed at a dedicated Classification Society approved panel PC, with outputs to networks, control systems, and reporting facilities.
Read More2018
1st November 2018 - Inside Our New Modern Manufacturing Facility at Peterborough
Earlier in the year we relocated our offices in Peterborough to a new location which included a complete fit out to allow for a purpose built modern manufacturing facility. The images below provide an insight into the work that we do focused on the manufacture and production of in-situ gas analysers for a global market place. The new facility specialised in the production of the P2000 and P5000 in-situ Continuous Emissions Monitoring (CEM) analysers that are flange mounted to the emissions point, with an in-situ sample cell inserted into a stack.



Our full office address for the new location is Protea Ltd, Peterborough, Unit 2 Venture Park, Stirling Way, Peterborough, Cambridgeshire, PE3 8YD, UK. The telephone number is +44 (0) 1733 263437 and the email address is mailto:sales@protea.ltd.uk. Protea offers both Infra-Red (IR) and Ultra Violet (UV) in-situ gas analysers. The in-situ CEM systems are multi-component and can monitor multiple gases species simultaneously. The analyser also monitors water vapour and so the pollutant gases can be reported on a wet or dry bases depending on the local environmental agencies requirements.
Read More1st June 2018 - Protea Awarded the RINA Marine Certificate for the P2000 CEMS
Protea have recently been awarded the RINA Certificate Marine Certificate for our Monitoring and control system continuous emissions monitor the P2000. The P2000 may be used for the continuous monitoring of emissions from the exhaust gas cleaning system. The actual reference standard is that the RINA rules for the classification of ships - Part C “Machinery, Systems and Fire Protection”, Chapter 3, Section 6, Tab.1 and IMO Res, MEPC.259(68) Chapter 6 “Emission Testing” as well as the relevant requirements of Revised MARPOL Annex VI and NOx Technical Code 2008.

Protea 2000 In-Situ Infra-red gas analyser connected to a Protea Control Unit forms the basis of a Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS). The Stack Mounted In-Situ analyser monitors the stack gas without the need for any sample handling equipment making it a cost-effective solution to Continuous Emission Monitoring and Process applications. The analyser monitors the stack gases “wet”, water vapour is continuously monitored enabling the pollutant gases can be reported on a wet or dry bases.
Read More14th May 2018 - Protea Open a Second New Manufacturing Facility in the UK
As part of our expansion plans into future years we are pleased to announce that our new manufacturing facility is now fully operational. The new facility is located in Peterborough and will focus on the design, manufacture and supply of in-situ continuous emissions monitoring analysers to a global market place.




The new location address can be found at:
Protea Ltd,
Unit 2 Venture Park,
Stirling Way,
Bretton,
Peterborough,
Cambridgeshire,
PE3 8YD,
United Kingdom.


